
Gastroenterology is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes referred to as the GI tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine as well as the accessory organs of digestion which includes the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver. The digestive system functions to move material through the GI tract via peristalsis, break down that material via digestion, absorb nutrients for use throughout the body, and remove waste from the body via defecation. Physicians who specialize in the medical specialty of gastroenterology are called gastroenterologists or sometimes GI doctors. Some of the most common conditions managed by gastroenterologists include gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, irritable bowel syndrome, irritable bowel disease which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, peptic ulcer disease, gallbladder and biliary tract disease, hepatitis, pancreatitis, colitis, colon polyps and cancer, nutritional problems, and many more.

The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid.

The gastrointestinal tract is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. Gastrointestinal is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines.

Defecation follows digestion, and is a necessary process by which organisms eliminate a solid, semisolid, or liquid waste material known as feces from the digestive tract via the anus. The act has a variety of names ranging from the common, like pooping or crapping, to the technical, e.g. bowel movement, to the obscene (shitting), to the euphemistic, to the juvenile. The topic, usually avoided in polite company, can become the basis for some potty humour.

A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of migrated gallstones within bile ducts.

Colostrum, or first milk, is the first form of milk produced by the mammary glands of humans and other mammals immediately following delivery of the newborn. It may be called beestings when referring to the first milk of a cow or similar animal. Most species will begin to generate colostrum just prior to giving birth. Colostrum has an especially high amount of bioactive compounds compared to mature milk to give the newborn the best possible start to life. Specifically, colostrum contains antibodies to protect the newborn against disease and infection, and immune and growth factors and other bioactives that help to activate a newborn's immune system, jumpstart gut function, and seed a healthy gut microbiome in the first few days of life. The bioactives found in colostrum are essential for a newborn's health, growth and vitality. Colostrum strengthens a baby's immune system and is filled with white blood cells to protect it from infection.

Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications can relate to hormonal dysfunction of the kidneys and include high blood pressure, bone disease, and anemia. Additionally CKD patients have markedly increased cardiovascular complications with increased risks of death and hospitalization.
The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as indexed by Clarivate's Web of Science.
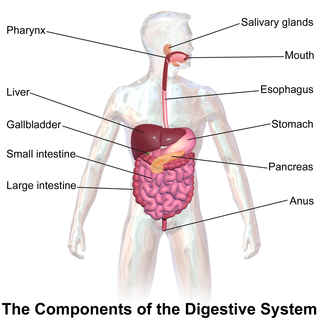
Gastrointestinal diseases refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum, and the accessory organs of digestion, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
JAMA Pediatrics is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published by the American Medical Association. It covers all aspects of pediatrics. The journal was established in 1911 as the American Journal of Diseases of Children and renamed in 1994 to Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, before obtaining its current title in 2013.

Emerging Infectious Diseases (EID) is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). EID is a public domain journal and covers global instances of new and reemerging infectious diseases, putting greater emphasis on disease emergence, prevention, control, and elimination. According to Journal Citation Reports, the journal's 2016 impact factor is 6.99, ranking it 4th out of 82 journals in the infectious disease category. The journal also has a 2016 Google Scholar h5-index score of 79, ranking it 2nd in both the epidemiology category and among open-access epidemiological journals, as well as 4th in the communicable diseases category and 1st among open-access communicable disease journals.

Nature Medicine is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published by Nature Portfolio covering all aspects of medicine. It was established in 1995. The journal seeks to publish research papers that "demonstrate novel insight into disease processes, with direct evidence of the physiological relevance of the results". As with other Nature journals, there is no external editorial board, with editorial decisions being made by an in-house team, although peer review by external expert referees forms a part of the review process. The editor-in-chief is João Monteiro.
Clinical Infectious Diseases is a peer-reviewed medical journal published by Oxford University Press covering research on the pathogenesis, clinical investigation, medical microbiology, diagnosis, immune mechanisms, and treatment of diseases caused by infectious agents. It includes articles on antimicrobial resistance, bioterrorism, emerging infections, food safety, hospital epidemiology, and HIV/AIDS. It also features highly focused brief reports, review articles, editorials, commentaries, and supplements. The journal is published on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. The editor-in-chief is infectious disease physician Paul Sax.

The Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease is a peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes an annual volume of review articles relevant to pathology. It was established in 2006 and is published by Annual Reviews. Its co-editors have been Jon C. Aster, Mel B. Feany, and Jayanta Debnath since 2021. As of 2022, Journal Citation Reports gives the journal a 2021 impact factor of 32.350, ranking it first of 77 journal titles in the category "Pathology".

The American Journal of Cardiology is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal in the field of cardiology and general cardiovascular disease. The editor-in-chief is William C. Roberts. It supersedes the Transactions of the American College of Cardiology which was published from 1951 to 1957 and the Bulletin of the American College of Cardiology, but it should not be confused with the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.

Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage to the liver leads to repair of liver tissue and subsequent formation of scar tissue. Over time, scar tissue can replace normal functioning tissue, leading to the impaired liver function of cirrhosis. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years. Early symptoms may include tiredness, weakness, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and discomfort in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. As the disease worsens, symptoms may include itchiness, swelling in the lower legs, fluid build-up in the abdomen, jaundice, bruising easily, and the development of spider-like blood vessels in the skin. The fluid build-up in the abdomen develop spontaneous infections. More serious complications include hepatic encephalopathy, bleeding from dilated veins in the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, and liver cancer.

The San Francisco Declaration on Research Assessment (DORA) intends to halt the practice of correlating the journal impact factor to the merits of a specific scientist's contributions. Also according to this statement, this practice creates biases and inaccuracies when appraising scientific research. It also states that the impact factor is not to be used as a substitute "measure of the quality of individual research articles, or in hiring, promotion, or funding decisions".
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) is part of the United States National Institutes of Health, which in turn is part of the Department of Health and Human Services. NIDDK is approximately the fifth-largest of the 27 NIH institutes. The institute's mission is to support research, training, and communication with the public in the topic areas of "diabetes and other endocrine and metabolic diseases; digestive diseases, nutritional disorders, and obesity; and kidney, urologic, and hematologic diseases". As of 2021, the Director of the institute is Griffin P. Rodgers, who assumed the position on an acting basis in 2006 and on a permanent basis in 2007.

The United European Gastroenterology (UEG) is a non-profit organisation combining European societies concerned with digestive health.
Pathogens and Disease is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on all pathogens. It was originally established in 1988 as FEMS Microbiology Immunology when it split from FEMS Microbiology Letters. It was renamed FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology in 1993, and obtained its current name in 2013.














