
The Salesians of Don Bosco (SDB), formally known as the Society of Saint Francis de Sales, is a religious congregation of men in the Catholic Church, founded in 1859 by the Italian priest John Bosco to help poor and migrant youngsters during the Industrial Revolution. The congregation was named after Francis de Sales, a 17th-century bishop of Geneva.

Bernard Joseph Francis Lonergan was a Canadian Jesuit priest, philosopher, and theologian, regarded by many as one of the most important thinkers of the 20th century.
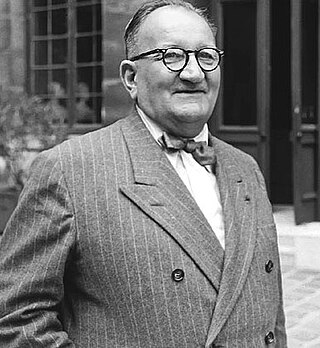
Étienne Henri Gilson was a French philosopher and historian of philosophy. A scholar of medieval philosophy, he originally specialised in the thought of Descartes; he also philosophized in the tradition of Thomas Aquinas, although he did not consider himself a neo-Thomist philosopher. In 1946 he attained the distinction of being elected an "Immortal" (member) of the Académie française. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature.

Angelo Scola is an Italian Cardinal of the Catholic Church, philosopher and theologian. He was Archbishop of Milan from 2011 to 2017. He served as Patriarch of Venice from 2002 to 2011. He has been a cardinal since 2003 and a bishop since 1991.

John Melchior Bosco, SDB, popularly known as Don Bosco, was an Italian Catholic priest, educator and writer of the 19th century. While working in Turin, where the population suffered many of the ill effects of industrialization and urbanization, he dedicated his life to the betterment and education of street children, juvenile delinquents, and other disadvantaged youth. He developed teaching methods based on love rather than punishment, a method that became known as the Salesian Preventive System.

A Candidate of Sciences or Candidate of Science is the first of two doctoral level scientific degrees in Russia, some of the Commonwealth of Independent States and was the first of two doctoral level degrees in some other countries. It is formally classified as UNESCO's ISCED level 8, "doctoral or equivalent." It may be recognized as a Doctor of Philosophy, usually in natural sciences, by scientific institutions in other countries. Former Soviet countries also have a more advanced degree, Doctor of Sciences.

Pontifical University of the Holy Cross is a Roman Catholic university under the Curial Congregation for Catholic Education, now entrusted to the Prelature of the Holy Cross and Opus Dei, or more commonly called Opus Dei. It was started in 1984 by Opus Dei, with the aim of offering the universal church an effective instrument for formation and research.

The Pontifical Urban University, also called the Urbaniana after its names in both Latin and Italian, is a pontifical university under the authority of the Congregation for the Evangelization of Peoples. The university's mission is to train priests, religious brothers and sisters, and lay people for service as missionaries. Its campus is located on the Janiculum Hill in Rome, on extraterritorial property of the Holy See.

Gatehouse School is a co-educational independent private primary school based on Sewardstone Road in Bethnal Green, London, educating pupils from the ages of three to eleven years. The youngest classes follow a Montessori-style education, but the influence of the national curriculum has brought the older classes more in line with mainstream schools. The school admits children from the full ability range, with an emphasis on the arts, including visits to museums and theatres, as well as sports and outward bound activities.

The Salesian Pontifical University is a pontifical university in Italy run by the Salesians of Don Bosco. It has three campuses, one in Rome, one in Turin, and one in Jerusalem. The Salesian Pontifical University is an ordinary member of the International Federation of Catholic Universities, the European Federation of Catholic Universities, the European University Association and the International Association of Universities.

Catholic University of Lyon (UCLy), also known as the Lyon Catholic Institute,, is a private university based in Lyon and Annecy, France.

The Rector Major of the Salesians is the head of all institutes and superior general of the Salesians of Don Bosco worldwide. It is the title of a Catholic priest that is elected as the general superior of the religious institute Salesians of Don Bosco. He is also considered the successor of Saint John Bosco in the top guidance of his Salesian Order. The first general superior of the order was Don Bosco himself from 1874, the year that the order was officially created and its Salesian Constitutions approved by the Holy See, until his death in 1888. Since then, the Salesians have elected their Superior in the General Chapter for a period of six years. Between 1888 and 2014 there have been ten successors of Don Bosco, seven of them of Italian nationality, one Argentine, one Mexican and one Spaniard. Following the Salesian tradition from their Italian origin, the Rector Major is addressed as Don (Father).

Krista Purana is an epic poem on the life of Jesus Christ written in a mix of Marathi and Konkani by Thomas Stephens (1549–1619). Adopting the literary form of the Hindu puranas, it retells the entire story of mankind from the creation days to the time of Jesus, in lyrical verse form. The Christian Puranas – 11,000 stanzas of 4 verses – were very popular in the churches of the area where they were sung on special occasions up to the 1930s. Although no copy of the original edition has yet been discovered, it is believed to have been first published at the College of Rachol in 1616, then re-published posthumously in 1649 and 1654.

Richard De Smet was a Belgian Jesuit priest, and missionary in India. As Indologist he became a renowned Sankara specialist.

Phyllis WallbankMBE was a British educationalist who, in 1948, founded the first all-age Montessori school in Great Britain and the Gatehouse Learning Centre, which took its name from the gatehouse of the Priory Church of St Bartholomew the Great in London.
The Journal of Special Education and Rehabilitation is an open-access peer-reviewed academic journal which publishes papers in the field of education. The journal's editors are Vladimir Trajkovski from Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje and Olivera Rashikj-Canevska Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje. It has been in publication since 1997 and is currently published by Institute of Special Education and Rehabilitation of the Faculty of Philosophy in Skopje and Macedonian Association of Special Educators.

Frederick G. Lawrence is an American hermeneutic philosopher and theologian, and a specialist in Bernard Lonergan, teaching in the Department of Theology at Boston College, Boston, US.
The Bulletin of the Council for Research in Music Education is a quarterly academic journal covering music education. It is published by the University of Illinois Press on behalf of the Council for Research in Music Education.
Nazzareno Camilleri (1906–1973) was a Maltese philosopher, theologian, and mystic. His areas of specialisation in philosophy were chiefly metaphysics and pedagogy.
Jesu Pudumai Doss, M.J. is a Catholic priest and a religious, specifically a Salesian of Don Bosco, from Chennai, India.















