Related Research Articles
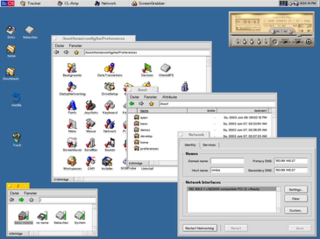
BeOS is a discontinued operating system for personal computers that was developed by Be Inc. It was conceived for the company's BeBox personal computer which was released in 1995. BeOS was designed for multitasking, multithreading, and a graphical user interface. The OS was later sold to OEMs, retail, and directly to users; its last version was released as freeware.

A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard.

The history of the graphical user interface, understood as the use of graphic icons and a pointing device to control a computer, covers a five-decade span of incremental refinements, built on some constant core principles. Several vendors have created their own windowing systems based on independent code, but with basic elements in common that define the WIMP "window, icon, menu and pointing device" paradigm.

Silicon Graphics, Inc. was an American high-performance computing manufacturer, producing computer hardware and software. Founded in Mountain View, California, in November 1981 by James Clark, its initial market was 3D graphics computer workstations, but its products, strategies and market positions developed significantly over time.

QNX is a commercial Unix-like real-time operating system, aimed primarily at the embedded systems market.

In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. A computer that uses such a processor is a 64-bit computer.
The history of macOS, Apple's current Mac operating system formerly named Mac OS X until 2011 and then OS X until 2016, began with the company's project to replace its "classic" Mac OS. That system, up to and including its final release Mac OS 9, was a direct descendant of the operating system Apple had used in its Mac computers since their introduction in 1984. However, the current macOS is a UNIX operating system built on technology that had been developed at NeXT from the 1980s until Apple purchased the company in early 1997.
Avadis "Avie" Tevanian is an American software engineer. At Carnegie Mellon University, he was a principal designer and engineer of the Mach operating system. He used that work at NeXT Inc. as the foundation of the NeXTSTEP operating system. He was senior vice president of software engineering at Apple from 1997 to 2003, and then chief software technology officer from 2003 to 2006. There, he redesigned NeXTSTEP to become macOS. Apple's macOS and iOS both incorporate the Mach Kernel, and iPadOS, watchOS, and tvOS are all derived from iOS. He was a longtime friend of Steve Jobs.

Be Inc. was an American computer company that created and developed the BeOS and BeIA operating systems, and the BeBox personal computer. It was founded in 1990 by former Apple Computer executive Jean-Louis Gassée, who also served as the company's CEO, and was based in Menlo Park, California.

OpenGL for Embedded Systems is a subset of the OpenGL computer graphics rendering application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D and 3D computer graphics such as those used by video games, typically hardware-accelerated using a graphics processing unit (GPU). It is designed for embedded systems like smartphones, tablet computers, video game consoles and PDAs. OpenGL ES is the "most widely deployed 3D graphics API in history".

Apple Remote Desktop (ARD) is a Macintosh application produced by Apple Inc., first released on March 14, 2002, that replaced a similar product called Apple Network Assistant. Aimed at computer administrators responsible for large numbers of computers and teachers who need to assist individuals or perform group demonstrations, Apple Remote Desktop allows users to remotely control or monitor other computers over a network. Mac Pro (2019), Mac mini with a 10Gb Ethernet card, and Mac Studio (2022) have Lights Out Management function and are able to power-on by Apple Remote Desktop.
Optimized Systems Software (OSS) was a company that produced disk operating systems, programming languages with integrated development environments, and applications primarily for Atari 8-bit computers. The founders of OSS previously developed Atari DOS, Atari BASIC, and the Atari Assembler Editor for Atari, Inc., and many OSS products are substantially improved versions. OS A+ and DOS XL are based on Atari DOS. BASIC A+, BASIC XL, and BASIC XE are based on Atari BASIC. EASMD and MAC/65 are modeled on the Atari Assembler Editor. Action! is an ALGOL-inspired compiled programming language with an integrated full-screen editor. OSS also sold some software for the Apple II.

Mac OS X Leopard is the sixth major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. Leopard was released on October 26, 2007 as the successor of Mac OS X Tiger, and is available in two editions: a desktop version suitable for personal computers, and a server version, Mac OS X Server. It retailed for $129 for the desktop version and $499 for Server. Leopard was superseded by Mac OS X Snow Leopard in 2009. Mac OS X Leopard is the last version of macOS that supports the PowerPC architecture as its successor, Mac OS X Snow Leopard, functions solely on Intel based Macs.

A Hackintosh is a computer that runs Apple's operating system macOS on computer hardware that is not authorized for the purpose by Apple. This can also include running Mac software on hardware it is not originally authorized for. This is due to the software license for macOS only permitting its use on in-house hardware built by Apple itself, in this case the Mac line.
This is a list of models and clones of Amiga computers.

The Apple–Intel architecture, or Mactel, is an unofficial name used for Macintosh personal computers developed and manufactured by Apple Inc. that use Intel x86 processors, rather than the PowerPC and Motorola 68000 ("68k") series processors used in their predecessors or the ARM-based Apple silicon SoCs used in their successors. As Apple changed the architecture of its products, they changed the firmware from the Open Firmware used on PowerPC-based Macs to the Intel-designed Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI). With the change in processor architecture to x86, Macs gained the ability to boot into x86-native operating systems, while Intel VT-x brought near-native virtualization with macOS as the host OS.
Benoit Schillings is a Belgian software engineer, who is the Chief Technology Officer (CTO) at Google[x] leading the early projects at X. He is known for being one of the lead developers of the Be Operating System (BeOS) and is a noted amateur astronomer.

Mac OS X Snow Leopard is the seventh major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers.

The Newton is a specified standard and series of personal digital assistants (PDAs) developed and marketed by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1993 to 1998. An early device in the PDA category — the term itself originating with the Newton — it was the first to feature handwriting recognition. Newton devices run on a proprietary operating system, Newton OS; unlike the company's Macintosh computers, Apple licensed the software to third-parties, who released Newton devices alongside Apple's own MessagePad line.
The following outline of Apple Inc. is a topical guide to the products, history, retail stores, corporate acquisitions, and personnel under the purview of the American multinational corporation:
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Hacker, Scot; Henry Bortman; Chris Herborth (1999). The BeOS Bible. California: Peachpit Press. ISBN 0-201-35377-6.
- 1 2 3 Tom Georgoulias (April 18, 2000). "Anno Dominic". frontwheeldrive.com. Archived from the original on April 10, 2006. Retrieved 2006-09-10.
- ↑ "Don't Moon the Ogre". BeDope.com. Retrieved 2006-09-10.
- 1 2 Andrew Orlowski (March 29, 2002). "Windows on a database – sliced and diced by BeOS vets". The Register . Retrieved 2006-08-10.
- ↑ Nicholas Heron (September 5, 2001). "Interview with QNX's Paul Leroux". OSNews. Retrieved 2006-09-10.
- 1 2 Dominic Giampaolo. "Personal homepage" . Retrieved 2006-09-10.