
Fair trade is a term for an arrangement designed to help producers in developing countries achieve sustainable and equitable trade relationships. The fair trade movement combines the payment of higher prices to exporters with improved social and environmental standards. The movement focuses in particular on commodities, or products that are typically exported from developing countries to developed countries but is also used in domestic markets, most notably for handicrafts, coffee, cocoa, wine, sugar, fruit, flowers and gold.

A supermarket is a self-service shop offering a wide variety of food, beverages and household products, organized into sections. This kind of store is larger and has a wider selection than earlier grocery stores, but is smaller and more limited in the range of merchandise than a hypermarket or big-box market. In everyday United States usage, however, "grocery store" is often used to mean "supermarket".
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and policy that taxes foreign products to encourage or safeguard domestic industry. Protective tariffs are among the most widely used instruments of protectionism, along with import quotas and export quotas and other non-tariff barriers to trade.

Consumer electronics or home electronics are electronic equipment intended for everyday use, typically in private homes. Consumer electronics include devices used for entertainment, communications and recreation. These products are usually referred to as black goods due to many products being housed in black or dark casings. This term is used to distinguish them from "white goods" which are meant for housekeeping tasks, such as washing machines and refrigerators, although nowadays, these would be considered black goods, some of these being connected to the Internet. In British English, they are often called brown goods by producers and sellers. In the 2010s, this distinction is absent in large big box consumer electronics stores, which sell entertainment, communication and home office devices, light fixtures and appliances, including the bathroom type.
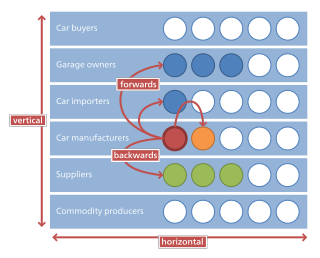
In microeconomics, management and international political economy, vertical integration is an arrangement in which the supply chain of a company is integrated and owned by that company. Usually each member of the supply chain produces a different product or (market-specific) service, and the products combine to satisfy a common need. It contrasts with horizontal integration, wherein a company produces several items that are related to one another. Vertical integration has also described management styles that bring large portions of the supply chain not only under a common ownership but also into one corporation.

A grocery store (AE), grocery shop (BE) or simply grocery is a foodservice retail store that primarily retails a general range of food products, which may be fresh or packaged. In everyday U.S. usage, however, "grocery store" is a synonym for supermarket, and is not used to refer to other types of stores that sell groceries. In the UK, shops that sell food are distinguished as grocers or grocery shops

Local purchasing is a preference to buy locally produced goods and services rather than those produced farther away. It is very often abbreviated as a positive goal, "buy local" or "buy locally', that parallels the phrase "think globally, act locally", common in green politics.
Vendor-managed inventory (VMI) is an inventory management practice in which a supplier of goods, usually the manufacturer, is responsible for optimizing the inventory held by a distributor.
Drop shipping is a form of retail business in which the seller accepts customer orders without keeping stock on hand. Instead, in a form of supply chain management, the seller transfers the orders and their shipment details either to the manufacturer, a wholesaler, another retailer, or a fulfillment house, which then ships the goods directly to the customer.

Business-to-business is a situation where one business makes a commercial transaction with another. This typically occurs when:

A Made in USA mark is a country of origin label affixed to American-made products that indicates the product is "all or virtually all" domestically produced, manufactured and assembled in the United States of America. The label is regulated by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
Green brands are those brands that consumers associate with environmental conservation and sustainable business practices.

An importer is the receiving country in an export from the sending country. Importation and exportation are the defining financial transactions of international trade. Import is part of the International Trade which involves buying and receiving of goods or services produced in another country. The seller of such goods and services is called an exporter, while the foreign buyer is known as an importer.

The availability and uptake of green electricity in the United Kingdom has increased in the 21st century. There are a number of suppliers offering green electricity in the United Kingdom. In theory these types of tariffs help to lower carbon dioxide emissions by increasing consumer demand for green electricity and encouraging more renewable energy plant to be built. Since Ofgem's 2014 regulations there are now set criteria defining what can be classified as a green source product. As well as holding sufficient guarantee of origin certificates to cover the electricity sold to consumers, suppliers are also required to show additionality by contributing to wider environmental and low carbon funds.
A marketing channel consists of the people, organizations, and activities necessary to transfer the ownership of goods from the point of production to the point of consumption. It is the way products get to the end-user, the consumer; and is also known as a distribution channel. A marketing channel is a useful tool for management, and is crucial to creating an effective and well-planned marketing strategy.

Retailing in India is one of the pillars of its economy and accounts for about 10 percent of its GDP. The Indian retail market is estimated to be worth $1.3 trillion as of 2022. India is one of the fastest growing retail markets in the world, with 1.4 billion people.

The Australian Companies Institute (Ausbuy) was, until 2016, a non-profit, non-political organisation that encouraged Australians to support Australian-owned and Australian-made products and services. Their goal was to keep the jobs and profits in Australia and for the decisions to be made by Australians.
Farm programs can be part of a concentrated effort to boost a country’s agricultural productivity in general or in specific sectors where they may have a comparative advantage. There are many different types of farm programs, with a variety of objectives and created with different economic mechanisms in mind. Some are meant to benefit farmers directly, while others seek to benefit consumers. They target food prices and quantity of food available on the market, as well as production and consumption of certain goods. Some are meant to benefit farmers directly, while others seek to benefit consumers. They target food prices and quantity of food available on the market, as well as production and consumption of certain goods.

Kurt Jetta is a consumer researcher who studies data about multinational corporations through his firm, TABS Analytics, which is based in Shelton, Connecticut. The corporations Jetta has analyzed include Amazon, Family Dollar, Dollar Tree, Walmart, Apple. In addition, Jetta has also studied the organic food industry, the vitamin industry, and the online grocery industry. Other investigations led by Jetta include sociological research that pertains to the purchasing habits of various ethnic groups. In the area of trade promotion, Jetta has developed an alternative methodology to current industry baseline models. Jetta also analyzes rewards programs. He was a 2017 Republican candidate in Florida’s 21st Congressional District.
The disruptive effect of e-commerce on the global retail industry has been referred to as the Amazon Effect: the term refers to Amazon.com's dominant role in the e-commerce market place and its leading role in driving the disruptive impact on the retail market and its supply chain.














