
Beesia is a genus of flowering plants in the buttercup family. It was named in 1915 after the plant nursery firm Bees of Chester, who financed the plant hunting trips of George Forrest and Frank Kingdon-Ward in China.

Gouania lupuloides, known as chewstick or whiteroot, is a neotropical plant of the family Rhamnaceae. It is occasionally used as a teeth-cleaning implement.
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors are compounds that slow or stop the action of the arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase enzyme, which is responsible for the production of inflammatory leukotrienes. The overproduction of leukotrienes is a major cause of inflammation in asthma, allergic rhinitis, and osteoarthritis.
Goniothalamus cheliensis is a species of plant in the Annonaceae family. It is native to China and Thailand. Bioactive molecules isolated from its roots have been reported to have cytotoxic activity in tests with cultured human cancer cells.

Xanthohumol is a natural product found in the female inflorescences of Humulus lupulus, also known as hops. This compound is also found in beer and belongs to a class of compounds that contribute to the bitterness and flavor of hops. Xanthohumol is a prenylated chalconoid, biosynthesized by a type III polyketide synthase (PKS) and subsequent modifying enzymes.
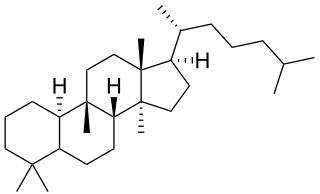
Cucurbitane is a class of tetracyclic chemical compounds with formula C
30H
54. It is a polycyclic hydrocarbon, specifically triterpene. It is also an isomer of lanostane, from which it differs by the formal shift of a methyl group from the 10 to the 9β position in the standard steroid numbering scheme.
Aurantiomides are quinazoline alkaloids isolated from the fungus Penicillium aurantiogriseum. Aurantiomide is contained in the traditional Chinese medicine LeZhe.

Halicylindramides are a group of antifungal peptides. The first compounds of this type, designated halicylindramides A through E, were isolated from sea sponges of the genus Halichondria. More compounds in the family, designated F, G and H, were found in sponges of the genus Petrosia. Halicylindramide A has been synthesized by chemists.

Ungiminorine is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Narcissus.
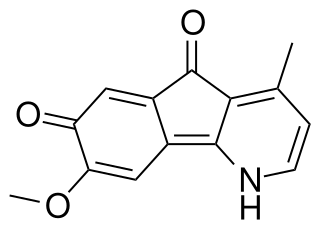
Isooncodine is an anticholinergic alkaloid. It was first synthesized in 1989 because it is an isomer of oncodine, an azafluorenone alkaloid derived from Meiogyne monosperma. It was first derived from the leaves of Polyalthia longifolia.

14-Norpseurotin A is an alkaloid and a bio-active metabolite of Aspergillus, featuring an oxa-spiro-lactam core.

The xenortides (A-D) are a class of linear peptides isolated from the bacterium Xenorhabdus nematophila, a symbiont of the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema carpocapsae. This class of compounds is known for their insect virulence and cytotoxic biological activities. The tryptamide containing compounds show higher biological activity than the phenylethylamides. The most biologically active compound was found to be xenortide B with a potency of less than 1.6 μM activity against Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense and Plasmodium falciparum (malaria), however it is also the most toxic to mammalian cells which limits its viability as a treatment.

Incarvillateine is a complex monoterpene alkaloid that is a derivative of α-truxillic acid. It can be isolated from the plant genus Incarvillea.

Incarvillea sinensis is a plant species in the genus Incarvillea.
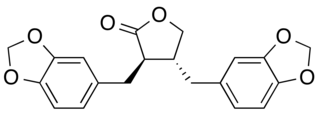
Hinokinin is a dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan, derived from various species of plants. It is a potential antichagonistic agent. In vitro, it has been shown to have potential neuroprotective effects as well as anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, antiviral and antifungal properties.
Nitensidine D is a toxic alkaloid natural product that was isolated from the leaves of the South American legume Pterogyne nitens. It is also hypothesized to be a possible intermediate in the still unknown, seemingly monoterpene based, terrestrial biosynthetic pathway for tetrodotoxin.
The iodate fluorides are chemical compounds which contain both iodate and fluoride anions (IO3− and F−). In these compounds fluorine is not bound to iodine as it is in fluoroiodates.

Plakortis is a genus of marine sponges in the order Homosclerophorida, first described by Franz Eilhard Schulze in 1880.

Penitanzacid F was found as one of the twelve new tanzawaic acid derivatives, which were the secondary metabolites of the fungi Pencillum sp. KWF32 isolated from the tissues of Bathymodiolus sp. collected in the cold spring area of the South China Sea in 2021.
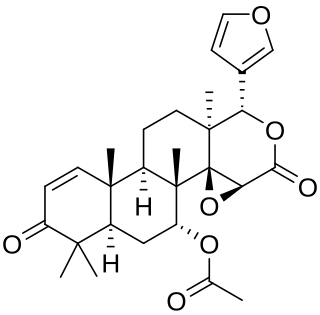
Gedunin is a pentacyclic triterpenoid with the molecular formula C28H34 O7. It is most notably found in Azadirachta indica, but is a constituent of several other plants. Gedunin shows therapeutic potential in the treatment of leukemia, and Parkinson's disease.















