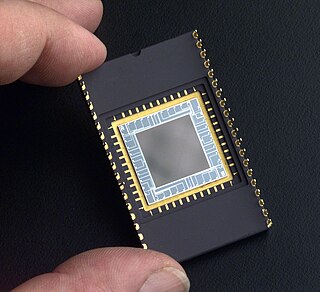
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging.

Digital video is an electronic representation of moving visual images (video) in the form of encoded digital data. This is in contrast to analog video, which represents moving visual images in the form of analog signals. Digital video comprises a series of digital images displayed in rapid succession, usually at 24, 25, 30, or 60 frames per second. Digital video has many advantages such as easy copying, multicasting, sharing and storage.

In digital imaging, a pixel, pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software.

A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices like smartphones with the same or more capabilities and features of dedicated cameras. High-end, high-definition dedicated cameras are still commonly used by professionals and those who desire to take higher-quality photographs.
The Foveon X3 sensor is a digital camera image sensor designed by Foveon, Inc., and manufactured by Dongbu Electronics. It uses an array of photosites that consist of three vertically stacked photodiodes. Each of the three stacked photodiodes has a different spectral sensitivity, allowing it to respond differently to different wavelengths. The signals from the three photodiodes are then processed as additive color data that are transformed to a standard RGB color space. In the late 1970s, a similar color sensor having three stacked photo detectors at each pixel location, with different spectral responses due to the differential absorption of light by the semiconductor, had been developed and patented by Kodak.

A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digital cameras, and camcorders to create a color image. The filter pattern is half green, one quarter red and one quarter blue, hence is also called BGGR, RGBG, GRBG, or RGGB.

A digital camera back is a device that attaches to the back of a camera in place of the traditional negative film holder and contains an electronic image sensor. This allows cameras that were designed to use film take digital photographs. These camera backs are generally expensive by consumer standards and are primarily built to be attached on medium- and large-format cameras used by professional photographers.

A digital single-lens reflex camera is a digital camera that combines the optics and mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a solid-state image sensor and digitally records the images from the sensor.
Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail. Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how close lines can be to each other and still be visibly resolved. Resolution units can be tied to physical sizes, to the overall size of a picture, or to angular subtense. Instead of single lines, line pairs are often used, composed of a dark line and an adjacent light line; for example, a resolution of 10 lines per millimeter means 5 dark lines alternating with 5 light lines, or 5 line pairs per millimeter. Photographic lens are most often quoted in line pairs per millimeter.

The Sigma SD10 is a digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) manufactured by the Sigma Corporation of Japan. It was announced on October 27, 2003, and is an evolution of the previous SD9 model, addressing many of the shortcomings of that camera. The Sigma SD10 cameras are unique in the digital DSLR field in using full-color sensor technology, and in that they only produce raw format images that require post-processing on a computer.

Image noise is random variation of brightness or color information in images, and is usually an aspect of electronic noise. It can be produced by the image sensor and circuitry of a scanner or digital camera. Image noise can also originate in film grain and in the unavoidable shot noise of an ideal photon detector. Image noise is an undesirable by-product of image capture that obscures the desired information. Typically the term “image noise” is used to refer to noise in 2D images, not 3D images.
A camera raw image file contains unprocessed or minimally processed data from the image sensor of either a digital camera, a motion picture film scanner, or other image scanner. Raw files are so named because they are not yet processed, and contain large amounts of potentially redundant data. Normally, the image is processed by a raw converter, in a wide-gamut internal color space where precise adjustments can be made before conversion to a viewable file format such as JPEG or PNG for storage, printing, or further manipulation. There are dozens of raw formats in use by different manufacturers of digital image capture equipment.

High-speed photography is the science of taking pictures of very fast phenomena. In 1948, the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) defined high-speed photography as any set of photographs captured by a camera capable of 69 frames per second or greater, and of at least three consecutive frames. High-speed photography can be considered to be the opposite of time-lapse photography.

Digital photography uses cameras containing arrays of electronic photodetectors interfaced to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to produce images focused by a lens, as opposed to an exposure on photographic film. The digitized image is stored as a computer file ready for further digital processing, viewing, electronic publishing, or digital printing. It is a form of digital imaging based on gathering visible light.

An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging.

The Canon EOS 30D is an 8.2-megapixel semi-professional digital single-lens reflex camera, initially announced on February 21, 2006. It is the successor of the Canon EOS 20D, and is succeeded by the EOS 40D. It can accept EF and EF-S lenses, and like its predecessor, it uses an APS-C sized image sensor, so it does not require the larger imaging circle necessary for 35 mm film and 'full-frame' digital cameras.

An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor, which was invented by Peter J.W. Noble in 1968, where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOS field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) are used as amplifiers. There are different types of APS, including the early NMOS APS and the now much more common complementary MOS (CMOS) APS, also known as the CMOS sensor. CMOS sensors are used in digital camera technologies such as cell phone cameras, web cameras, most modern digital pocket cameras, most digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLRs), mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras (MILCs), and lensless imaging for cells.

In digital imaging, a color filter array (CFA), or color filter mosaic (CFM), is a mosaic of tiny color filters placed over the pixel sensors of an image sensor to capture color information.

The Sigma SD14 is a digital single-lens reflex camera produced by the Sigma Corporation of Japan. It is fitted with a Sigma SA mount which takes Sigma SA lenses.

In digital photography, the image sensor format is the shape and size of the image sensor.

















