
George of Brandenburg-Ansbach, known as George the Pious, was a Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach from the House of Hohenzollern.

Worms is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, situated on the Upper Rhine about 60 km (40 mi) south-southwest of Frankfurt am Main. It had about 82,000 inhabitants as of 2015.

The Diet of Worms of 1521 was an imperial diet of the Holy Roman Empire called by Emperor Charles V and conducted in the Imperial Free City of Worms. Martin Luther was summoned to the Diet in order to renounce or reaffirm his views in response to a Papal bull of Pope Leo X. In answer to questioning, he defended these views and refused to recant them. At the end of the Diet, the Emperor issued the Edict of Worms, a decree which condemned Luther as "a notorious heretic" and banned citizens of the Empire from propagating his ideas. Although the Protestant Reformation is usually considered to have begun in 1517, the edict signals the first overt schism.

The Protestant Union, also known as the Evangelical Union, Union of Auhausen, German Union or the Protestant Action Party, was a coalition of Protestant German states. It was formed on 14 May 1608 by Frederick IV, Elector Palatine in order to defend the rights, land and safety of each member. It included both Calvinist and Lutheran states, and dissolved in 1621.

Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse, nicknamed der Großmütige, was a champion of the Reformation and one of the most important of the early Protestant rulers in Germany.

The Schmalkaldic War was the short period of violence from 1546 until 1547 between the forces of Emperor Charles V of the Holy Roman Empire, commanded by the Duke of Alba and the Duke of Saxony, and the Lutheran Schmalkaldic League within the domains of the Holy Roman Empire.

The Reichskammergericht was one of the two highest judicial institutions in the Holy Roman Empire, the other one being the Aulic Council in Vienna. It was founded in 1495 by the Imperial Diet in Worms. All legal proceedings in the Holy Roman Empire could be brought to the Imperial Chamber Court, except if the ruler of the territory had a so-called privilegium de non appellando, in which case the highest judicial institution was found by the ruler of that territory. Another exception was criminal law in which the Imperial Chamber Court could intervene only if basic procedural rules had been violated.

The Diet of Augsburg were the meetings of the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire held in the German city of Augsburg. Both an Imperial City and the residence of the Augsburg prince-bishops, the town had hosted the Estates in many such sessions since the 10th century. In 1282, the diet of Augsburg assigned the control of Austria to the House of Habsburg. In the 16th century, twelve of thirty-five imperial diets were held in Augsburg, a result of the close financial relationship between the Augsburg-based banking families such as the Fugger and the reigning Habsburg emperors, particularly Maximilian I and his grandson Charles V. Nevertheless, the meetings of 1518, 1530, 1547/48 and 1555, during the Reformation and the ensuing religious war between the Catholic emperor and the Protestant Schmalkaldic League, are especially noteworthy. With the Peace of Augsburg, the cuius regio, eius religio principle let each prince decide the religion of his subjects and inhabitants who could not conform could leave.

On April 19, 1529, six princes and representatives of 14 Imperial Free Cities petitioned the Imperial Diet at Speyer against an imperial ban of Martin Luther, as well as the proscription of his works and teachings, and called for the unhindered spread of the evangelical faith.

Julius von Pflug was the last Catholic bishop of the Diocese of Naumburg from 1542 until his death. He was one of the most significant reformers involved with the Protestant Reformation.
The Diet of Speyer or the Diet of Spires was a Diet of the Holy Roman Empire held in 1529 in the Imperial City of Speyer. The Diet condemned the results of the Diet of Speyer of 1526 and prohibited future reformation. It resulted in the Protestation at Speyer.
The Diet of Speyer or the Diet of Spires was an Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire in 1526 in the Imperial City of Speyer in present-day Germany. The Diet's ambiguous edict resulted in a temporary suspension of the Edict of Worms and aided the expansion of Protestantism. Those results were repudiated in the Diet of Speyer (1529).

Lutheranism as a religious movement originated in the early 16th century Holy Roman Empire as an attempt to reform the Roman Catholic Church. The movement originated with the call for a public debate regarding several issues within the Catholic Church by Martin Luther, then a professor of Bible at the young University of Wittenberg. Lutheranism soon became a wider religious and political movement within the Holy Roman Empire owing to support from key electors and the widespread adoption of the printing press. This movement soon spread throughout northern Europe and became the driving force behind the wider Protestant Reformation. Today, Lutheranism has spread from Europe to all six populated continents.
The Colloquy of Regensburg, historically called the Colloquy of Ratisbon, was a conference held at Regensburg (Ratisbon) in Bavaria in 1541, during the Protestant Reformation, which marks the culmination of attempts to restore religious unity in the Holy Roman Empire by means of theological debate between the Protestants and the Catholics.

The German-speaking states of the early modern period were divided politically and religiously. Religious tensions between the states comprising the Holy Roman Empire had existed during the preceding period of the Late Middle Ages —notably erupting in Bohemia with the Hussite Wars (1419–1434). However, the defining religious movement of this period, the Reformation, would result in unprecedented levels of violence and political upheaval for the region.

The Augsburg Confession, also known as the Augustan Confession or the Augustana from its Latin name, Confessio Augustana, is the primary confession of faith of the Lutheran Church and one of the most important documents of the Protestant Reformation. The Augsburg Confession was written in both German and Latin and was presented by a number of German rulers and free-cities at the Diet of Augsburg on 25 June 1530.
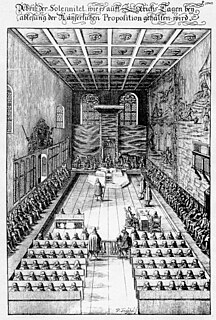
The Imperial Diet was the deliberative body of the Holy Roman Empire. It was not a legislative body in the contemporary sense; its members envisioned it more like a central forum where it was more important to negotiate than to decide.
The name imperial government denotes two organs, created in 1500 and 1521, in the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation to enable a unified political leadership, with input from the Princes. Both were composed of the emperor or his deputy and 20 — later 22 — representatives of the Imperial States and in both cases, the imperial city of Nuremberg was the seat of government. The creation of a functional imperial government was the central plank of the Imperial Reform the princes attempted in the early 16th Century. Both attempts failed after a short time, due to the resistance of the Emperor and the divergent interests of princes.

George I of Pomerania was a Duke of Pomerania from the House of Griffins.
The history of Speyer begins with the establishment of a Roman camp in 10 BCE, making it one of Germany's oldest cities. Its name evolved from Spira, first mentioned in 614. As of 1294 a Free Imperial City, the town became renowned for its Romanesque cathedral, its vibrant Jewish community, its seat of the Imperial Chamber Court, for 50 diets that took place within its walls, most notably 1526 and 1529, and last but not least, for the Protestation at Speyer. For several centuries from the Middle Ages into the early modern period, Speyer was one of the main centres of gravity of the Holy Roman Empire.













