The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
In computer science and information science, an ontology encompasses a representation, formal naming, and definition of the categories, properties, and relations between the concepts, data, and entities that substantiate one, many, or all domains of discourse. More simply, an ontology is a way of showing the properties of a subject area and how they are related, by defining a set of concepts and categories that represent the subject.
Semantic similarity is a metric defined over a set of documents or terms, where the idea of distance between items is based on the likeness of their meaning or semantic content as opposed to lexicographical similarity. These are mathematical tools used to estimate the strength of the semantic relationship between units of language, concepts or instances, through a numerical description obtained according to the comparison of information supporting their meaning or describing their nature. The term semantic similarity is often confused with semantic relatedness. Semantic relatedness includes any relation between two terms, while semantic similarity only includes "is a" relations. For example, "car" is similar to "bus", but is also related to "road" and "driving".
KAON is an ontology infrastructure developed by the University of Karlsruhe and the Research Center for Information Technologies in Karlsruhe. Its first incarnation was developed in 2002 and supported an enhanced version of RDF ontologies. Several tools like the graphical ontology editor OIModeler or the KAON Server were based on KAON.
Semantic MediaWiki (SMW) is an extension to MediaWiki that allows for annotating semantic data within wiki pages, thus turning a wiki that incorporates the extension into a semantic wiki. Data that has been encoded can be used in semantic searches, used for aggregation of pages, displayed in formats like maps, calendars and graphs, and exported to the outside world via formats like RDF and CSV.
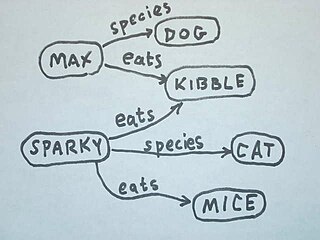
The ultimate goal of semantic technology is to help machines understand data. To enable the encoding of semantics with the data, well-known technologies are RDF and OWL. These technologies formally represent the meaning involved in information. For example, ontology can describe concepts, relationships between things, and categories of things. These embedded semantics with the data offer significant advantages such as reasoning over data and dealing with heterogeneous data sources.

The Karlsruhe Institute of Technology is an elite public research university in the German state Baden-Württemberg and a national research center in the Helmholtz Association that is one of the largest educational institutions and the largest research institution by funding in Germany. KIT was created in 2009 when the University of Karlsruhe, founded in 1825 as a public research university and also known as the "Fridericiana", merged with the Karlsruhe Research Center, which had originally been established in 1956 as a national nuclear research center.
Ontology learning is the automatic or semi-automatic creation of ontologies, including extracting the corresponding domain's terms and the relationships between the concepts that these terms represent from a corpus of natural language text, and encoding them with an ontology language for easy retrieval. As building ontologies manually is extremely labor-intensive and time-consuming, there is great motivation to automate the process.
Semantic analytics, also termed semantic relatedness, is the use of ontologies to analyze content in web resources. This field of research combines text analytics and Semantic Web technologies like RDF. Semantic analytics measures the relatedness of different ontological concepts.
Dieter Fensel is a German researcher in the field of formal languages and the semantic web. He is University Professor at the University of Innsbruck, where he directs the Semantic Technologies Institute Innsbruck, a research center associated with the university.
Amit Sheth is a computer scientist at University of South Carolina in Columbia, South Carolina. He is the founding Director of the Artificial Intelligence Institute, and a Professor of Computer Science and Engineering. From 2007 to June 2019, he was the Lexis Nexis Ohio Eminent Scholar, director of the Ohio Center of Excellence in Knowledge-enabled Computing, and a Professor of Computer Science at Wright State University. Sheth's work has been cited by over 48,800 publications. He has an h-index of 106, which puts him among the top 100 computer scientists with the highest h-index. Prior to founding the Kno.e.sis Center, he served as the director of the Large Scale Distributed Information Systems Lab at the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia.

In computer science, information science and systems engineering, ontology engineering is a field which studies the methods and methodologies for building ontologies, which encompasses a representation, formal naming and definition of the categories, properties and relations between the concepts, data and entities. In a broader sense, this field also includes a knowledge construction of the domain using formal ontology representations such as OWL/RDF. A large-scale representation of abstract concepts such as actions, time, physical objects and beliefs would be an example of ontological engineering. Ontology engineering is one of the areas of applied ontology, and can be seen as an application of philosophical ontology. Core ideas and objectives of ontology engineering are also central in conceptual modeling.
The ontoprise GmbH was a provider of Semantic Web infrastructure technologies and products used to support dynamic semantic information integration and information management processes at the enterprise level. Its primary place of business was located at Karlsruhe, Germany.
Knowledge extraction is the creation of knowledge from structured and unstructured sources. The resulting knowledge needs to be in a machine-readable and machine-interpretable format and must represent knowledge in a manner that facilitates inferencing. Although it is methodically similar to information extraction (NLP) and ETL, the main criterion is that the extraction result goes beyond the creation of structured information or the transformation into a relational schema. It requires either the reuse of existing formal knowledge or the generation of a schema based on the source data.
Semantic Technology Institute (STI) International is an association of global experts in semantics and services, located in Austria. It has members mostly from Europe, but also from South Korea, Malaysia, and Singapore.
María-Esther Vidal Serodio is a Venezuelan professor at the Computer Science Department of the Simón Bolívar University since 2005 and dean assistant for research and development in applied science and engineering since 2011, on-leave since 2015. She currently leads the Semantic Web Group, which includes members from multiple fields such as databases, distributed systems and artificial intelligence, and whose research is focused on the solving problems from said fields.

Pascal Hitzler is a German American computer scientist specializing in Semantic Web and Artificial Intelligence. He is endowed Lloyd T. Smith Creativity in Engineering Chair and Director of the Center for Artificial Intelligence and Data Science at Kansas State University, and the founding Editor-in-Chief of the Semantic Web journal and the IOS Press book series Studies on the Semantic Web.

Ali Sunyaev is a professor for computer science and director of the Institute of Applied Informatics and Formal Description Methods at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT).

In knowledge representation and reasoning, knowledge graph is a knowledge base that uses a graph-structured data model or topology to integrate data. Knowledge graphs are often used to store interlinked descriptions of entities – objects, events, situations or abstract concepts – while also encoding the semantics underlying the used terminology.

Zdenko "Denny" Vrandečić is a Croatian computer scientist. He was a co-developer of Semantic MediaWiki and Wikidata, the lead developer of the Wikifunctions project, and an employee of the Wikimedia Foundation as a Head of Special Projects, Structured Content. He published modules for the German role-playing game The Dark Eye.








