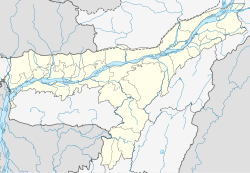
Assam is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of 78,438 km2 (30,285 sq mi). It is the second largest state in northeastern India by area and the largest in terms of population, with more than 31 million inhabitants. The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a 22-kilometre-wide (14 mi) strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assamese and Bodo are two of the official languages for the entire state and Meitei (Manipuri) is recognised as an additional official language in three districts of Barak Valley and Hojai district. in Hojai district and for the Barak valley region, alongside Bengali, which is also an official language in the Barak Valley.

The Insurgency in Northeast India involves multiple separatist and jihadist militant groups operating in some of India's northeastern states, which are connected to the rest of India by the Siliguri Corridor, a strip of land as narrow as 14.29 miles (23.00 km) wide.

Karbi Anglong district is an administrative unit in the Indian state of Assam. It is an autonomous district administered by the Karbi Anglong Autonomous Council (KAAC) according to the provisions of the Sixth Schedule of the constitution of India. The district headquarters is in Diphu.

Dima Hasao district, is an administrative district in the state of Assam, India. As of 2011, it is the least populous district of Assam.

The Dimasa Kingdom also known as Kachari kingdom was a late medieval/early modern kingdom in Assam, Northeast India ruled by Dimasa kings. The Dimasa kingdom and others that developed in the wake of the Kamarupa kingdom were examples of new states that emerged from indigenous communities in medieval Assam as a result of socio-political transformations in these communities. The British finally annexed the kingdom: the plains in 1832 and the hills in 1834. This kingdom gave its name to undivided Cachar district of colonial Assam. And after independence the undivided Cachar district was split into three districts in Assam: Dima Hasao district, Cachar district, Hailakandi district. The Ahom Buranjis called this kingdom Timisa.

The Dimasa people or Dimasa Kachari people are an ethnolinguistic community presently inhabiting in Assam and Nagaland states in Northeastern India. They speak Dimasa, a Tibeto-Burman language. This community is fairly homogeneous and exclusive, with members required to draw from both parents' separate clans. Dimasa kingdom, one of many early states in Assam following the downfall of Kamarupa kingdom, was established by these people.
The Dimasa language is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken by the Dimasa people of the Northeastern Indian states of Assam and Nagaland. The Dimasa language is known to Dimasas as "Grao-Dima" and it is similar to Boro, Kokborok and Garo languages. The Dimasa language is one of the oldest languages spoken in North East India, particularly in Assam, Nagaland.
Dimasa may refer to the following entities in Northeast India :
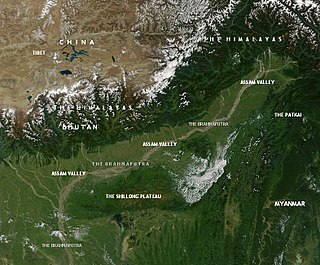
This article discusses the geological origin, geomorphic characteristics, and climate of the northeastern Indian state of Assam. Extending from 89° 42′ E to 96° E longitude and 24° 8′ N to 28° 2′ N latitude, it has an area of 78,438 km2, similar to that of Ireland or Austria.

The Barak Valley is the southernmost region and administrative division of the Indian state of Assam. It is named after the Barak river. The Barak valley consists of three administrative districts of Assam namely - Cachar, Karimganj, and Hailakandi. The main and largest city is Silchar, which seats the headquarter of Cachar district and also serves as administrative divisional office of Barak valley division. The valley is bordered by Mizoram and Tripura to the south, Bangladesh and Meghalaya to the west and Manipur to the east respectively. Once North Cachar Hills was a part of Cachar district which became a subdivision in 1951 and eventually a separate district. On 1 July 1983, Karimganj district was curved out from the eponymous subdivision of Cachar district. In 1989 the subdivision of Hailakandi was upgraded into Hailakandi district.
Dima Halam Daogah was an Indian extremist group operating mainly in Assam and Nagaland. The group laid down their arms in January 2013, and claimed to represent the Dimasa and their goal to create a Dimaland or Dimaraji in the two states.
The Sakachep, also known as the Khelma, are an indigenous tribe predominantly residing in the northeastern states of India, including Assam, Meghalaya, and Nagaland. They are renowned for their rich cultural heritage and are concentrated in regions such as Dima Hasao, Barak Valley, Karbi Anglong in Assam, Jaintia Hills in Meghalaya, and Paren District in Nagaland.

Karbi Longri N.C. Hills Liberation Front was a militant group operating in Karbi Anglong district and Dima Hasao district of Assam, India. Thong Teron was the general secretary of KLNLF. Karbi Anglong NC Hills People's Resistance was the armed wing of the organization. KLNLF emerged from the United People's Democratic Solidarity, being against the peace talks between the UDPS and the government. After the split, there has been turf wars between the two groups.

The Karbi language is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken by the Karbi people of Northeastern India.
United People's Democratic Solidarity was formed in March 1999 with the merger of two terrorist outfits in Assam's Karbi Anglong district, the Karbi National Volunteers (KNV) and Karbi People's Front (KPF).
Assam – 16th largest, 15th most populous and 26th most literate state of the 28 states of the democratic Republic of India. Assam is at 14th position in life expectancy and 8th in female-to-male sex ratio. Assam is the 21st most media exposed states in India. The Economy of Assam is largely agriculture based with 69% of the population engaged in it. Growth rate of Assam's income has not kept pace with that of India's during the Post-British Era; differences increased rapidly since the 1970s. While the Indian economy grew at 6 percent per annum over the period of 1981 to 2000, the same of Assam's grew only by 3.3 percent.

The West Karbi Anglong district is an administrative unit in the Indian state of Assam. It is a relatively new district formed out of the existing Karbi Anglong district in 2016. The administrative headquarters of the district is located at Hamren. The district is a part of the Karbi Anglong Autonomous Council and is administered according to the provisions of the Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution.

Central Assam is an administrative division of Assam under the jurisdiction of a Division Commissioner, who is officially stationed at Nagaon. It consists of the following districts: Dima Hasao, Karbi Anglong, West Karbi Anglong, Hojai, Nagaon and Marigaon.