
An alpha helix is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil.

A transmembrane protein is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents.

Peripheral membrane proteins, or extrinsic membrane proteins, are membrane proteins that adhere only temporarily to the biological membrane with which they are associated. These proteins attach to integral membrane proteins, or penetrate the peripheral regions of the lipid bilayer. The regulatory protein subunits of many ion channels and transmembrane receptors, for example, may be defined as peripheral membrane proteins. In contrast to integral membrane proteins, peripheral membrane proteins tend to collect in the water-soluble component, or fraction, of all the proteins extracted during a protein purification procedure. Proteins with GPI anchors are an exception to this rule and can have purification properties similar to those of integral membrane proteins.

Peter B. Moore is Sterling Professor emeritus of Chemistry, Professor of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry at Yale University. He has dedicated his entire career to understanding the structure, function, and mechanism of the ribosome.

Frederic Middlebrook Richards, commonly referred to as Fred Richards, was an American biochemist and biophysicist known for solving the pioneering crystal structure of the ribonuclease S enzyme in 1967 and for defining the concept of solvent-accessible surface. He contributed many key experimental and theoretical results and developed new methods, garnering over 20,000 journal citations in several quite distinct research areas. In addition to the protein crystallography and biochemistry of ribonuclease S, these included solvent accessibility and internal packing of proteins, the first side-chain rotamer library, high-pressure crystallography, new types of chemical tags such as biotin/avidin, the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) chemical shift index, and structural and biophysical characterization of the effects of mutations.

Richard Henderson is a British molecular biologist and biophysicist and pioneer in the field of electron microscopy of biological molecules. Henderson shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2017 with Jacques Dubochet and Joachim Frank. "Thanks to his work, we can look at individual atoms of living nature, thanks to cryo-electron microscopes we can see details without destroying samples, and for this he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry."

Kenneth Stewart Cole was an American biophysicist described by his peers as "a pioneer in the application of physical science to biology". Cole was awarded the National Medal of Science in 1967.
Joseph Stewart Fruton, born Joseph Fruchtgarten, was a Polish-American biochemist and historian of science. His most significant scientific work involved synthetic peptides and their interactions with proteases; with his wife Sofia Simmonds he also published an influential textbook, General Biochemistry. From 1970 until his death, Fruton worked extensively on the history of science, particularly the history of biochemistry and molecular biology.
Orientations of Proteins in Membranes (OPM) database provides spatial positions of membrane protein structures with respect to the lipid bilayer. Positions of the proteins are calculated using an implicit solvation model of the lipid bilayer. The results of calculations were verified against experimental studies of spatial arrangement of transmembrane and peripheral proteins in membranes.
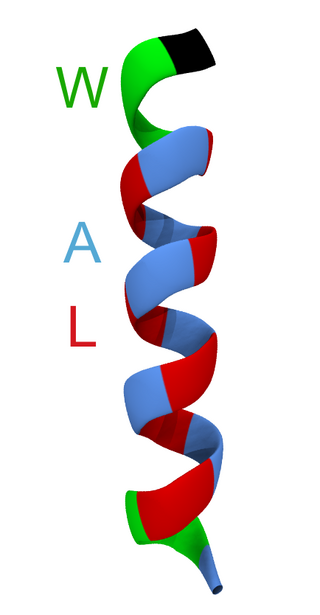
WALP peptides are a class of synthesized, membrane-spanning α-helices composed of tryptophan (W), alanine (A), and leucine (L) amino acids. They are designed to study properties of proteins in lipid membranes such as orientation, extent of insertion, and hydrophobic mismatch.
Stephen H. White is an American Biophysicist, academic, and author. He is a Professor Emeritus of Physiology and Biophysics at the University of California, Irvine.

Mark Andrew Lemmon an English-born biochemist, is the Alfred Gilman Professor and Department Chair of Pharmacology at Yale University where he also directs the Cancer Biology Institute.
Kalpathy Ramaier Katchap Easwaran is an Indian molecular biophysicist, academic and a former Astra Chair Professor and chairman of the department of molecular biophysics of the Indian Institute of Science. He is known for his contributions in the development of anti-fungal drugs and for his researches on ionophores and ion-transport across membranes. He is an elected fellow of the Indian National Science Academy and the Indian Academy of Sciences. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards, in 1984, for his contributions to biological sciences.
Membranome database provides structural and functional information about more than 6000 single-pass (bitopic) transmembrane proteins from Homo sapiens, Arabidopsis thaliana, Dictyostelium discoideum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Escherichia coli and Methanocaldococcus jannaschii. Bitopic membrane proteins consist of a single transmembrane alpha-helix connecting water-soluble domains of the protein situated at the opposite sides of a biological membrane. These proteins are frequently involved in the signal transduction and communication between cells in multicellular organisms.
Jason S. Lewis is a British radiochemist whose work relates to oncologic therapy and diagnosis. His research focus is a molecular imaging-based program focused on radiopharmaceutical development as well as the study of multimodality small- and biomolecule-based agents and their clinical translation. He has worked on the development of small molecules as well as radiolabeled peptides and antibodies probing the overexpression of receptors and antigens on tumors.
Karen Renee Gibson Fleming is a Professor of Biophysics at Johns Hopkins University. She investigates the energetics of transmembrane helix-helix interactions. Fleming was awarded the 2020 Protein Society Carl Brändén Award.
Shuguang Zhang is an American biochemist. He is at the MIT Media Lab's Laboratory for Molecular Architecture. Shuguang Zhang's research focuses on designs of biological molecules, particularly proteins and peptides. He has published over 200 scientific papers, which have cumulatively been cited over 40,300 times with an h-index of 96. On the “Updated science-wide author databases of standardizes citation indicators”, he is ranked 18th worldwide in the field of Biomedical Engineering. Zhang is also a co-founder and board member of Molecular Frontiers Foundation, which organizes annual Molecular Frontiers Symposia in Sweden and around the world. The selected winners are awarded Molecular Frontiers Inquiry Prize.
Robert Michael Stroud is a British biophysicist best known for his contributions to structural biology as means of determining the function of proteins, enzymes and integral membrane proteins. He was a professor of Chemistry at Caltech in the early 1970s and professor of Biochemistry and Biophysics, and of Pharmaceutical Chemistry at the University of California in San Francisco since 1976. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2003.
Julian Munson Sturtevant was an American chemist and educator. Sturtevant was Professor Emeritus of Chemistry, Molecular Biophysics, and Biochemistry at Yale University.

Bonnie Ann Wallace, FRSC is a British and American biophysicist and biochemist. She is a professor of molecular biophysics in the department of biological sciences, formerly the department of crystallography, at Birkbeck College, University of London, U.K.









