Document imaging is an information technology category for systems capable of replicating documents commonly used in business. Document imaging systems can take many forms including microfilm, on demand printers, facsimile machines, copiers, multifunction printers, document scanners, computer output microfilm (COM) and archive writers. Document Imaging means the conversion of paper files (of any size or description) or microfilm / fiche to digital images.
The UK have been working slowly over the last decade to transition to digital processes. In 2013, the government launched an online claims portal to help keep track of and manage claims efficiently and quickly. Created to deal with claims of up to £25,000, the portal applies to organisations on the receiving end of employer liability and public liability claims. On May 31, 2021, a new separate system was launched called Official Injury Claim. This service deals with motor accidents and handles personal injury claims up to £5,000. Virtual hearings conducted over the telephone and video links are becoming more common practice, which is extremely useful in sensitive court cases. Over the recent years, partly driven by GDPR, many law firms have been forced to rethink the way they manage data. Paper case files and manual processes were still very much prevalent in the legal sector pre-Covid. The current crisis, though, has completely shifted the way law firms work; they have had to quickly adopt new ways of working. It has presented a window of opportunity for private law firms to review company structures and identify inefficiencies that have existed for years. The need for an efficient method of working was highlighted further during the lockdown when employees without electronic access to documentation struggled to work from home. [1]
Document imaging is a part of enterprise content management. [2] In the early days of content management technologies, the term "document imaging" was used interchangeably with "document image management" as the industry tried to separate itself from the micrographic and reprographic technologies.[ citation needed ]
In the late 1980s, a new document management technology emerged: electronic document management. This technology was built around the need to manage and secure the escalating volume of electronic documents (spreadsheets, word-processing documents, PDFs, e-mails) generated in organizations. [3]
Customer identity document scanning and storage is used for the purpose of age verification, identifying barred members and identifying individuals to the authorities in the case of criminal incidents. They are typically used at nightclubs, casinos, music venues, and many entities governed under the US Customer Identification Program (CIP). [4]
Systems used include Id Scan Biometrics's Scan Net and ID Vista products. [5] Id Scan Biometrics system was developed by Tamlyn Thompson in 2005.[ citation needed ]
UK licensing authorities are increasingly requiring nightclubs to scan and retain clubbers' ID details. Privacy and data security concerns have been raised by customers and the protest group NO2ID. [5] [6] [7] For example, Clubscan was an ID card scanning system invented in 2003.[ citation needed ] It took scanned images of nightclub patrons' ID documents and stored their personal details, for the purpose of age verification, identifying barred members and identifying individuals to the authorities in the case of criminal incidents. Clubscan is now discontinued and replaced by SCAN NET (the Safer Clubbing At Night Network) and serving over 1200 connected venues in the UK.
POD receipt can be generated into a digital image and full POD status report is generated into an excel spreadsheet. With e-retrieval of shipping documents, [8] basic functions are dimensionalized, and newly streamlined administrative operations suddenly become a very strategic step in a business model.
A document management system (DMS) is usually a computerized system used to store, share, track and manage files or documents. Some systems include history tracking where a log of the various versions created and modified by different users is recorded. The term has some overlap with the concepts of content management systems. It is often viewed as a component of enterprise content management (ECM) systems and related to digital asset management, document imaging, workflow systems and records management systems.
Interactive voice response (IVR) is a technology that allows telephone users to interact with a computer-operated telephone system through the use of voice and DTMF tones input with a keypad. In telephony, IVR allows customers to interact with a company's host system via a telephone keypad or by speech recognition, after which services can be inquired about through the IVR dialogue. IVR systems can respond with pre-recorded or dynamically generated audio to further direct users on how to proceed. IVR systems deployed in the network are sized to handle large call volumes and also used for outbound calling as IVR systems are more intelligent than many predictive dialer systems.
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics and features. Biometric authentication is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify individuals in groups that are under surveillance.
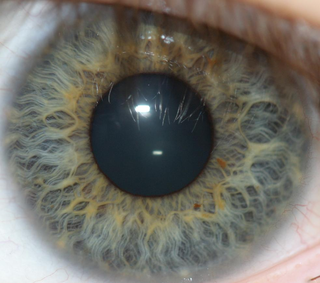
Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual's eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance. The discriminating powers of all biometric technologies depend on the amount of entropy they are able to encode and use in matching. Iris recognition is exceptional in this regard, enabling the avoidance of "collisions" even in cross-comparisons across massive populations. Its major limitation is that image acquisition from distances greater than a meter or two, or without cooperation, can be very difficult. However, the technology is in development and iris recognition can be accomplished from even up to 10 meters away or in a live camera feed.

A facial recognition system is a technology potentially capable of matching a human face from a digital image or a video frame against a database of faces. Such a system is typically employed to authenticate users through ID verification services, and works by pinpointing and measuring facial features from a given image.
Records management, also known as records and information management, is an organizational function devoted to the management of information in an organization throughout its life cycle, from the time of creation or receipt to its eventual disposition. This includes identifying, classifying, storing, securing, retrieving, tracking and destroying or permanently preserving records. The ISO 15489-1: 2001 standard defines records management as "[the] field of management responsible for the efficient and systematic control of the creation, receipt, maintenance, use and disposition of records, including the processes for capturing and maintaining evidence of and information about business activities and transactions in the form of records".
Automatic identification and data capture (AIDC) refers to the methods of automatically identifying objects, collecting data about them, and entering them directly into computer systems, without human involvement. Technologies typically considered as part of AIDC include QR codes, bar codes, radio frequency identification (RFID), biometrics, magnetic stripes, optical character recognition (OCR), smart cards, and voice recognition. AIDC is also commonly referred to as "Automatic Identification", "Auto-ID" and "Automatic Data Capture".
Enterprise content management (ECM) extends the concept of content management by adding a timeline for each content item and, possibly, enforcing processes for its creation, approval, and distribution. Systems using ECM generally provide a secure repository for managed items, analog or digital. They also include one methods for importing content to manage new items, and several presentation methods to make items available for use. Although ECM content may be protected by digital rights management (DRM), it is not required. ECM is distinguished from general content management by its cognizance of the processes and procedures of the enterprise for which it is created.
Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) refers to strategies for administering storage systems on computing devices.
Product information management (PIM) is the process of managing all the information required to market and sell products through distribution channels. This product data is created by an internal organization to support a multichannel marketing strategy. A central hub of product data can be used to distribute information to sales channels such as e-commerce websites, print catalogues, marketplaces such as Amazon and Google Shopping, social media platforms like Instagram and electronic data feeds to trading partners. Moreover, the significant role that PIM plays is reducing the abandonment rate by giving better product information.
A card reader is a data input device that reads data from a card-shaped storage medium and provides the data to a computer. Card readers can acquire data from a card via a number of methods, including: optical scanning of printed text or barcodes or holes on punched cards, electrical signals from connections made or interrupted by a card's punched holes or embedded circuitry, or electronic devices that can read plastic cards embedded with either a magnetic strip, computer chip, RFID chip, or another storage medium.
Electronic discovery refers to discovery in legal proceedings such as litigation, government investigations, or Freedom of Information Act requests, where the information sought is in electronic format. Electronic discovery is subject to rules of civil procedure and agreed-upon processes, often involving review for privilege and relevance before data are turned over to the requesting party.
Electronic authentication is the process of establishing confidence in user identities electronically presented to an information system. Digital authentication, or e-authentication, may be used synonymously when referring to the authentication process that confirms or certifies a person's identity and works. When used in conjunction with an electronic signature, it can provide evidence of whether data received has been tampered with after being signed by its original sender. Electronic authentication can reduce the risk of fraud and identity theft by verifying that a person is who they say they are when performing transactions online.
Search engine indexing is the collecting, parsing, and storing of data to facilitate fast and accurate information retrieval. Index design incorporates interdisciplinary concepts from linguistics, cognitive psychology, mathematics, informatics, and computer science. An alternate name for the process, in the context of search engines designed to find web pages on the Internet, is web indexing.
Document capture software refers to applications that provide the ability and feature set to automate the process of scanning paper documents or importing electronic documents, often for the purposes of feeding advanced document classification and data collection processes. Most scanning hardware, both scanners and copiers, provides the basic ability to scan to any number of image file formats, including: PDF, TIFF, JPG, BMP, etc. This basic functionality is augmented by document capture software, which can add efficiency and standardization to the process.
Executive Technologies, Inc. develops Enterprise Content Management, document management and document imaging software. The product is available for Cloud and on-premises use and uses Microsoft SQL for the document repository.
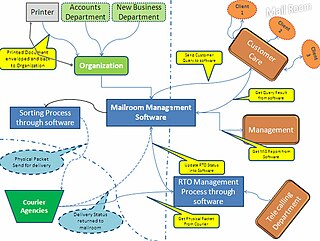
Digital mailroom is the automation of incoming mail processes. Using document scanning and document capture technologies, companies can digitise incoming mail and automate the classification and distribution of mail within the organization. Both paper and electronic mail (email) can be managed through the same process allowing companies to standardize their internal mail distribution procedures and adhere to company compliance policies.
A whole new range of techniques has been developed to identify people since the 1960s from the measurement and analysis of parts of their bodies to DNA profiles. Forms of identification are used to ensure that citizens are eligible for rights to benefits and to vote without fear of impersonation while private individuals have used seals and signatures for centuries to lay claim to real and personal estate. Generally, the amount of proof of identity that is required to gain access to something is proportionate to the value of what is being sought. It is estimated that only 4% of online transactions use methods other than simple passwords. Security of systems resources generally follows a three-step process of identification, authentication and authorization. Today, a high level of trust is as critical to eCommerce transactions as it is to traditional face-to-face transactions.
Biometrics refers to the automated recognition of individuals based on their biological and behavioral characteristics, not to be confused with statistical biometrics; which is used to analyse data in the biological sciences. Biometrics for the purposes of identification may involve DNA matching, facial recognition, fingerprints, retina and iris scanning, voice analysis, handwriting, gait, and even body odor.

The Documento Nacional de Identidad (DNI) (Spanish for 'National Identity Document') is the only personal identity card recognized by the Peruvian Government for all civil, commercial, administrative, judicial acts and, in general, for all those cases in which, by legal mandate, it must be presented. It is a public document, personal, and non-transferable and also constitutes the only title of right to the suffrage of the person in whose favor it has been granted. Its issuance is in charge of the National Registry of Identification and Civil Status (RENIEC).