
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis of 1962, the Caribbean Crisis, or the Missile Scare, was a 13-day confrontation between the United States and the Soviet Union initiated by Soviet ballistic missile deployment in Cuba. The confrontation is often considered the closest the Cold War came to escalating into a full-scale nuclear war.

The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Nuclear physicist Robert Oppenheimer was the director of the Los Alamos Laboratory that designed the actual bombs. As engineer districts by convention carried the name of the city where they were located, the Army component of the project was designated the Manhattan District; Manhattan gradually superseded the official codename, Development of Substitute Materials, for the entire project. Along the way, the project absorbed its earlier British counterpart, Tube Alloys. The Manhattan Project began modestly in 1939, but grew to employ more than 130,000 people and cost nearly US$2 billion. Over 90 percent of the cost was for building factories and to produce fissile material, with less than 10 percent for development and production of the weapons. Research and production took place at more than thirty sites across the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada.
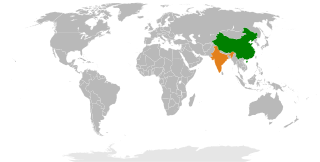
The Sino-Indian War, also known as the Indo-China War and Sino-Indian Border Conflict, was a war between China and India that occurred in 1962. A Chinese disputed Himalayan border was the main cause of the war. There had been a series of violent border skirmishes between the two countries after the 1959 Tibetan uprising, when India granted asylum to the Dalai Lama. India initiated a defensive Forward Policy from 1960 to hinder Chinese military patrols and logistics, in which it placed outposts along the border, including several north of the McMahon Line, the eastern portion of the Line of Actual Control proclaimed by Chinese Premier Zhou Enlai in 1959.

Marie Antoinette was the last queen of France before the French Revolution. She was born an archduchess of Austria and was the penultimate child and youngest daughter of Empress Maria Theresa and Emperor Francis I. She became dauphine of France in May 1770 at age 14 upon her marriage to Louis-Auguste, heir apparent to the French throne. On 10 May 1774, her husband ascended the throne as Louis XVI and she became queen.

The 1962 FIFA World Cup was the seventh FIFA World Cup, the quadrennial international football championship for men's national teams. It was held from 30 May to 17 June 1962 in Chile. The qualification rounds took place between August 1960 and December 1961, with 56 teams entering from six confederations, and fourteen qualifying for the finals tournament alongside Chile, the hosts, and Brazil, the eventual champions.

Operation Northwoods was a proposed false flag operation against the Cuban government that originated within the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) and the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) of the United States government in 1962. The proposals called for the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) or other U.S. government operatives to both stage and actually commit acts of terrorism against American military and civilian targets, blaming them on the Cuban government, and using it to justify a war against Cuba. The possibilities detailed in the document included the possible assassination of Cuban immigrants, sinking boats of Cuban refugees on the high seas, hijacking planes to be shot down or given the appearance of being shot down, blowing up a U.S. ship, and orchestrating violent terrorism in U.S. cities. The proposals were rejected by President John F. Kennedy, who was later assassinated.
Bossa nova is a style of Brazilian music, which was developed and popularized in the 1950s and 1960s and is today one of the best-known Brazilian music styles abroad. The phrase bossa nova means literally "new trend" or "new wave". A lyrical fusion of samba and jazz, bossa nova acquired a large following in the 1960s, initially among young musicians and college students.

Sword-and-sandal, also known as peplum, is a subgenre of largely Italian-made historical or Biblical epics mostly set in the Greco-Roman or medieval period. These films attempted to emulate the big-budget Hollywood historical epics of the time, such as Spartacus, Samson and Delilah and The Ten Commandments. These films dominated the Italian film industry from 1958 to 1965, eventually being replaced in 1965 by the spaghetti Western and Eurospy films.

The Douglas C-47 Skytrain or Dakota is a military transport aircraft developed from the civilian Douglas DC-3 airliner. It was used extensively by the Allies during World War II and remained in front-line service with various military operators for many years.

Edwin McMasters Stanton was an American lawyer and politician who served as Secretary of War under the Lincoln Administration during most of the American Civil War. Stanton's management helped organize the massive military resources of the North and guide the Union to victory. However, he was criticized by many Union generals for perceived over-cautiousness and micromanagement. He also organized the manhunt for Abraham Lincoln's assassin, John Wilkes Booth.
The 1962 British Empire and Commonwealth Games were held in Perth, Western Australia, from 22 November to 1 December 1962. Athletic events were held at Perry Lakes Stadium in the suburb of Floreat and swimming events at Beatty Park in North Perth. They were held after the 1962 Commonwealth Paraplegic Games for wheelchair athletes.

The 1962 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate which was held in the middle of President John F. Kennedy's term. His Democratic Party made a net gain of four seats from the Republicans, increasing their control of the Senate.

The 1962–63 European Cup was the eighth season of the European Cup, a football competition for European clubs. The competition was won by Milan, who beat defending champions Benfica in the final at Wembley Stadium in London. Milan's victory was the first by an Italian club.

The 1962 Asian Games also known as the 4th Asian Games, IV Asiad, and Jakarta 1962, was the fourth iteration of pan-Asian multi-event games sanctioned by the Asian Games Federation (AGF). The games were held from 24 August to 4 September 1962, in Jakarta, Indonesia. It was the first-ever international multi-sport event hosted by the then-17 year old Southeast Asian country. This was the first of two Asian Games hosted by the city as of 2018, the second was held in 2018, with Palembang as the co-host.

John Adams was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States, from 1797 to 1801. Before his presidency, he was a leader of the American Revolution that achieved independence from Great Britain, and he served as the first vice president of the United States. Adams was a dedicated diarist and regularly corresponded with many important figures in early American history, including his wife and adviser Abigail Adams, and Thomas Jefferson.

Crambinae is a large subfamily of the lepidopteran family Crambidae, the crambid snout moths. It currently includes over 1,800 species worldwide. The larvae are root feeders or stem borers, mostly on grasses. A few species are pests of sod grasses, maize, sugar cane, rice, and other Poaceae. The monophyly of this group is supported by the structure of the tympanal organs and the phallus attached medially to the juxta.

James Buchanan Jr. was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 15th president of the United States (1857–1861). He previously served as Secretary of State (1845–1849) and represented Pennsylvania in both houses of the U.S. Congress. He was a states' rights advocate, and minimized the role of the federal government in the nation's closing era of slavery. He is therefore consistently ranked by historians as one of the least effective presidents in history, for his failure to mitigate the national disunity that led to the American Civil War.
The Rajasthan Legislative Assembly or the Rajasthan Vidhan Sabha is the unicameral legislature of the Indian state of Rajasthan.
















