An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen ion, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.
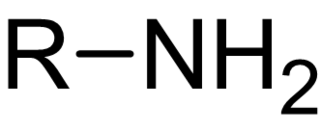
In chemistry, amines are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Formally, amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline. Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine.

In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula R−C(=O)−NR′R″, where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid with the hydroxyl group replaced by an amine group ; or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group joined to an amine group.

In chemistry, an ester is a functional group derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
In chemistry, an amphoteric compound is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. What exactly this can mean depends on which definitions of acids and bases are being used.

In organosulfur chemistry, a sulfonate is a salt, anion or ester of a sulfonic acid. Its formula is R−S(=O)2−O−, containing the functional group −S(=O)2−O−, where R is typically an organyl group, amino group or a halogen atom. Sulfonates are the conjugate bases of sulfonic acids. Sulfonates are generally stable in water, non-oxidizing, and colorless. Many useful compounds and even some biochemicals feature sulfonates.

In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula R2NC(O)OR and structure >N−C(=O)−O−, which are formally derived from carbamic acid. The term includes organic compounds, formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion H2NCOO−.

Amidines are organic compounds with the functional group RC(NR)NR2, where the R groups can be the same or different. They are the imine derivatives of amides (RC(O)NR2). The simplest amidine is formamidine, HC(=NH)NH2.

Phosphorous acid is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic, not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds. Organic derivatives of phosphorous acid, compounds with the formula RPO3H2, are called phosphonic acids.
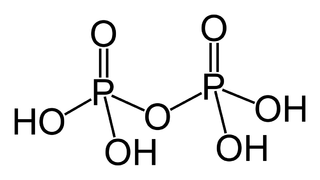
In chemistry, a phosphoric acid, in the general sense, is a phosphorus oxoacid in which each phosphorus (P) atom is in the oxidation state +5, and is bonded to four oxygen (O) atoms, one of them through a double bond, arranged as the corners of a tetrahedron. Two or more of these PO4 tetrahedra may be connected by shared single-bonded oxygens, forming linear or branched chains, cycles, or more complex structures. The single-bonded oxygen atoms that are not shared are completed with acidic hydrogen atoms. The general formula of a phosphoric acid is Hn+2−2xPnO3n+1−x, where n is the number of phosphorus atoms and x is the number of fundamental cycles in the molecule's structure, between 0 and n + 2/2.
In chemistry, phosphorus oxoacid is a generic name for any acid whose molecule consists of atoms of phosphorus, oxygen, and hydrogen. There is a potentially infinite number of such compounds. Some of them are unstable and have not been isolated, but the derived anions and organic groups are present in stable salts and esters. The most important ones—in biology, geology, industry, and chemical research—are the phosphoric acids, whose esters and salts are the phosphates.

Neuraminic acid (5-amino-3,5-dideoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulosonic acid) is an acidic (in particular ulosonic) amino sugar with a backbone formed by nine carbon atoms. Although 9-carbon sugars do not occur naturally, neuraminic acid may be regarded as a theoretical 9-carbon ketose in which the first link of the chain (the –CH2OH at position 1) is oxidised into a carboxyl group (–C(=O)OH), the hydroxyl group at position 3 is deoxidised (oxygen is removed from it), and the hydroxyl group at position 5 is substituted with an amino group (–NH2). Neuraminic acid may also be visualized as the product of an aldol-condensation of pyruvic acid and D-mannosamine (2-amino-2-deoxy-mannose).
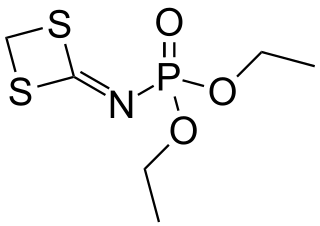
In organophosphorus chemistry, phosphoramidates are a class of phosphorus compounds structurally related to phosphates via the substitution of an −O− group for an amine group. They are derivatives of phosphoramidic acids, which possess the structure O=P(OH)(NR2)2 or O=P(OH)2(NR2).

In organic chemistry, alkanolamines are organic compounds that contain both hydroxyl and amino functional groups on an alkane backbone. Most alkanolamines are colorless.

In organosulfur chemistry, sulfenamides are a class of organosulfur compounds characterized by the general formula R−S−N(−R)2, where the R groups are hydrogen, alkyl, or aryl. Sulfenamides have been used extensively in the vulcanization of rubber using sulfur. They are related to the oxidized compounds known as sulfinamides and sulfonamides.
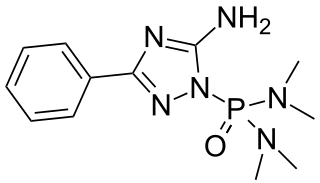
Triamiphos (chemical formula: C12H19N6OP) is an organophosphate used as a pesticide and fungicide. It is used to control powdery mildews on apples and ornamentals. It was discontinued by the US manufacturer in 1998.

In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group is an organosulfur group with the structure R−S(=O)2−NR2. It consists of a sulfonyl group connected to an amine group. Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group.

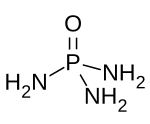
Phosphoramide is a chemical compound with the molecular formula O=P(NH2)3. It is a derivative of phosphoric acid in which each of the hydroxyl groups have been replaced with an amino group. In bulk, the compound is a white solid which is soluble in polar solvents.
Transition metal amino acid complexes are a large family of coordination complexes containing the conjugate bases of the amino acids, the 2-aminocarboxylates. Amino acids are prevalent in nature, and all of them function as ligands toward the transition metals. Not included in this article are complexes of the amides and ester derivatives of amino acids. Also excluded are the polyamino acids including the chelating agents EDTA and NTA.
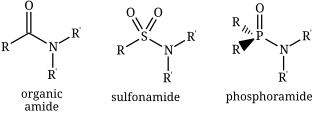
In chemistry, the term amide ( or or ) is a compound with the functional group RnE(=O)xNR2, where x is not zero, E is some element, and each R represents an organic group or hydrogen. It is a derivative of an oxoacid RnE(=O)xOH with an hydroxy group –OH replaced by an amine group –NR2.