
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca was a Spanish conquistador who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of what is now mainland Mexico under the rule of the king of Castile in the early 16th century. Cortés was part of the generation of Spanish explorers and conquistadors who began the first phase of the Spanish colonization of the Americas.
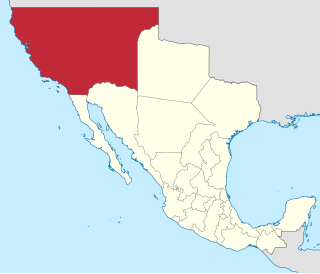
Alta California, also known as Nueva California among other names, was a province of New Spain formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of Las Californias, but was made a separate province in 1804. Following the Mexican War of Independence, it became a territory of Mexico in April 1822 and was renamed Alta California in 1824.

José de la Cruz Porfirio Díaz Mori, known as Porfirio Díaz, was a Mexican general, politician and dictator who served seven terms as President of Mexico, a total of 31 years, from 28 November 1876 to 6 December 1876, 17 February 1877 to 1 December 1880 and from 1 December 1884 to 25 May 1911. The entire period from 1876 to 1911 is often referred to as the Porfiriato, and has been characterized as a de facto dictatorship.

Emiliano Zapata Salazar was a Mexican revolutionary. He was a leading figure in the Mexican Revolution of 1910–1920, the main leader of the people's revolution in the Mexican state of Morelos, and the inspiration of the agrarian movement called Zapatismo.

Benito Pablo Juárez García was a Mexican Liberal lawyer and statesman who served as the 26th president of Mexico from 1858 until his death in office in 1872. Of Zapotec ancestry, he was the first and only indigenous president of Mexico and the first democratically elected indigenous president in the postcolonial Americas. Previously, he had served as Governor of Oaxaca and had later ascended to a variety of federal posts including Secretary of the Interior, Secretary of Public Education, and President of the Supreme Court. During his presidency he led the Liberals to victory in the Reform War and in the Second French intervention in Mexico.

The Mexican Revolution was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from 20 November 1910 to 1 December 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It resulted in the destruction of the Federal Army and its replacement by a revolutionary army, and the transformation of Mexican culture and government. The northern Constitutionalist faction prevailed on the battlefield and drafted the present-day Constitution of Mexico, which aimed to create a strong central government. Revolutionary generals held power from 1920 to 1940. The revolutionary conflict was primarily a civil war, but foreign powers, having important economic and strategic interests in Mexico, figured in the outcome of Mexico's power struggles; the U.S. involvement was particularly high. The conflict led to the deaths of around one million people, mostly noncombatants.

Arturo García Bustos was a Mexican painter and print maker. He is known as one of “Los Fridos” students who studied under Frida Kahlo at her home in Coyoacán.

The second French intervention in Mexico, also known as the Second Franco-Mexican War (1861–1867), was a military invasion of the Republic of Mexico by the French Empire of Napoleon III, purportedly to force the collection of Mexican debts in conjunction with Great Britain and Spain. Mexican conservatives supported the invasion, since they had been defeated by the liberal government of Benito Juárez in a three-year civil war. Defeated on the battlefield, conservatives sought the aid of France to effect regime change and establish a monarchy in Mexico, a plan that meshed with Napoleon III's plans to re-establish the presence of the French Empire in the Americas. Although the French invasion displaced Juárez's Republican government from the Mexican capital and the monarchy of Archduke Maximilian was established, the Second Mexican Empire collapsed within a few years. Material aid from the United States, whose four-year civil war ended in 1865, invigorated the Republican fight against the regime of Maximilian, and the 1866 decision of Napoleon III to withdraw military support for Maximilian's regime accelerated the monarchy's collapse. Maximilian and two Mexican generals were executed by firing squad on 19 June 1867, ending this period of Mexican history.
Diego Durán was a Dominican friar best known for his authorship of one of the earliest Western books on the history and culture of the Aztecs, The History of the Indies of New Spain, a book that was much criticised in his lifetime for helping the "heathen" maintain their culture.

The Marquessate of the Valley of Oaxaca is a hereditary marquessal title in the Spanish nobility and a former seignorial estate in New Spain. It was granted to Don Hernán Cortés, conquistador who led the conquest of the Aztec Empire, by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in 1529. Despite its name, the marquessate covered a much larger area than the Oaxaca Valley, comprising a vast stretch of land in the present-day Mexican states of Oaxaca, Morelos, Veracruz, Michoacán and Mexico.

The state of Oaxaca in southern Mexico has a noteworthy tradition of finely crafted textiles, particularly handmade embroidery and woven goods that frequently use a backstrap loom. Oaxaca is home to several different groups of indigenous peoples, each of which has a distinctive textile tradition.
Huamelula is a town and municipality in Oaxaca in south-western Mexico. It is in the west of the Tehuantepec District in the west of the Istmo Region, on the Pacific coast.

The Indigenous people of Oaxaca are descendants of the inhabitants of what is now the state of Oaxaca, Mexico, who were present before the Spanish invasion. Several cultures flourished in the ancient region of Oaxaca from as far back as 2000 BC, of whom the Zapotecs and Mixtecs were perhaps the most advanced, with complex social organization and sophisticated arts.

The Plan of San Diego was a plan drafted in San Diego, Texas, in 1915 by a group of unidentified Mexican and Tejano rebels who hoped to seize Arizona, New Mexico, California, and Texas from the United States. The plan was never attempted. It called for a general uprising in February, 1915, and the assassination of every non-Hispanic Caucasian male over 16 years of age. The arena included all of South Texas. Germans were excluded from the killings. The San Diego Plan collapsed immediately on discovery.

The state of Oaxaca, Mexico has a total population of about 3.5 million, with women outnumbering men by 150,000 and about 60% of the population under the age of 30. It is ranked tenth in population in the country. Fifty three percent of the population lives in rural areas. Most of the state’s population growth took place between 1980 and 1990. Life expectancy is 71.7 for men and 77.4 for women, just under the national average. Births far outpace deaths. In 2007, there were 122,579 births and 19,439 deaths. Approximately 85% profess the Catholic faith.
In the Central Valley region of the Southern Mexican state of Oaxaca archeologists discovered evidence of historic settlements. Aztecs from Tenochtitlan on the volcanic plateau to the North around what today is Mexico City first arrived in this region around 1250 AD establishing military rule in the 15th century until the arrival of the Spanish. After the fall of Tenochtitlan, the Spanish took over Oaxaca which led to the eventual decrease of the Native population and the increase in African slaves. The region was then settled by mostly Spanish immigrants from Europe and the African slaves they brought with them. Oaxaca was considered a department after the Mexican War of Independence, but after the fall of emperor Agustín de Iturbide, it became a state in 1824 with José Murguia as its first governor. During the 19th century, Oaxaca was split between liberal and conservative factions. The political and military struggles between the factions resulted in wars and intrigues. A series of major disasters occurred in the state from the 1920s to the 1940s. In the 1940s and 1950s, new infrastructure projects were begun. From the 1980s to the present, there has been much development of the tourism industry in the state.

Ixcateopan is an archaeological site located in the town and municipality of Ixcateopan de Cuauhtémoc, 36 kilometers from Taxco, in the isolated and rugged mountains of the northern part of the Mexican state of Guerrero.
Highland Oaxaca Chontal, or Chontal de la Sierra de Oaxaca, is one of the Chontal languages of Oaxaca, Mexico. It is sometimes called Tequistlatec, but is not the same as Tequistlatec proper, which is extinct.
Juan Bautista and Jacinto de los Ángeles were Mexican Roman Catholics. The pair were both instructed to protect moral practices in their town and to ensure that the faith was safeguarded in the face of pagan and tribal beliefs and practices. But this put them into conflict with some locals who decided to hunt them down and kill them after the pair interrupted a ritual and confiscated their possessions. The two men were slain after being captured in a local Dominican convent and after having professed their faith to their attackers.

The Restored Republic was the era of Mexican history between 1867 and 1876, starting with the liberal triumph over the Second French Intervention in Mexico and the fall of the Second Mexican Empire and ending with Porfirio Diaz's ascension to the presidency. It was followed by the three-decade dictatorship known as the Porfiriato.














