Marys River is a 40-mile (64 km) tributary of the Willamette River in the U.S. state of Oregon. From its source at the confluence of its east and west forks near Summit, it flows generally southeast from the Central Oregon Coast Range to Corvallis.

The Newaukum River is a tributary of the Chehalis River in the U.S. state of Washington. It has three main branches, the North Fork, South Fork, and Middle Fork Newaukum Rivers. The length of the three forks and the mainstem river is 56.7 miles (91.2 km).

The Feather River is the principal tributary of the Sacramento River, in the Sacramento Valley of Northern California. The river's main stem is about 73 miles (117 km) long. Its length to its most distant headwater tributary is just over 210 miles (340 km). The main stem Feather River begins in Lake Oroville, where its four long tributary forks join together—the South Fork, Middle Fork, North Fork, and West Branch Feather Rivers. These and other tributaries drain part of the northern Sierra Nevada, and the extreme southern Cascades, as well as a small portion of the Sacramento Valley. The total drainage basin is about 6,200 square miles (16,000 km2), with approximately 3,604 square miles (9,330 km2) above Lake Oroville.

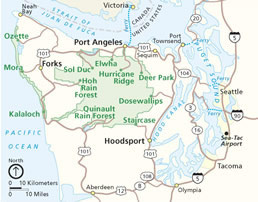
The Bogachiel River is a river of the Olympic Peninsula in the U.S. state of Washington. It originates near Bogachiel Peak, flows west through the mountains of Olympic National Park. After emerging from the park it joins the Sol Duc River, forming the Quillayute River, which empties into the Pacific Ocean near La Push, Washington.

The Skokomish River is a river in Mason County, Washington, United States. It is the largest river flowing into Hood Canal, a western arm of Puget Sound. From its source at the confluence of the North and South Forks the main stem Skokomish River is approximately 9 miles (14 km) long. The longer South Fork Skokomish River is 40 miles (64 km), making the length of the whole river via its longest tributary about 49 miles (79 km). The North Fork Skokomish River is approximately 34 miles (55 km) long. A significant part of the Skokomish River's watershed is within Olympic National Forest and Olympic National Park.
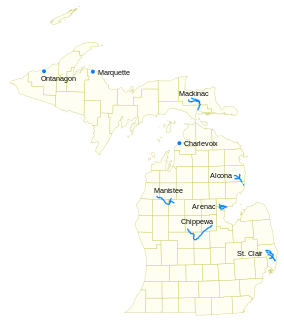
Pine River may refer to any of the following streams in the U.S. state of Michigan:
- Pine River. The main branch forms with the confluence of the East and West Branches of the Pine River at 44°29′38″N83°23′16″W in Alcona County. The South Branch joins approximately 1.5 miles (2.4 km) to the south and flows into Iosco County, where it empties into Van Etten Lake at 44°29′38″N83°23′16″W northwest of Oscoda.
- Pine River. The main branch is formed by the confluence of the North and Middle Branches northeast of Standish and flows into the Saginaw Bay of Lake Huron at 43°58′32″N83°51′16″W. The South Branch Pine River joins the main stream at 43°59′08″N83°53′17″W.
- Pine River is a short waterway, which along with Round Lake, connects Lake Charlevoix with Lake Michigan at Charlevoix.
- Pine River rises in Chippewa County and flows south through Mackinac County into the St. Martin Bay of Lake Huron at 46°03′09″N84°39′22″W The North Pine River, also known as the North Branch Pine River, joins at 46°12′20″N84°36′17″W. Another tributary, Hemlock Creek, is also known as Pine River.
- Pine River, also known as the South Branch Manistee River, rises in southeast Wexford County, flows southwest across northwest Osceola County, then west and north through the northeast corner of Lake County and back into southwest Wexford County, emptying into the Tippy Dam Pond on the Manistee River at 44°13′37″N85°54′27″W. The main stream is formed from the confluence of the East Branch Pine River with the North Branch Pine River at 44°06′02″N85°31′40″W. Another tributary, the Spaulding Creek, is also known as the Little Pine River
- Pine River, in Marquette County, is a very short stream draining Pine Lake into Lake Superior at 46°53′27″N87°52′13″W, north of the Huron Mountains.
- Pine River rises in from Pine Lake in eastern Mecosta County, flows mostly south and east through Isabella County, then south along eastern edge of Montcalm County, then east and north through Gratiot County and Midland County, emptying into the Chippewa River at 43°36′06″N84°17′33″W, just about two miles before it joins the Tittabawassee River near Midland. The South Branch Pine River joins the main stream at 43°30′37″N85°00′02″W Another tributary, Miller Creek, is also sometimes known as Pine River or the West Branch Pine River. The North Branch Pine River joins the main stream at 43°26′03″N84°50′18″W.
- Pine River empties into the St. Clair River at 42°49′13″N82°29′08″W on the south side of St. Clair. The South Branch Pine River joins the main stream at 42°58′11″N82°37′10″W. Another tributary, Quakenbush Drain, is also sometimes known as Pine River.
- Pine Creek empties into Lake Superior and is also known as the Pine River.

The Tule River, also called Rio de San Pedro or Rio San Pedro, is a 71.4-mile (114.9 km) river in Tulare County in the U.S. state of California. The river originates in the Sierra Nevada east of Porterville and consists of three forks, North, Middle and South. The North Fork and Middle Fork meet above Springville. The South Fork meets the others at Lake Success. Downstream of Success Dam, the river flows west through Porterville. The river used to empty into Tulare Lake, but its waters have been diverted for irrigation. However, the river does reach Tulare Lake during floods. Tulare Lake is the terminal sink of an endorheic basin that historically also received the Kaweah and Kern Rivers as well as southern distributaries of the Kings.

The San Jacinto River is a 42-mile-long (68 km) river in Riverside County, California. The river's headwaters are in San Bernardino National Forest, but the lower portion of the 765-square-mile (1,980 km2) watershed is urban and agricultural land. As a partially endorheic watershed that is contiguous with other Great Basin watersheds, the western side of the San Jacinto Basin is a portion of the Great Basin Divide.

The Quinault River is a 69-mile (111 km) long river located on the Olympic Peninsula in the U.S. state of Washington. It originates deep in the Olympic Mountains in the Olympic National Park. It flows southwest through the "Enchanted Valley" to opposite Quinault Canyon. Several miles above Lake Quinault the river is joined by its main tributary, the North Fork Quinault River. The main stem Quinault River above this confluence is sometimes called the East Fork Quinault River. Below the confluence the river marks the boundary of Olympic National Park for several miles before emptying into Lake Quinault. After the lake, the Quinault River flows southwest, reaching the Pacific at Taholah. From Lake Quinault to the ocean, the river is contained within the Quinault Indian Reservation.

Cherry Creek is a large, swift-flowing stream in the Sierra Nevada mountain range, and is the largest tributary of the Tuolumne River. The creek is 40 miles (64 km) long measured to its farthest headwaters; the main stem itself is 26 miles (42 km) long, draining a watershed of 234 square miles (610 km2) in the Stanislaus National Forest. Part of the drainage also extends into the northwest corner of Yosemite National Park.

The Rio Chama, a major tributary river of the Rio Grande, is located in the U.S. states of Colorado and New Mexico. The river is about 130 miles (210 km) long altogether. From its source to El Vado Dam its length is about 50 miles (80 km), from El Vado Dam to Abiquiu Dam is about 51 miles (82 km), and from Abiquiu Dam to its confluence with the Rio Grande is about 34 miles (55 km).

The Sol Duc River is a river in the U.S. state of Washington. About 78 miles (126 km) long, it flows west through the northwest part of the Olympic Peninsula, from the Olympic Mountains of Olympic National Park and Olympic National Forest, then through the broad Sol Duc Valley. Near the Pacific Ocean the Sol Duc River joins the Bogachiel River, forming the Quillayute River, which flows about 4 miles (6.4 km) to the Pacific Ocean at La Push. Although the Quillayute River is short, its large tributary rivers—the Sol Duc, Bogachiel, Calawah, and Dickey Rivers—drain the largest watershed of the northern Olympic Peninsula, 629 square miles (1,630 km2). The Sol Duc's watershed is the largest of the Quillayute's tributaries, at 219 square miles (570 km2).

Hylebos Creek is a stream located in the U.S. state of Washington near Tacoma and emptying into Commencement Bay, part of Puget Sound. It flows through southern King County and northern Pierce County, through the cities of Tacoma, Federal Way, Milton, and Fife, as well as the Puyallup Indian Reservation.

Ash Creek is a short stream in Polk County, in the U.S. state of Oregon. Formed by the merger of its north and middle forks near Monmouth, it flows generally east to meet the Willamette River at Independence. The creek passes under Oregon Route 51 just before entering the river. The creek's mouth is about 95 miles (153 km) upstream of the Willamette's confluence with the Columbia River.

Dairy Creek is a 10.55-mile (16.98 km) tributary of the Tualatin River in the U.S. state of Oregon. It begins at the confluence of its east and west forks near the unincorporated community of Schefflin and meanders southeast across the Tualatin Valley to the Tualatin River near Hillsboro, in Washington County. East Fork Dairy Creek begins at 45.788446°N 123.041498°W in Columbia County, slightly north of its border with Washington County, and flows generally south for 22 miles (35 km). West Fork Dairy Creek, also about 22 miles (35 km) long, forms at 45.7553899°N 123.178168°W, near the unincorporated community of Tophill, and flows generally southeast. Before railroads displaced river boats on the Tualatin, some steamships also worked the lower section of Dairy Creek, with plans to go as far up stream as Centerville.

The Hoquiam River is a stream in the U.S. state of Washington. It has three main tributaries, the East Fork, West Fork, and Middle Fork Hoquiam Rivers. The main stem Hoquiam River is formed by the confluence of the West and East Forks. The Middle Fork is a tributary of the West Fork.

The Satsop River is a stream in the U.S. state of Washington. It has three main tributary forks, the East Fork, West Fork, and Middle Fork Satsop Rivers. The main stem Satsop River is formed by the confluence of the West and East Forks. The Middle Fork is a tributary of the East Fork. The three forks are much longer than the main stem Satsop itself, which flows south from the confluence only a few miles to join the Chehalis River near Satsop, Washington. Other significant tributaries include the Canyon River and Little River, both tributaries of the West Fork Satsop, and Decker Creek, a tributary of the East Fork Satsop River. The Satsop River's major tributaries originate in the Olympic Mountains and its southern foothills, the Satsop Hills, within Grays Harbor and Mason counties. Most of the Satsop River's watershed consists of heavily wooded hill lands. The upper tributaries extend into Olympic National Forest, approaching but not quite reaching Olympic National Park.

The Clearwater River is in the northwestern United States, in north central Idaho. Its length is 74.8 miles (120.4 km), it flows westward from the Bitterroot Mountains along the Idaho-Montana border, and joins the Snake River at Lewiston. In October 1805, the Lewis and Clark Expedition descended the Clearwater River in dugout canoes, putting in at "Canoe Camp," five miles (8 km) downstream from Orofino; they reached the Columbia Bar and the Pacific Ocean about six weeks later.

The Foss River is a stream in the U.S. state of Washington. It has two main forks, the East Fork Foss River and the West Fork Foss River. The main stem is formed by the confluence of the two forks. The river and its forks rise near in the Alpine Lakes Wilderness area of Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest in the Cascade Mountains and flows generally north, joining the Tye River to form the South Fork Skykomish River. The Foss River's waters eventually empty into Puget Sound near Everett via the Skykomish River and Snohomish River.

The Jemez River is a tributary of the Rio Grande in the U.S. state of New Mexico. The river is formed by the confluence of the East Fork Jemez River and San Antonio Creek, which drain a number of tributaries in the area of the Jemez Mountains and Santa Fe National Forest. The Jemez River is about 50 miles (80 km) long, or about 80 miles (130 km) long if its longest headwater tributary, San Antonio Creek, is included. The East Fork Jemez River is about 22 miles (35 km) long. Both San Antonio Creek and the East Fork Jemez River flow through intricate meanders along their courses. The East Fork Jemez is a National Wild and Scenic River.