NTFS is a proprietary journaling file system developed by Microsoft. Starting with Windows NT 3.1, it is the default file system of the Windows NT family.

Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk, before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions.. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it can be difficult to properly size partitions, resulting in having one partition with much free space and another nearly totally allocated.
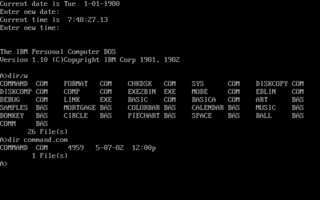
IBM PC DOS, an acronym for IBM personal computer disk operating system, is a discontinued operating system for the IBM Personal Computer, manufactured and sold by IBM from the early 1980s into the 2000s.
The Tandy 2000 is a personal computer introduced by Radio Shack in September 1983 based on the 8 MHz Intel 80186 microprocessor running MS-DOS. By comparison, the IBM PC XT used the older 4.77 MHz 8088 processor, and the IBM PC AT would later use the newer 6 MHz Intel 80286. Due to the 16-bit-wide data bus and more efficient instruction decoding of the 80186, the Tandy 2000 ran significantly faster than other PC compatibles, and slightly faster than the PC AT. The Tandy 2000 was the company's first computer built around an Intel x86 series microprocessor; previous models used the Z80 and 68000 CPUs.

For computer file systems, fdisk is a command-line utility that provides disk partitioning functions. It is available in DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, and Microsoft Windows operating systems, and in certain ports of FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonFly BSD and macOS for compatibility reasons. In versions of the Windows NT operating system line from Windows 2000 onwards, fdisk is replaced by a more advanced tool called diskpart. Similar utilities exist for Unix-like systems, for example, BSD disklabel.
Stac Electronics, originally incorporated as State of the Art Consulting and later shortened to Stac, Inc., was a technology company founded in 1983. It is known primarily for its Lempel–Ziv–Stac lossless compression algorithm and Stacker disk compression utility for compressing data for storage.

Norton Utilities is a utility software suite designed to help analyze, configure, optimize and maintain a computer. The current version of Norton Utilities is Norton Utilities 16 for Windows XP/Vista/7/8 was released 26 October 2012.

Atari DOS is the disk operating system used with the Atari 8-bit family of computers. Operating system extensions loaded into memory were required in order for an Atari computer to manage files stored on a disk drive. These extensions to the operating system added the disk handler and other file management features.
Executable compression is any means of compressing an executable file and combining the compressed data with decompression code into a single executable. When this compressed executable is executed, the decompression code recreates the original code from the compressed code before executing it. In most cases this happens transparently so the compressed executable can be used in exactly the same way as the original. Executable compressors are often referred to as "runtime packers", "software packers", "software protectors".

PC Tools was a collection of software utilities for DOS developed by Central Point Software.
A disk compression software utility increases the amount of information that can be stored on a hard disk drive of given size. Unlike a file compression utility, which compresses only specified files—and which requires the user to designate the files to be compressed—an on-the-fly disk compression utility works automatically through resident software without the user needing to be aware of its existence. On-the-fly disk compression is therefore also known as transparent, real-time or online disk compression.
DriveSpace is a disk compression utility supplied with MS-DOS starting from version 6.0 in 1993. The purpose of DriveSpace is to increase the amount of data the user could store on disks by transparently compressing and decompressing data on-the-fly. It is primarily intended for use with hard drives, but use for floppy disks is also supported.
MSX-DOS is a discontinued disk operating system developed by Microsoft for the 8-bit home computer standard MSX, and is a cross between MS-DOS 1.25 and CP/M-80 2.

Microsoft Drive Optimizer is a utility in Microsoft Windows designed to increase data access speed by rearranging files stored on a disk to occupy contiguous storage locations, a technique called defragmentation. Defragmenting a disk minimizes head travel, which reduces the time it takes to read files from and write files to the disk. As a result of the decreased read and write times, Microsoft Drive Optimizer decreases system startup times for systems starting from magnetic storage devices such as a hard drive. However, defragmentation cannot be run on storage devices such as solid state drives, USB drives or SD cards that use flash memory to increase speeds, as these drives do not use a head. Defragmentation may decrease lifespan for certain technologies, e.g. solid state drives. Microsoft Drive Optimizer was first officially shipped with Windows XP.
Amiga support and maintenance software performs service functions such as formatting media for a specific filesystem, diagnosing failures that occur on formatted media, data recovery after media failure, and installation of new software for the Amiga family of personal computers—as opposed to application software, which performs business, education, and recreation functions.
The TRS-80 Model 4 is the last Z80-based home computer family by Radio Shack, sold from April 1983 through autumn 1991.

MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and some operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS". MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatible personal computers during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system.

DOS is a platform-independent acronym for Disk Operating System which later became a common shorthand for disk-based operating systems on IBM PC compatibles. DOS primarily consists of Microsoft's MS-DOS and a rebranded IBM version under the name PC DOS, both of which were introduced in 1981. Later compatible systems from other manufacturers include DR DOS (1988), ROM-DOS (1989), PTS-DOS (1993), and FreeDOS (1998). MS-DOS dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995.
A disk utility is a utility program that allows a user to perform various functions on a computer disk, such as disk partitioning and logical volume management, as well as multiple smaller tasks such as changing drive letters and other mount points, renaming volumes, disk checking, and disk formatting, which are otherwise handled separately by multiple other built-in commands. Each operating system (OS) has its own basic disk utility, and there are also separate programs which can recognize and adjust the different filesystems of multiple OSes. Types of disk utilities include disk checkers, disk cleaners and disk space analyzers









