
Hudson Strait in Nunavut links the Atlantic Ocean and the Labrador Sea to Hudson Bay in Canada. This strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik, with its eastern entrance marked by Cape Chidley in Newfoundland and Labrador and Nunavut and Resolution Island, off Baffin Island. The strait is about 750 km (470 mi) long with an average width of 125 km (78 mi), varying from 70 km (43 mi) at the eastern entrance to 240 km (150 mi) at Deception Bay.
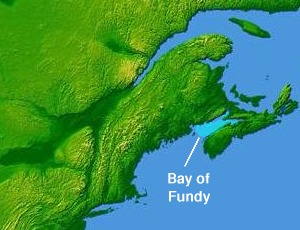
The Bay of Fundy is a bay between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the U.S. state of Maine. It is an arm of the Gulf of Maine. Its tidal range is the highest in the world. The name is probably a corruption of the French word fendu, meaning 'split'.

The Gulf of St. Lawrence fringes the shores of the provinces of Quebec, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland and Labrador, in Canada, plus the islands Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, possessions of France, in North America.

The Minas Basin is an inlet of the Bay of Fundy and a sub-basin of the Fundy Basin located in Nova Scotia, Canada. It is known for its extremely high tides.

Spencer's Island is a rural community in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, located at the western end of Greville Bay on the Bay of Fundy. The community is named after a small island 45°19′50″N64°41′30″W of the same name located offshore from nearby Cape Spencer. According to local oral history, the island, cape and community trace their name to a man named Spencer who is buried on the island. However the name more likely comes from Lord Spencer, a British statesman at the time the community was settled.

Advocate Harbour is a rural community located in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, Canada.

The Hopewell Rocks, also called the Flowerpot Rocks or simply the Rocks, are rock formations known as sea stacks caused by tidal erosion in the Hopewell Rocks Ocean Tidal Exploration Site at the Hopewell Rocks Provincial Park in New Brunswick, Canada. They stand 12–21 metres tall.

Cape Split is a headland located on the Bay of Fundy coast of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. The Battle off Cape Split happened during the American Revolution.
The Glooscap Trail is a scenic roadway in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.
The Fundy Shore Ecotour is a former scenic drive and network of tourist destinations in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia and encircles several sub-basins of the Bay of Fundy, which contains the highest tidal range on the planet.

Nova Scotia is a province located in Eastern Canada fronting the Atlantic Ocean. One of the Maritime Provinces, Nova Scotia's geography is complex, despite its relatively small size in comparison to other Canadian provinces.

Cape Chignecto Provincial Park is a Canadian provincial park located in Nova Scotia. A wilderness park, it derives its name from Cape Chignecto, a prominent headland which divides the Bay of Fundy with Chignecto Bay to the north and the Minas Channel leading to the Minas Basin to the east. The park, which opened in 1998, is the largest provincial park in Nova Scotia. It also anchors one end of the UNESCO Cliffs of Fundy Global Geopark.

Partridge Island is a significant historical, cultural and geological site located near the mouth of Parrsboro Harbour and the town of Parrsboro on the Minas Basin, in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, Canada. It attracts many visitors including sightseers, swimmers, photographers, hikers and amateur geologists. Partridge Island is actually a peninsula that is connected to the mainland by a sandbar isthmus. According to local legend, the isthmus was created during the Saxby Gale of 1869. The hiking trail to the top of the island affords scenic views of key landforms on the Minas Basin including Cape Blomidon, Cape Split and Cape Sharp. The nearby Ottawa House By-the-Sea Museum contains artifacts and exhibits illustrating the history of the former village at Partridge Island, which dates from the 1770s. Partridge Island is a favourite hunting ground for rockhounds because its ancient sandstone and basalt cliffs are steadily eroded by the fast-moving currents of the world's highest tides. Rocks and debris worn away from its cliffs are dragged down the beach making it possible to find gemstones, exotic-looking zeolite minerals and fossils. Fossil hunters are warned, however, that although one or two loose specimens may be collected, Nova Scotia law requires that they be sent or taken to a museum for further study, and no fossils may be excavated from bedrock without a permit.

Burntcoat Head is an unincorporated rural Canadian community in Hants County, Nova Scotia. The area is known for having the largest tidal range of any location in the world. It is also home to Burntcoat Head Park, which offers public access to the ocean floor.

Eatonville is a former lumber and shipbuilding village in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia. It includes a large tidal harbour at the mouth of the Eatonville Brook beside several dramatic sea stacks known as the "Three Sisters". It was founded in 1826 and abandoned in the 1940s. The site of the village is now part of Cape Chignecto Provincial Park.
Hall's Harbour is a fishing community in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, located in Kings County on the North Mountain along the shore of the Bay of Fundy.
Scots Bay, also spelled "Scott's Bay" and "Scotts Bay," is a community in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, located in Kings County.

Apple River is a community in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, located in Cumberland County.

The Digby Gut is a narrow channel connecting the Bay of Fundy with the Annapolis Basin. The town of Digby, Nova Scotia is located on the inner portion of the western side of the Gut. The eastern entrance is marked by the Point Prim Lighthouse. Strong tidal currents, numerous rocky ledges, frequent fogs and unpredictable winds make it a dangerous passage requiring a pilot or local knowledge. Tide flows create 5 knot tidal currents and create numerous whirlpools and eddies. The gut is about a half nautical mile in width and bordered by high rocky cliffs. It marks a break in the North Mountain ridge along the Annapolis Valley and is the eastern end of Digby Neck. Digby Gut had its origins as the northern terminus of the ancient Bear River, part of which is now a drowned river valley.

Cape d'Or is a headland located near Advocate, Cumberland County, on the Bay of Fundy coast of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.

















