The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.

Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 to 400 nm, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. It can also damage skin and/or give a painful sunburn.

Sunscreen, also known as sunblock or suntan lotion, is a lotion, spray, gel, foam, stick or other topical product that absorbs or reflects some of the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation and thus helps protect against sunburn. Diligent use of sunscreen can also help to slow or temporarily prevent the development of wrinkles, dark spots and sagging skin.

Photochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the chemical effects of light. Generally, this term is used to describe a chemical reaction caused by absorption of ultraviolet, visible light (400–750 nm) or infrared radiation (750–2500 nm).

Sun tanning or simply tanning is the process whereby skin color is darkened or tanned. It is most often a result of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or from artificial sources, such as a tanning lamp found in indoor tanning beds. People who deliberately tan their skin by exposure to the sun engage in a passive recreational activity of sun bathing. Some people use chemical products which can produce a tanning effect without exposure to ultraviolet radiation, known as sunless tanning.
The ultraviolet index, or UV index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of sunburn-producing ultraviolet (UV) radiation at a particular place and time. The scale was developed by Canadian scientists in 1992, and then adopted and standardized by the UN's World Health Organization and World Meteorological Organization in 1994. It is primarily used in daily forecasts aimed at the general public, and is increasingly available as an hourly forecast as well.
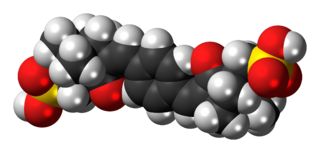
Ecamsule is an organic compound which is added to many sunscreens to filter out UVA rays. It is a benzylidene camphor derivative, many of which are known for their excellent photostability.

Octyl methoxycinnamate or ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate (INCI) or octinoxate (USAN), trade names Eusolex 2292 and Uvinul MC80, is an organic compound that is an ingredient in some sunscreens and lip balms. It is an ester formed from methoxycinnamic acid and 2-ethylhexanol. It is a liquid that is insoluble in water.

Psoralen is the parent compound in a family of naturally occurring organic compounds known as the linear furanocoumarins. It is structurally related to coumarin by the addition of a fused furan ring, and may be considered as a derivative of umbelliferone. Psoralen occurs naturally in the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia, as well as in the common fig, celery, parsley, West Indian satinwood, and in all citrus fruits. It is widely used in PUVA treatment for psoriasis, eczema, vitiligo, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; these applications are typically through the use of medications such as Methoxsalen. Many furanocoumarins are extremely toxic to fish, and some are deposited in streams in Indonesia to catch fish.
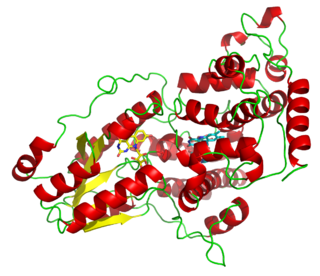
Photolyases are DNA repair enzymes that repair damage caused by exposure to ultraviolet light. These enzymes require visible light both for their own activation and for the actual DNA repair. The DNA repair mechanism involving photolyases is called photoreactivation. They mainly convert pyrimidine dimers into a normal pair of pyrimidine bases.

UV filters are compounds, mixtures, or materials that block or absorb ultraviolet (UV) light. One of the major applications of UV filters is their use as sunscreens to protect skin from sunburn and other sun/UV related damage. After the invention of digital cameras changed the field of photography, UV filters have been used to coat glass discs fitted to camera lenses to protect hardware that is sensitive to UV light.
Photoprotection is the biochemical process that helps organisms cope with molecular damage caused by sunlight. Plants and other oxygenic phototrophs have developed a suite of photoprotective mechanisms to prevent photoinhibition and oxidative stress caused by excess or fluctuating light conditions. Humans and other animals have also developed photoprotective mechanisms to avoid UV photodamage to the skin, prevent DNA damage, and minimize the downstream effects of oxidative stress.

Pyrimidine dimers are molecular lesions formed from thymine or cytosine bases in DNA via photochemical reactions. Ultraviolet light (UV) induces the formation of covalent linkages between consecutive bases along the nucleotide chain in the vicinity of their carbon–carbon double bonds. The dimerization reaction can also occur among pyrimidine bases in dsRNA —uracil or cytosine. Two common UV products are cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and 6–4 photoproducts. These premutagenic lesions alter the structure and possibly the base-pairing. Up to 50–100 such reactions per second might occur in a skin cell during exposure to sunlight, but are usually corrected within seconds by photolyase reactivation or nucleotide excision repair. Uncorrected lesions can inhibit polymerases, cause misreading during transcription or replication, or lead to arrest of replication. Pyrimidine dimers are the primary cause of melanomas in humans.

Indirect DNA damage occurs when a UV-photon is absorbed in the human skin by a chromophore that does not have the ability to convert the energy into harmless heat very quickly. Molecules that do not have this ability have a long-lived excited state. This long lifetime leads to a high probability for reactions with other molecules—so-called bimolecular reactions. Melanin and DNA have extremely short excited state lifetimes in the range of a few femtoseconds (10−15s). The excited state lifetime of compounds used in sunscreens such as menthyl anthranilate, avobenzone or padimate O is 1,000 to 1,000,000 times longer than that of melanin, and therefore they may cause damage to living cells that come in contact with them.
Tanning activators are chemicals that increase the effect of UV-radiation on the human skin.

Drometrizole trisiloxane (INCI) is a lipophilic benzotriazole derivative marketed as Mexoryl XL by L'Oréal and is used in sunscreens to absorb UV radiation. It is a broad-spectrum UV absorber with two absorption peaks, one at 303 nm (UVB) and one at 344 nm (UVA). Just like Mexoryl SX (ecamsule), it is used exclusively in products by L'Oréal owned brands. Drometrizole trisiloxane and ecamsule are often used together, because they show a synergistic effect in protection.
Non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) is a mechanism employed by plants and algae to protect themselves from the adverse effects of high light intensity. It involves the quenching of singlet excited state chlorophylls (Chl) via enhanced internal conversion to the ground state, thus harmlessly dissipating excess excitation energy as heat through molecular vibrations. NPQ occurs in almost all photosynthetic eukaryotes, and helps to regulate and protect photosynthesis in environments where light energy absorption exceeds the capacity for light utilization in photosynthesis.

Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include: red or reddish skin that is hot to the touch or painful, general fatigue, and mild dizziness. Excessive UV radiation can be life-threatening in extreme cases. Excessive UV radiation is the leading cause of, primarily, non-malignant skin tumors. Sunburn is an inflammatory response in the tissue triggered by direct DNA damage by UV radiation. When the cells' DNA is overly damaged by UV radiation, type I cell-death is triggered and the tissue is replaced. Sun protective measures including sunscreen and sun protective clothing are widely accepted to prevent sunburn and some types of skin cancer. Special populations, including children, are especially susceptible to sunburn and protective measures should be used to prevent damage.
Photoaging or photoageing is a term used for the characteristic changes to skin induced by chronic UVA and UVB exposure. Tretinoin is the best studied retinoid in the treatment of photoaging
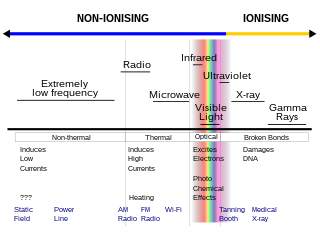
Non-ionizingradiation refers to any type of electromagnetic radiation that does not carry enough energy per quantum to ionize atoms or molecules—that is, to completely remove an electron from an atom or molecule. Instead of producing charged ions when passing through matter, non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation has sufficient energy only for excitation, the movement of an electron to a higher energy state. In contrast, ionizing radiation has a higher frequency and shorter wavelength than non-ionizing radiation, and can be a serious health hazard; exposure to it can cause burns, radiation sickness, cancer, and genetic damage. Using ionizing radiation requires elaborate radiological protection measures, which in general are not required with non-ionizing radiation.













