Related Research Articles
Knowledge representation and reasoning is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) dedicated to representing information about the world in a form that a computer system can use to solve complex tasks, such as diagnosing a medical condition or having a natural-language dialog. Knowledge representation incorporates findings from psychology about how humans solve problems and represent knowledge, in order to design formalisms that make complex systems easier to design and build. Knowledge representation and reasoning also incorporates findings from logic to automate various kinds of reasoning.

The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
In information science, an ontology encompasses a representation, formal naming, and definitions of the categories, properties, and relations between the concepts, data, or entities that pertain to one, many, or all domains of discourse. More simply, an ontology is a way of showing the properties of a subject area and how they are related, by defining a set of terms and relational expressions that represent the entities in that subject area. The field which studies ontologies so conceived is sometimes referred to as applied ontology.
OIL can be regarded as an ontology infrastructure for the Semantic Web. OIL is based on concepts developed in Description Logic (DL) and frame-based systems and is compatible with RDFS.

The Digital Enterprise Research Institute (DERI) is a former research institute at NUI Galway. It is now part of the Insight Centre for Data Analytics. Insight was established in 2013 by Science Foundation Ireland with funding of €75m.

Semantic MediaWiki (SMW) is an extension to MediaWiki that allows for annotating semantic data within wiki pages, thus turning a wiki that incorporates the extension into a semantic wiki. Data that has been encoded can be used in semantic searches, used for aggregation of pages, displayed in formats like maps, calendars and graphs, and exported to the outside world via formats like RDF and CSV.
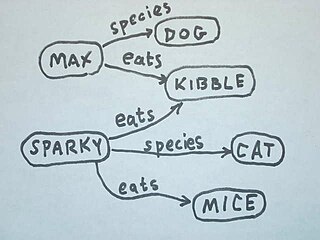
The ultimate goal of semantic technology is to help machines understand data. To enable the encoding of semantics with the data, well-known technologies are RDF and OWL. These technologies formally represent the meaning involved in information. For example, ontology can describe concepts, relationships between things, and categories of things. These embedded semantics with the data offer significant advantages such as reasoning over data and dealing with heterogeneous data sources.

Rudi Studer is a German computer scientist and professor emeritus at KIT, Germany. He served as head of the knowledge management research group at the Institute AIFB and one of the directors of the Karlsruhe Service Research Institute (KSRI). He is a former president of the Semantic Web Science Association, an STI International Fellow, and a member of numerous programme committees and editorial boards. He was one of the inaugural editors-in-chief of the Journal of Web Semantics, a position he held until 2007. He is a co-author of the "Semantic Wikipedia" proposal which led to the development of Wikidata.

Frank van Harmelen is a Dutch computer scientist and professor in Knowledge Representation & Reasoning in the AI department at the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam. He was scientific director of the LarKC project (2008-2011), "aiming to develop the Large Knowledge Collider, a platform for very large scale semantic web reasoning."

In computing, linked data is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but rather than using them to serve web pages only for human readers, it extends them to share information in a way that can be read automatically by computers. Part of the vision of linked data is for the Internet to become a global database.
Seekda is an Austrian web service search engine. It was created by Seekda GmbH, a hospitality management software company and a provider in the field of e-tourism.
What you see is what you meant (WYSIWYM) is a text editing interaction technique that emerged from two projects at University of Brighton. It allows users to create abstract knowledge representations such as those required by the Semantic Web using a natural language interface. Natural language understanding (NLU) technology is not employed. Instead, natural language generation (NLG) is used in a highly interactive manner.

In computer science, information science and systems engineering, ontology engineering is a field which studies the methods and methodologies for building ontologies, which encompasses a representation, formal naming and definition of the categories, properties and relations between the concepts, data and entities of a given domain of interest. In a broader sense, this field also includes a knowledge construction of the domain using formal ontology representations such as OWL/RDF. A large-scale representation of abstract concepts such as actions, time, physical objects and beliefs would be an example of ontological engineering. Ontology engineering is one of the areas of applied ontology, and can be seen as an application of philosophical ontology. Core ideas and objectives of ontology engineering are also central in conceptual modeling.
Ontology engineering aims at making explicit the knowledge contained within software applications, and within enterprises and business procedures for a particular domain. Ontology engineering offers a direction towards solving the inter-operability problems brought about by semantic obstacles, i.e. the obstacles related to the definitions of business terms and software classes. Ontology engineering is a set of tasks related to the development of ontologies for a particular domain.
Semantic Technology Institute (STI) International is an association of global experts in semantics and services, located in Austria. It has members mostly from Europe, but also from South Korea, Malaysia, and Singapore.

John Domingue is a British academic, and Professor of Computer Science at the Knowledge Media Institute at the Open University in Milton Keynes, and researcher in the semantic web, linked data, services, blockchain and education.
The German software company fluid Operations AG (fluidOps) was founded in 2008, and specializes in cloud management and semantic technology. Fluid Operations' product portfolio includes the semantic integration platform Information Workbench and eCloudManager. Additionally, fluid Operations offers an open source software, the VMFS Driver. In 2018, fluidOps joined Veritas Technologies to empower organizations to discover the Truth in Information.
Semantic Web - Interoperability, Usability, Applicability is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by IOS Press. It was established in 2010 and covers the foundations and applications of semantic web technologies, knowledge graph, and linked data. The journal uses an open peer-review process. The journal publishes its metadata online in the form of linked data and provides scientometrics such as the geographic distribution of authors, citation networks, trends in research topics over time, and so forth. The founding editors-in-chief are Pascal Hitzler and Krzysztof Janowicz (2010-).

Pascal Hitzler is a German American computer scientist specializing in Semantic Web and Artificial Intelligence. He is endowed Lloyd T. Smith Creativity in Engineering Chair, one of the Directors of the Institute for Digital Agriculture and Advanced Analytics (ID3A) and Director of the Center for Artificial Intelligence and Data Science (CAIDS) at Kansas State University, and the founding Editor-in-Chief of the Semantic Web journal and the IOS Press book series Studies on the Semantic Web.

Data Commons is an open-source platform created by Google that provides an open knowledge graph, combining economic, scientific and other public datasets into a unified view. Ramanathan V. Guha, a creator of web standards including RDF, RSS, and Schema.org, founded the project, which is now led by Prem Ramaswami.

Zdenko "Denny" Vrandečić is a Croatian computer scientist. He was a co-developer of Semantic MediaWiki and Wikidata, the lead developer of the Wikifunctions project, and an employee of the Wikimedia Foundation as a Head of Special Projects, Structured Content. He published modules for the German role-playing game The Dark Eye.
References
- ↑ Phelan, Shane (October 26, 2010), "Academics rack up €108,000 taxpayer bill for private jets", Irish Independent .
- ↑ Semantic Technology Institute about seekda (Retrieved 29 November 2007)
- ↑ List of publications from the DBLP Bibliography Server
- ↑ List of written or edited books
- ↑ "Invited speakers at Web Intelligence 07 Conference". Archived from the original on 2007-11-02. Retrieved 2007-11-29.