Related Research Articles
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Silicone</span> Family of polymers of the repeating form [R2Si–O–SiR2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/37/Caulking.jpg/320px-Caulking.jpg)
In organosilicon and polymer chemistry, a silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer composed of repeating units of siloxane. They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, grease, rubber, resin, and caulk.
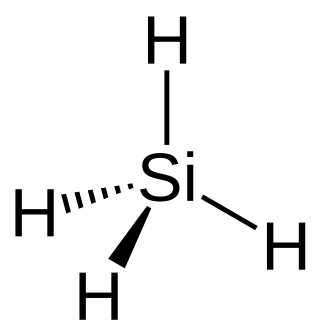
Silane (Silicane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula SiH4. It is a colourless, pyrophoric, toxic gas with a sharp, repulsive, pungent smell, somewhat similar to that of acetic acid. Silane is of practical interest as a precursor to elemental silicon. Silane with alkyl groups are effective water repellents for mineral surfaces such as concrete and masonry. Silanes with both organic and inorganic attachments are used as coupling agents. They are commonly used to apply coatings to surfaces or as an adhesion promoter.

Trichlorosilane is an inorganic compound with the formula HCl3Si. It is a colourless, volatile liquid. Purified trichlorosilane is the principal precursor to ultrapure silicon in the semiconductor industry. In water, it rapidly decomposes to produce a siloxane polymer while giving off hydrochloric acid. Because of its reactivity and wide availability, it is frequently used in the synthesis of silicon-containing organic compounds.
Chloromethane, also called methyl chloride, Refrigerant-40, R-40 or HCC 40, is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3Cl. One of the haloalkanes, it is a colorless, sweet-smelling, flammable gas. Methyl chloride is a crucial reagent in industrial chemistry, although it is rarely present in consumer products, and was formerly utilized as a refrigerant. Most chloromethane is biogenic.
Silicon tetrachloride or tetrachlorosilane is the inorganic compound with the formula SiCl4. It is a colorless volatile liquid that fumes in air. It is used to produce high purity silicon and silica for commercial applications. It is a part of the chlorosilane family.
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), also known as dimethylpolysiloxane or dimethicone, is a silicone polymer with a wide variety of uses, from cosmetics to industrial lubrication.

In organosilicon chemistry, a siloxane is an organic compound containing a functional group of two silicon atoms bound to an oxygen atom: Si−O−Si. The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae H[OSiH2]nOH and [OSiH2]n. Siloxanes also include branched compounds, the defining feature of which is that each pair of silicon centres is separated by one oxygen atom. The siloxane functional group forms the backbone of silicones [−R2Si−O−SiR2−]n, the premier example of which is polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The functional group R3SiO− is called siloxy. Siloxanes are manmade and have many commercial and industrial applications because of the compounds’ hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and high flexibility.
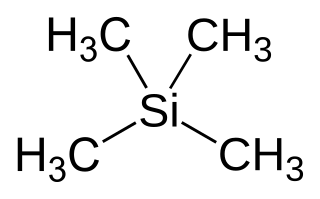
Tetramethylsilane (abbreviated as TMS) is the organosilicon compound with the formula Si(CH3)4. It is the simplest tetraorganosilane. Like all silanes, the TMS framework is tetrahedral. TMS is a building block in organometallic chemistry but also finds use in diverse niche applications.
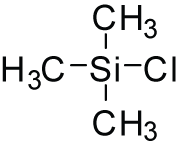
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound, with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry.

Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an inorganic compound.
Hydrosilanes are tetravalent silicon compounds containing one or more Si-H bond. The parent hydrosilane is silane (SiH4). Commonly, hydrosilane refers to organosilicon derivatives. Examples include phenylsilane (PhSiH3) and triethoxysilane ((C2H5O)3SiH). Polymers and oligomers terminated with hydrosilanes are resins that are used to make useful materials like caulks.
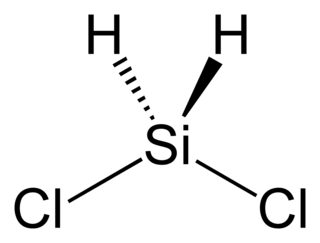
Dichlorosilane, or DCS as it is commonly known, is a chemical compound with the formula H2SiCl2. In its major use, it is mixed with ammonia (NH3) in LPCVD chambers to grow silicon nitride in semiconductor processing. A higher concentration of DCS·NH3 (i.e. 16:1), usually results in lower stress nitride films.
Dimethyldichlorosilane is a tetrahedral organosilicon compound with the formula Si(CH3)2Cl2. At room temperature it is a colorless liquid that readily reacts with water to form both linear and cyclic Si-O chains. Dimethyldichlorosilane is made on an industrial scale as the principal precursor to dimethylsilicone and polysilane compounds.

Methyltrichlorosilane, also known as trichloromethylsilane, is a monomer and organosilicon compound with the formula CH3SiCl3. It is a colorless liquid with a sharp odor similar to that of hydrochloric acid. As methyltrichlorosilane is a reactive compound, it is mainly used a precursor for forming various cross-linked siloxane polymers.
The direct process, also called the direct synthesis, Rochow process, and Müller-Rochow process is the most common technology for preparing organosilicon compounds on an industrial scale. It was first reported independently by Eugene G. Rochow and Richard Müller in the 1940s.
In organosilicon chemistry, polysilazanes are polymers in which silicon and nitrogen atoms alternate to form the basic backbone. Since each silicon atom is bound to two separate nitrogen atoms and each nitrogen atom to two silicon atoms, both chains and rings of the formula [R2Si−NR]n occur. R can be hydrogen atoms or organic substituents. If all substituents R are hydrogen atoms, the polymer is designated as perhydropolysilazane, polyperhydridosilazane, or inorganic polysilazane ([H2Si−NH]n). If hydrocarbon substituents are bound to the silicon atoms, the polymers are designated as Organopolysilazanes. Molecularly, polysilazanes [R2Si−NH]n are isoelectronic with and close relatives to polysiloxanes [R2Si−O]n (silicones).
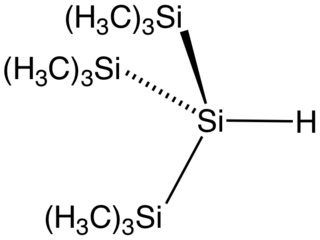
Tris(trimethylsilyl)silane is the organosilicon compound with the formula (Me3Si)3SiH (where Me = CH3). It is a colorless liquid that is classified as a hydrosilane since it contains an Si-H bond. The compound is notable as having a weak Si-H bond, with a bond dissociation energy estimated at 84 kcal/mol. For comparison, the Si-H bond in trimethylsilane is 94 kcal/mol. With such a weak bond, the compound is used as a reagent to deliver hydrogen atoms. The compound has been described as an environmentally benign analogue of tributyltin hydride.

Tetrakis(trimethylsilyl)silane is the organosilicon compound with the formula (Me3Si)4Si (where Me = CH3). It is a colorless sublimable solid with a high melting point. The molecule has tetrahedral symmetry. The compound is notable as having silicon bonded to four other silicon atoms, like in elemental silicon.
In organosilicon chemistry, silanes are a diverse class of charge-neutral organic compounds with the general formula SiR4. The R substituents can any combination of organic or inorganic groups. Most silanes contain Si-C bonds, and are discussed under organosilicon compounds. Some contain Si-H bonds and are discussed under hydrosilanes.

Hexachlorodisiloxane is a chemical compound composed of chlorine, silicon, and oxygen. Structurally, it is the symmetrical ether of two trichlorosilyl groups, and can be synthesized via high-temperature oxidation of silicon tetrachloride:
References
- ↑ Rösch, L.; John, P.; Reitmeier, R. (2003). "Organic Silicon Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a24_021. ISBN 978-3527306732..
- ↑ P. W. Schenk (1963). "Silicon and Germanium". In G. Brauer (ed.). Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Vol. 2page=691. NY, NY: Academic Press.