
The Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA) is an act of the United States Congress, passed in 1986 as part of the Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA). It requires hospital emergency departments that accept payments from Medicare to provide an appropriate medical screening examination (MSE) for anyone seeking treatment for a medical condition regardless of citizenship, legal status, or ability to pay. Participating hospitals may not transfer or discharge patients needing emergency treatment except with the informed consent or stabilization of the patient or when the patient's condition requires transfer to a hospital better equipped to administer the treatment.

In the United States, Medicaid is a government program that provides health insurance for adults and children with limited income and resources. The program is partially funded and primarily managed by state governments, which also have wide latitude in determining eligibility and benefits, but the federal government sets baseline standards for state Medicaid programs and provides a significant portion of their funding.

Medicare is a federal health insurance program in the United States for people age 65 or older and younger people with disabilities, including those with end stage renal disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. It was begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration and is now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS).
In the United States, charity care is health care provided for free or at reduced prices to low income patients. The percentage of doctors providing charity care dropped from 76% in 1996–97 to 68% in 2004–2005. Potential reasons for the decline include changes in physician practice patterns and increasing financial pressures. In 2006, Senate investigators found that many hospitals did not inform patients that charity care was available. Some for-profit hospitals provided as much charity care as some non-profit hospitals. Investigators also found non-profit hospitals charging poor, uninsured patients more than they did patients with health insurance. Hospitals must provide some charity care if they wish to maintain non-profit status.
Health care prices in the United States of America describe market and non-market factors that determine pricing, along with possible causes as to why prices are higher than in other countries.
A public hospital, or government hospital, is a hospital which is government owned and is predominantly funded by the government and operates predominantly off the money that is collected from taxpayers to fund healthcare initiatives. In almost all the developed countries but the United States of America, and in most of the developing countries, this type of hospital provides medical care almost free of charge to patients, covering expenses and wages by government reimbursement.
The Balanced Budget Act of 1997 was an omnibus legislative package enacted by the United States Congress, using the budget reconciliation process, and designed to balance the federal budget by 2002. This act was enacted during Bill Clinton's second term as president.
In the United States, health insurance helps pay for medical expenses through privately purchased insurance, social insurance, or a social welfare program funded by the government. Synonyms for this usage include "health coverage", "health care coverage", and "health benefits". In a more technical sense, the term "health insurance" is used to describe any form of insurance providing protection against the costs of medical services. This usage includes both private insurance programs and social insurance programs such as Medicare, which pools resources and spreads the financial risk associated with major medical expenses across the entire population to protect everyone, as well as social welfare programs like Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program, which both provide assistance to people who cannot afford health coverage.
Healthcare reform in the United States has a long history. Reforms have often been proposed but have rarely been accomplished. In 2010, landmark reform was passed through two federal statutes: the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA), signed March 23, 2010, and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010, which amended the PPACA and became law on March 30, 2010.

In the United States, health insurance coverage is provided by several public and private sources. During 2019, the U.S. population overall was approximately 330 million, with 59 million people 65 years of age and over covered by the federal Medicare program. The 273 million non-institutionalized persons under age 65 either obtained their coverage from employer-based or non-employer based sources, or were uninsured. During the year 2019, 89% of the non-institutionalized population had health insurance coverage. Separately, approximately 12 million military personnel received coverage through the Veteran's Administration and Military Health System.
The Empowering Patients First Act is legislation sponsored by Rep. Tom Price, first introduced as H.R. 3400 in the 111th Congress. The bill was initially intended to be a Republican alternative to the America's Affordable Health Choices Act of 2009, but has since been positioned as a potential replacement to the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA). The bill was introduced in the 112th Congress as H.R. 3000, and in the 113th Congress as H.R. 2300. As of October 2014, the bill has 58 cosponsors. An identical version of the bill has been introduced in the Senate by Senator John McCain as S. 1851.
There were a number of different health care reforms proposed during the Obama administration. Key reforms address cost and coverage and include obesity, prevention and treatment of chronic conditions, defensive medicine or tort reform, incentives that reward more care instead of better care, redundant payment systems, tax policy, rationing, a shortage of doctors and nurses, intervention vs. hospice, fraud, and use of imaging technology, among others.

The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) and colloquially as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama on March 23, 2010. Together with the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 amendment, it represents the U.S. healthcare system's most significant regulatory overhaul and expansion of coverage since the enactment of Medicare and Medicaid in 1965. Most of the act's provisions are still in effect.
An accountable care organization (ACO) is a healthcare organization that ties provider reimbursements to quality metrics and reductions in the cost of care. ACOs in the United States are formed from a group of coordinated health-care practitioners. They use alternative payment models, normally, capitation. The organization is accountable to patients and third-party payers for the quality, appropriateness and efficiency of the health care provided. According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, an ACO is "an organization of health care practitioners that agrees to be accountable for the quality, cost, and overall care of Medicare beneficiaries who are enrolled in the traditional fee-for-service program who are assigned to it".
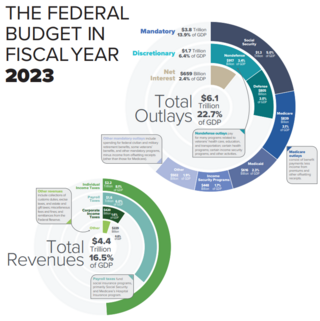
The United States federal budget consists of mandatory expenditures, discretionary spending for defense, Cabinet departments and agencies, and interest payments on debt. This is currently over half of U.S. government spending, the remainder coming from state and local governments.
Health care finance in the United States discusses how Americans obtain and pay for their healthcare, and why U.S. healthcare costs are the highest in the world based on various measures.
The 340B Drug Pricing Program is a US federal government program created in 1992 that requires drug manufacturers to provide outpatient drugs to eligible health care organizations and covered entities at significantly reduced prices. The intent of the program is to allow covered entities to "stretch scarce federal resources as far as possible, reaching more eligible patients and providing more comprehensive services." Maintaining services and lowering medication costs for patients is consistent with the purpose of the program, which is named for the section authorizing it in the Public Health Service Act (PHSA) It was enacted by Congress as part of a larger bill signed into law by President George H. W. Bush.

The SGR Repeal and Medicare Provider Payment Modernization Act of 2014 is a bill that would replace the Sustainable Growth Rate (SGR) formula, which determines the annual updates to payment rates for physicians’ services in Medicare, with new systems for establishing those payment rates.

America's Essential Hospitals is an industry trade group that represents more than 300 hospitals that fill a safety net role in their communities. The association, a nonprofit organization based in Washington, DC, was formed in 1981 as the National Association of Public Hospitals.
A safety net hospital is a type of medical center in the United States that by legal obligation or mission provides healthcare for individuals regardless of their insurance status or ability to pay. This legal mandate forces safety net hospitals (SNHs) to serve all populations. Such hospitals typically serve a proportionately higher number of uninsured, Medicaid, Medicare, Children's Health Insurance Program (CHiP), low-income, and other vulnerable individuals than their "non-safety net hospital" counterpart. Safety net hospitals are not defined by their ownership terms; they can be either publicly or privately owned. The mission of safety net hospitals is rather to provide the best possible care for those who are barred from health care due to the various possible adverse circumstances. These circumstances mostly revolve around problems with financial payments, insurance plans, or health conditions. Safety net hospitals are known for maintaining an open-door policy for their services.




