
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA.

A chromosome is a package of DNA with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are the histones. These proteins, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation.

Ploidy is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present : monoploid, diploid, triploid, tetraploid, pentaploid, hexaploid, heptaploid or septaploid, etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes.
A trisomy is a type of polysomy in which there are three instances of a particular chromosome, instead of the normal two. A trisomy is a type of aneuploidy.
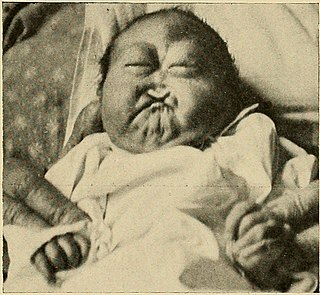
Patau syndrome is a syndrome caused by a chromosomal abnormality, in which some or all of the cells of the body contain extra genetic material from chromosome 13. The extra genetic material disrupts normal development, causing multiple and complex organ defects.

Trisomy 18, also known as Edwards syndrome, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of a third copy of all or part of chromosome 18. Many parts of the body are affected. Babies are often born small and have heart defects. Other features include a small head, small jaw, clenched fists with overlapping fingers, and severe intellectual disability.

Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division (mitosis/meiosis). There are three forms of nondisjunction: failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis I, failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis II, and failure of sister chromatids to separate during mitosis. Nondisjunction results in daughter cells with abnormal chromosome numbers (aneuploidy).

Mosaicism or genetic mosaicism is a condition in which a multicellular organism possesses more than one genetic line as the result of genetic mutation. This means that various genetic lines resulted from a single fertilized egg. Mosaicism is one of several possible causes of chimerism, wherein a single organism is composed of cells with more than one distinct genotype.

A small supernumerary marker chromosome (sSMC) is an abnormal extra chromosome. It contains copies of parts of one or more normal chromosomes and like normal chromosomes is located in the cell's nucleus, is replicated and distributed into each daughter cell during cell division, and typically has genes which may be expressed. However, it may also be active in causing birth defects and neoplasms. The sSMC's small size makes it virtually undetectable using classical cytogenetic methods: the far larger DNA and gene content of the cell's normal chromosomes obscures those of the sSMC. Newer molecular techniques such as fluorescence in situ hybridization, next generation sequencing, comparative genomic hybridization, and highly specialized cytogenetic G banding analyses are required to study it. Using these methods, the DNA sequences and genes in sSMCs are identified and help define as well as explain any effect(s) it may have on individuals.
Trisomy 8 causes Warkany syndrome 2, a human chromosomal disorder caused by having three copies (trisomy) of chromosome 8. It can appear with or without mosaicism.
Full trisomy 9 is a rare and fatal chromosomal disorder caused by having three copies (trisomy) of chromosome number 9. It can be a viable condition if trisomy affects only part of the cells of the body (mosaicism) or in cases of partial trisomy in which cells have a normal set of two entire chromosomes 9 plus part of a third copy, usually of the short arm of the chromosome.
Gene dosage is the number of copies of a particular gene present in a genome. Gene dosage is related to the amount of gene product the cell is able to express. Since a gene acts as a template, the number of templates in the cell contributes to the amount of gene product able to be produced. However, the amount of gene product produced in a cell is more commonly dependent on regulation of gene expression. The normal gene dosage is dependent on the species; humans generally have two doses -- one copy from the mother and one from the father. Changes in gene dosage can be a result of copy number variation, or aneuploidy. These changes can have significant phenotypic consequences.

Distal trisomy 10 is a rare chromosomal disorder that causes several physical defects and intellectual disability.
The Pallister–Killian syndrome (PKS), also termed tetrasomy 12p mosaicism or the Pallister mosaic aneuploidy syndrome, is an extremely rare and severe genetic disorder. PKS is due to the presence of an extra and abnormal chromosome termed a small supernumerary marker chromosome (sSMC). sSMCs contain copies of genetic material from parts of virtually any other chromosome and, depending on the genetic material they carry, can cause various genetic disorders and neoplasms. The sSMC in PKS consists of multiple copies of the short arm of chromosome 12. Consequently, the multiple copies of the genetic material in the sSMC plus the two copies of this genetic material in the two normal chromosome 12's are overexpressed and thereby cause the syndrome. Due to a form of genetic mosaicism, however, individuals with PKS differ in the tissue distributions of their sSMC and therefore show different syndrome-related birth defects and disease severities. For example, individuals with the sSMC in their heart tissue are likely to have cardiac structural abnormalities while those without this sSMC localization have a structurally normal heart.

Triploid syndrome, also called triploidy, is a chromosomal disorder in which a fetus has three copies of every chromosome instead of the normal two. If this occurs in only some cells, it is called mosaic triploidy and is less severe.
Trisomy 22 is a chromosomal disorder in which three copies of chromosome 22 are present rather than two. It is a frequent cause of spontaneous abortion during the first trimester of pregnancy. Progression to the second trimester and live birth are rare. This disorder is found in individuals with an extra copy or a variation of chromosome 22 in some or all cells of their bodies.
Tetrasomy 9p is a rare chromosomal disorder characterized by the presence of two extra copies of the short arm of chromosome 9, in addition to the usual two. Symptoms of tetrasomy 9p vary widely among affected individuals but typically include varying degrees of delayed growth, abnormal facial features and intellectual disability. Symptoms of the disorder are comparable to those of trisomy 9p.

Tetrasomy X, also known as 48,XXXX, is a chromosomal disorder in which a female has four, rather than two, copies of the X chromosome. It is associated with intellectual disability of varying severity, characteristic "coarse" facial features, heart defects, and skeletal anomalies such as increased height, clinodactyly, and radioulnar synostosis. Tetrasomy X is a rare condition, with few medically recognized cases; it is estimated to occur in approximately 1 in 50,000 females.

Pentasomy X, also known as 49,XXXXX, is a chromosomal disorder in which a female has five, rather than two, copies of the X chromosome. Pentasomy X is associated with short stature, intellectual disability, characteristic facial features, heart defects, skeletal anomalies, and pubertal and reproductive abnormalities. The condition is exceptionally rare, with an estimated prevalence between 1 in 85,000 and 1 in 250,000.

Trisomy X, also known as triple X syndrome and characterized by the karyotype 47,XXX, is a chromosome disorder in which a female has an extra copy of the X chromosome. It is relatively common and occurs in 1 in 1,000 females, but is rarely diagnosed; fewer than 10% of those with the condition know they have it.
















