
Berkner Island is an Antarctic ice rise, where bedrock below sea level has caused the surrounding ice sheet to create a dome. If the ice cap were removed, the island would be under water. Berkner "Island" is high and completely ice-covered and about 320 kilometres (200 mi) long and 150 kilometres (93 mi) wide, with an area of 44,000 km2 (17,000 sq mi). It is surrounded by the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf. The northernmost point of the Berkner is about 20 kilometres (12 mi) from the open sea. It lies in the overlapping portion of the Argentine and the British Antarctic territorial claims.
Support Force Glacier is a major glacier in the Pensacola Mountains, draining northward between the Forrestal Range and Argentina Range to the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf. Mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and US Navy air photos, 1956-66. Named by US-ACAN for the U.S. Naval Support Force Antarctica, which provided logistical support for the United States Antarctic Program during this period.

Ellsworth Land is that portion of the Antarctic continent bounded on the west by Marie Byrd Land, on the north by Bellingshausen Sea, on the northeast by the base of Antarctic Peninsula, and on the east by the western margin of Ronne Ice Shelf. It extends between 103°24'W and 79°45'W. The area west of 90°W is unclaimed, the area between 84°W and 90°W is claimed by Chile only, and the remainder by Chile and the United Kingdom as a part of the British Antarctic Territory. Eights Coast stretches between 103°24'W and 89°35'W, and Bryan Coast between 89°35'W and 79°45'W.

Luitpold Coast is that portion of the coast of Coats Land extending from the vicinity of Hayes Glacier, at 27°54′W, to 36°W, which is regarded as the eastern limit of the Filchner Ice Shelf. It was discovered by Wilhelm Filchner, leader of the Second German Antarctic Expedition, 1911–12, and named for Luitpold, Prince Regent of Bavaria.

Foundation Ice Stream is a major ice stream in Antarctica's Pensacola Mountains. The ice stream drains northward for 150 nautical miles along the west side of the Patuxent Range and the Neptune Range to enter the Ronne Ice Shelf westward of Dufek Massif. The United States Geological Survey mapped the stream from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1956–66. The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names named the stream in recognition of the National Science Foundation, which provided major support to the U.S. Antarctic Research Program during this period.
Fowler Ice Rise is a very large Antarctic ice rise between Evans Ice Stream and Carlson Inlet, in the southwest part of the Ronne Ice Shelf. The feature appears to be completely ice-covered except for the Haag Nunataks, which protrude above the surface in the northwestern portion. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from Landsat imagery taken 1973–74, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Captain Alfred N. Fowler, U.S. Navy, Commander of the U.S. Naval Support Force, Antarctica, 1972–74.
Carlson Inlet is an ice-filled inlet, 100 miles (160 km) long and 25 miles (40 km) wide, lying between Fletcher Ice Rise and Fowler Ice Rise in the southwest part of the Ronne Ice Shelf. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant Ronald F. Carlson, U.S. Navy, pilot of R4D-8 and C-130 aircraft with Squadron VX-6, who made innumerable flights in support of International Geophysical Year and United States Antarctic Research Program field parties in the 1950s and 1960s. On December 14, 1961, he commanded a C-130 Hercules flight from McMurdo Station across the Ellsworth Mountains, during which he observed, photographed and roughly sketched this inlet.
Ketchum Glacier is an eastward flowing glacier at the base of Palmer Land, Antarctica, about 50 nautical miles (90 km) long, descending between the Latady Mountains and the Scaife Mountains into Gardner Inlet. It was discovered by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, under Finn Ronne, who named it for Commander Gerald Ketchum, U.S. Navy, commander of the icebreaker USS Burton Island (AG-88) which broke the ice to free the RARE from Marguerite Bay for the return home.

The McDonald Ice Rumples constitute an ice rise in the Brunt Ice Shelf bordering the Weddell Sea in Antarctica, covering an area of 3 by 2 nautical miles.

The George VI Ice Shelf is an extensive ice shelf that occupies George VI Sound which separates Alexander Island from Palmer Land in Antarctica. The ice shelf extends from Ronne Entrance, at the southwest end of the sound, to Niznik Island, about 30 nautical miles (56 km) south of the north entrance between Cape Brown and Cape Jeremy. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in association with George VI Sound.
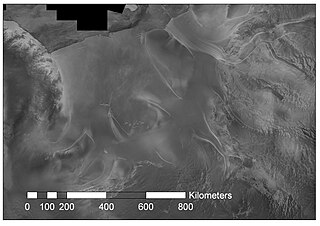
Rutford Ice Stream is a major Antarctic ice stream, about 290 kilometres (180 mi) long and over 24 kilometres (15 mi) wide, which drains southeastward between the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains and Fletcher Ice Rise into the southwest part of Ronne Ice Shelf. Named by US-ACAN for geologist Robert Hoxie Rutford, a member of several USARP expeditions to Antarctica; leader of the University of Minnesota Ellsworth Mountains Party, 1963-1964. Rutford served as Director of the Division of Polar Programs, National Science Foundation, 1975-1977.
Fletcher Ice Rise, or Fletcher Promontory, is a large ice rise, 100 miles (160 km) long and 40 miles (64 km) wide, at the southwest side of the Ronne Ice Shelf, Antarctica. The feature is completely ice covered and rises between Rutford Ice Stream and Carlson Inlet. The ice rise was observed, photographed and roughly sketched by Lieutenant Ronald F. Carlson, U.S. Navy, in the course of a C-130 aircraft flight of December 14–15, 1961 from McMurdo Sound to this vicinity and returning. It was mapped in detail by the U.S. Geological Survey from Landsat imagery taken 1973–74, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Joseph O. Fletcher, director of the Office of Polar Programs, National Science Foundation, 1971–74.
Dott Ice Rise is a peninsula-like feature that is ice-drowned except for the Barrett Nunataks, about 20 nautical miles (40 km) long, extending eastward from the Heritage Range of the Ellsworth Mountains and terminating at Constellation Inlet at the southwest edge of Ronne Ice Shelf. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–66, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Robert H. Dott, a United States Antarctic Research Program geologist and senior U.S. representative at Bernardo O'Higgins Base, summer 1961-62.
Fleet Point is a rocky point 4 nautical miles (7 km) northwest of Tent Nunatak on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. The point has a rocky spine ranging from 260 to 870 metres in height. The point appears in the aerial photographs of several American expeditions: United States Antarctic Service, 1939–41; Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48; U.S. Navy photos, 1968. It was mapped by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) 1963–64, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Michael Fleet, General Assistant with the BAS Larsen Ice Shelf party, 1963–64.

Gould Bay is a bay located at the junction of the Filchner Ice Shelf with the northeast corner of Berkner Island, in the southern Weddell Sea. It was discovered by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48, under the leadership of Commander Finn Ronne, U.S. Navy Reserve, who named this bay for Laurence M. Gould, geologist, geographer, and second in command of the Byrd Antarctic Expedition, 1928–30.
Matthews Glacier is a glacier on the east side of the Wilkins Mountains, Antarctica, draining south to enter the Ronne Ice Shelf just west of Dodson Peninsula. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for J.D. Matthews, an engineman at South Pole Station in 1963.
The Kershaw Ice Rumples are a large area of disturbed ice between Fletcher Ice Rise and Korff Ice Rise, in the southwestern part of the Ronne Ice Shelf, Antarctica. The feature appears in U.S. Navy aerial photographs taken in the 1960s and in imagery obtained by the NASA Earth Resources Technology Satellite (ERTS-1), 1973–74. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for John E.G. Kershaw, a senior pilot with the British Antarctic Survey, 1974–75.

The Lassiter Coast is the portion of the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula that extends from Cape Mackintosh to Cape Adams. The northern portion of this coast was discovered and photographed from the air by the United States Antarctic Service in 1940. During 1947 the entire extent of the coast was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) under Finn Ronne, who in conjunction with the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey charted it from the ground.










