In organic chemistry, an acetal is a functional group with the connectivity R2C(OR')2. Here, the R groups can be organic fragments (a carbon atom, with arbitrary other atoms attached to that) or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments not hydrogen. The two R' groups can be equivalent to each other (a "symmetric acetal") or not (a "mixed acetal"). Acetals are formed from and convertible to aldehydes or ketones and have the same oxidation state at the central carbon, but have substantially different chemical stability and reactivity as compared to the analogous carbonyl compounds. The central carbon atom has four bonds to it, and is therefore saturated and has tetrahedral geometry.
Contents
- Acetalization and ketalization
- Examples
- Sugars
- Chiral derivatives
- Formaldehyde and acetaldehyde
- Unusual acetals
- Flavors and fragrances
- Related compounds
- See also
- References
The term ketal is sometimes used to identify structures associated with ketones (both R groups organic fragments rather than hydrogen) rather than aldehydes and, historically, the term acetal was used specifically for the aldehyde-related cases (having at least one hydrogen in place of an R on the central carbon). [1] The IUPAC originally deprecated the usage of the word ketal altogether, but has since reversed its decision.[ citation needed ] However, in contrast to historical usage, ketals are now a subset of acetals, a term that now encompasses both aldehyde- and ketone-derived structures.[ citation needed ]
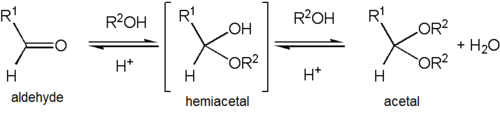
If one of the R groups has an oxygen as the first atom (that is, there are more than two oxygens single-bonded to the central carbon), the functional group is instead an orthoester. In contrast to variations of R, both R' groups are organic fragments. If one R' is a hydrogen, the functional group is instead a hemiacetal, while if both are H, the functional group is a ketone hydrate or aldehyde hydrate.
Formation of an acetal occurs when the hydroxyl group of a hemiacetal becomes protonated and is lost as water. The carbocation that is produced is then rapidly attacked by a molecule of alcohol. Loss of the proton from the attached alcohol gives the acetal.
Acetals are stable compared to hemiacetals but their formation is a reversible equilibrium as with esters. As a reaction to create an acetal proceeds, water must be removed from the reaction mixture, for example, with a Dean–Stark apparatus, lest it hydrolyse the product back to the hemiacetal. The formation of acetals reduces the total number of molecules present (carbonyl + 2 alcohol → acetal + water) and therefore is generally not favourable with regard to entropy. One situation where it is not entropically unfavourable is when a single diol molecule is used rather than two separate alcohol molecules (carbonyl + diol → acetal + water).