Related Research Articles
Discrete mathematics is the study of mathematical structures that can be considered "discrete" rather than "continuous". Objects studied in discrete mathematics include integers, graphs, and statements in logic. By contrast, discrete mathematics excludes topics in "continuous mathematics" such as real numbers, calculus or Euclidean geometry. Discrete objects can often be enumerated by integers; more formally, discrete mathematics has been characterized as the branch of mathematics dealing with countable sets. However, there is no exact definition of the term "discrete mathematics".

Ronald Lewis Graham was an American mathematician credited by the American Mathematical Society as "one of the principal architects of the rapid development worldwide of discrete mathematics in recent years". He was president of both the American Mathematical Society and the Mathematical Association of America, and his honors included the Leroy P. Steele Prize for lifetime achievement and election to the National Academy of Sciences.
Combinatorics is a branch of mathematics concerning the study of finite or countable discrete structures.
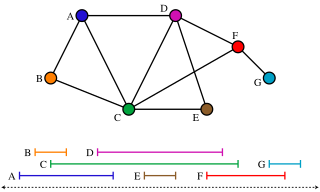
In graph theory, an interval graph is an undirected graph formed from a set of intervals on the real line, with a vertex for each interval and an edge between vertices whose intervals intersect. It is the intersection graph of the intervals.
Discrete geometry and combinatorial geometry are branches of geometry that study combinatorial properties and constructive methods of discrete geometric objects. Most questions in discrete geometry involve finite or discrete sets of basic geometric objects, such as points, lines, planes, circles, spheres, polygons, and so forth. The subject focuses on the combinatorial properties of these objects, such as how they intersect one another, or how they may be arranged to cover a larger object.

In graph theory, a perfect graph is a graph in which the chromatic number equals the size of the maximum clique, both in the graph itself and in every induced subgraph. In all graphs, the chromatic number is greater than or equal to the size of the maximum clique, but they can be far apart. A graph is perfect when these numbers are equal, and remain equal after the deletion of arbitrary subsets of vertices.
In the mathematical area of graph theory, a chordal graph is one in which all cycles of four or more vertices have a chord, which is an edge that is not part of the cycle but connects two vertices of the cycle. Equivalently, every induced cycle in the graph should have exactly three vertices. The chordal graphs may also be characterized as the graphs that have perfect elimination orderings, as the graphs in which each minimal separator is a clique, and as the intersection graphs of subtrees of a tree. They are sometimes also called rigid circuit graphs or triangulated graphs: a chordal completion of a graph is typically called a triangulation of that graph.

In graph theory, a factor of a graph G is a spanning subgraph, i.e., a subgraph that has the same vertex set as G. A k-factor of a graph is a spanning k-regular subgraph, and a k-factorization partitions the edges of the graph into disjoint k-factors. A graph G is said to be k-factorable if it admits a k-factorization. In particular, a 1-factor is a perfect matching, and a 1-factorization of a k-regular graph is a proper edge coloring with k colors. A 2-factor is a collection of cycles that spans all vertices of the graph.
In graph theory, a path decomposition of a graph G is, informally, a representation of G as a "thickened" path graph, and the pathwidth of G is a number that measures how much the path was thickened to form G. More formally, a path-decomposition is a sequence of subsets of vertices of G such that the endpoints of each edge appear in one of the subsets and such that each vertex appears in a contiguous subsequence of the subsets, and the pathwidth is one less than the size of the largest set in such a decomposition. Pathwidth is also known as interval thickness, vertex separation number, or node searching number.

Daniel J. Kleitman is an American mathematician and professor of applied mathematics at MIT. His research interests include combinatorics, graph theory, genomics, and operations research.

In graph theory, the handshaking lemma is the statement that, in every finite undirected graph, the number of vertices that touch an odd number of edges is even. For example, if there is a party of people who shake hands, the number of people who shake an odd number of other people's hands is even. The handshaking lemma is a consequence of the degree sum formula, also sometimes called the handshaking lemma, according to which the sum of the degrees equals twice the number of edges in the graph. Both results were proven by Leonhard Euler in his famous paper on the Seven Bridges of Königsberg that began the study of graph theory.

In graph theory, boxicity is a graph invariant, introduced by Fred S. Roberts in 1969.
G. W. Peck is a pseudonymous attribution used as the author or co-author of a number of published academic papers in mathematics. Peck is sometimes humorously identified with George Wilbur Peck, a former governor of the US state of Wisconsin.
Ronald Cedric Read was a British mathematician, latterly a professor emeritus of mathematics at the University of Waterloo, Canada. He published many books and papers, primarily on enumeration of graphs, graph isomorphism, chromatic polynomials, and particularly, the use of computers in graph-theoretical research. A majority of his later work was done in Waterloo. Read received his Ph.D. (1959) in graph theory from the University of London.
George Barry Purdy was a mathematician and computer scientist who specialized in cryptography, combinatorial geometry, and number theory. Purdy received his Ph.D. from the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign in 1972, officially under the supervision of Paul T. Bateman, but his de facto adviser was Paul Erdős. He was on the faculty in the mathematics department at Texas A&M University for 11 years, and was appointed the Geier Professor of computer science at the University of Cincinnati in 1986.
Fred Stephen Roberts is an American mathematician, a professor of mathematics at Rutgers University, and a former director of DIMACS.

In graph theory, a branch of mathematics, Fleischner's theorem gives a sufficient condition for a graph to contain a Hamiltonian cycle. It states that, if is a 2-vertex-connected graph, then the square of is Hamiltonian. It is named after Herbert Fleischner, who published its proof in 1974.
Edward R. Scheinerman is an American mathematician, working in graph theory and order theory. He is a professor of applied mathematics, statistics, and computer science at Johns Hopkins University. His contributions to mathematics include Scheinerman's conjecture, now proven, stating that every planar graph may be represented as an intersection graph of line segments.
In graph theory, a branch of mathematics, an indifference graph is an undirected graph constructed by assigning a real number to each vertex and connecting two vertices by an edge when their numbers are within one unit of each other. Indifference graphs are also the intersection graphs of sets of unit intervals, or of properly nested intervals. Based on these two types of interval representations, these graphs are also called unit interval graphs or proper interval graphs; they form a subclass of the interval graphs.
In graph theory, the (a, b)-decomposition of an undirected graph is a partition of its edges into a + 1 sets, each one of them inducing a forest, except one which induces a graph with maximum degree b. If this graph is also a forest, then we call this a F(a, b)-decomposition.
References
- ↑ Douglas Brent West at the Mathematics Genealogy Project
- ↑ Peck, G. W. (2002), "Kleitman and combinatorics: a celebration", Discrete Mathematics , 257 (2–3): 193–224, doi:10.1016/S0012-365X(02)00595-2, MR 1935723 .