In mathematics, a continuous function is a function for which sufficiently small changes in the input result in arbitrarily small changes in the output. Otherwise, a function is said to be a discontinuous function. A continuous function with a continuous inverse function is called a homeomorphism.
In mathematics, a series is, roughly speaking, a description of the operation of adding infinitely many quantities, one after the other, to a given starting quantity. The study of series is a major part of calculus and its generalization, mathematical analysis. Series are used in most areas of mathematics, even for studying finite structures, through generating functions. In addition to their ubiquity in mathematics, infinite series are also widely used in other quantitative disciplines such as physics, computer science, statistics and finance.
In mathematics, the Laplace transform is an integral transform named after its inventor Pierre-Simon Laplace. It takes a function of a real variable t to a function of a complex variable s.

In mathematics, real analysis is the branch of mathematical analysis that studies the behavior of real numbers, sequences and series of real numbers, and real-valued functions. Some particular properties of real-valued sequences and functions that real analysis studies include convergence, limits, continuity, smoothness, differentiability and integrability.
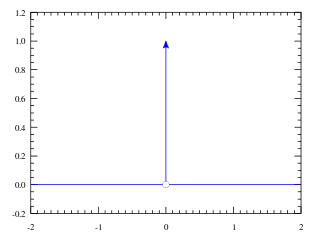
In mathematics, the Dirac delta function is a generalized function or distribution introduced by the physicist Paul Dirac. It is used to model the density of an idealized point mass or point charge as a function equal to zero everywhere except for zero and whose integral over the entire real line is equal to one. As there is no function that has these properties, the computations made by the theoretical physicists appeared to mathematicians as nonsense until the introduction of distributions by Laurent Schwartz to formalize and validate the computations. As a distribution, the Dirac delta function is a linear functional that maps every function to its value at zero. The Kronecker delta function, which is usually defined on a discrete domain and takes values 0 and 1, is a discrete analog of the Dirac delta function.

In mathematics, mathematical physics and the theory of stochastic processes, a harmonic function is a twice continuously differentiable function f : U → R where U is an open subset of Rn that satisfies Laplace's equation, i.e.
The power spectrum of a time series describes the distribution of power into frequency components composing that signal. According to Fourier analysis, any physical signal can be decomposed into a number of discrete frequencies, or a spectrum of frequencies over a continuous range. The statistical average of a certain signal or sort of signal as analyzed in terms of its frequency content, is called its spectrum.

In mathematics, the oscillation of a function or a sequence is a number that quantifies how much a sequence or function varies between its extreme values as it approaches infinity or a point. As is the case with limits there are several definitions that put the intuitive concept into a form suitable for a mathematical treatment: oscillation of a sequence of real numbers, oscillation of a real valued function at a point, and oscillation of a function on an interval.
In mathematics, the question of whether the Fourier series of a periodic function converges to the given function is researched by a field known as classical harmonic analysis, a branch of pure mathematics. Convergence is not necessarily given in the general case, and certain criteria must be met for convergence to occur.
In mathematics, the Dini and Dini–Lipschitz tests are highly precise tests that can be used to prove that the Fourier series of a function converges at a given point. These tests are named after Ulisse Dini and Rudolf Lipschitz.
In mathematics, the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) is a form of Fourier analysis that is applicable to a sequence of values.

In mathematics, classical Wiener space is the collection of all continuous functions on a given domain, taking values in a metric space. Classical Wiener space is useful in the study of stochastic processes whose sample paths are continuous functions. It is named after the American mathematician Norbert Wiener.
In mathematics, uniform integrability is an important concept in real analysis, functional analysis and measure theory, and plays a vital role in the theory of martingales. The definition used in measure theory is closely related to, but not identical to, the definition typically used in probability.
The Bochner–Riesz mean is a summability method often used in harmonic analysis when considering convergence of Fourier series and Fourier integrals. It was introduced by Salomon Bochner as a modification of the Riesz mean.

In mathematical analysis, the Dirichlet kernel is the collection of functions
In mathematical analysis, Dini continuity is a refinement of continuity. Every Dini continuous function is continuous. Every Lipschitz continuous function is Dini continuous.
In mathematics, Dini's criterion is a condition for the pointwise convergence of Fourier series, introduced by Ulisse Dini (1880).

Ulisse Dini was an Italian mathematician and politician, born in Pisa. He is known for his contribution to real analysis, partly collected in his book "Fondamenti per la teorica delle funzioni di variabili reali".

Michiel Hazewinkel is a Dutch mathematician, and Emeritus Professor of Mathematics at the Centre for Mathematics and Computer and the University of Amsterdam, particularly known for his 1978 book Formal groups and applications and as editor of the Encyclopedia of Mathematics.

The Encyclopedia of Mathematics is a large reference work in mathematics. It is available in book form and on CD-ROM.













