
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motion of the object. In one with anticlockwise rotation, the force acts to the right. Deflection of an object due to the Coriolis force is called the Coriolis effect. Though recognized previously by others, the mathematical expression for the Coriolis force appeared in an 1835 paper by French scientist Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis, in connection with the theory of water wheels. Early in the 20th century, the term Coriolis force began to be used in connection with meteorology.

A mass driver or electromagnetic catapult is a proposed method of non-rocket spacelaunch which would use a linear motor to accelerate and catapult payloads up to high speeds. Existing and contemplated mass drivers use coils of wire energized by electricity to make electromagnets, though a rotary mass driver has also been proposed. Sequential firing of a row of electromagnets accelerates the payload along a path. After leaving the path, the payload continues to move due to momentum.
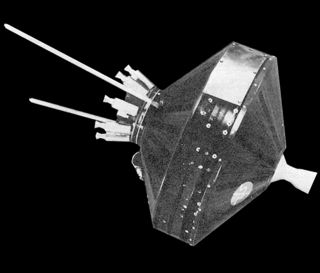
Pioneer 0 was a failed United States space probe that was designed to go into orbit around the Moon, carrying a television camera, a micrometeorite detector and a magnetometer. It was part of the first International Geophysical Year (IGY) science payload. It was designed and operated by the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division as the first spacecraft in the Pioneer program and was the first attempted launch beyond Earth orbit by any country, but the rocket failed shortly after launch. The probe was intended to be called Pioneer, but the launch failure precluded that name.

Luna 3, or E-2A No.1 was a Soviet spacecraft launched in 1959 as part of the Luna programme. It was the first mission to photograph the far side of the Moon and the third Soviet space probe to be sent to the neighborhood of the Moon. Though it returned rather poor pictures, the historic, never-before-seen views of the far side of the Moon caused excitement and interest when they were published around the world, and a tentative Atlas of the Far Side of the Moon was created after image processing improved the pictures.

A gravity assist, gravity assist maneuver, swing-by, or generally a gravitational slingshot in orbital mechanics, is a type of spaceflight flyby which makes use of the relative movement and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the path and speed of a spacecraft, typically to save propellant and reduce expense.

A launch pad is an above-ground facility from which a rocket-powered missile or space vehicle is vertically launched. The term launch pad can be used to describe just the central launch platform, or the entire complex. The entire complex will include a launch mount or launch platform to physically support the vehicle, a service structure with umbilicals, and the infrastructure required to provide propellants, cryogenic fluids, electrical power, communications, telemetry, rocket assembly, payload processing, storage facilities for propellants and gases, equipment, access roads, and drainage.

A reusable launch vehicle has parts that can be recovered and reflown, while carrying payloads from the surface to outer space. Rocket stages are the most common launch vehicle parts aimed for reuse. Smaller parts such as rocket engines and boosters can also be reused, though reusable spacecraft may be launched on top of an expendable launch vehicle. Reusable launch vehicles do not need to make these parts for each launch, therefore reducing its launch cost significantly. However, these benefits are diminished by the cost of recovery and refurbishment.

AS-202 was the second uncrewed, suborbital test flight of a production Block I Apollo command and service module launched with the Saturn IB launch vehicle. It was launched on August 25, 1966, and was the first flight which included the spacecraft guidance, navigation control system and fuel cells. The success of this flight enabled the Apollo program to judge the Block I spacecraft and Saturn IB ready to carry men into orbit on the next mission, AS-204.

An orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which a spacecraft is placed on a trajectory where it could remain in space for at least one orbit. To do this around the Earth, it must be on a free trajectory which has an altitude at perigee around 80 kilometers (50 mi); this is the boundary of space as defined by NASA, the US Air Force and the FAA. To remain in orbit at this altitude requires an orbital speed of ~7.8 km/s. Orbital speed is slower for higher orbits, but attaining them requires greater delta-v. The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale has established the Kármán line at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) as a working definition for the boundary between aeronautics and astronautics. This is used because at an altitude of about 100 km (62 mi), as Theodore von Kármán calculated, a vehicle would have to travel faster than orbital velocity to derive sufficient aerodynamic lift from the atmosphere to support itself.

A space rendezvous is a set of orbital maneuvers during which two spacecraft, one of which is often a space station, arrive at the same orbit and approach to a very close distance. Rendezvous requires a precise match of the orbital velocities and position vectors of the two spacecraft, allowing them to remain at a constant distance through orbital station-keeping. Rendezvous may or may not be followed by docking or berthing, procedures which bring the spacecraft into physical contact and create a link between them.

The European Launcher Development Organisation (ELDO) is a former European space research organisation. It was first developed in order to establish a satellite launch vehicle for Europe. The three-stage rocket developed was named Europa, after the mythical Greek goddess. Overall, there were 10 launches that occurred under ELDO's funding. The organisation consisted of Belgium, Britain, France, Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands. Australia was an associate member of the organisation.

A shooting range, firing range, gun range or shooting ground is a specialized facility, venue, or field designed specifically for firearm usage qualifications, training, practice, or competitions. Some shooting ranges are operated by military or law enforcement agencies, though the majority of ranges are privately owned by civilians and sporting clubs and cater mostly to recreational shooters. Each facility is typically overseen by one or more supervisory personnel, known as a Range Officer (RO), or sometimes a range master in the United States. Supervisory personnel are responsible for ensuring that all safety rules and relevant laws are followed at all times.

A launch vehicle is typically a rocket-powered vehicle designed to carry a payload from Earth's surface or lower atmosphere to outer space. The most common form is the ballistic missile-shaped multistage rocket, but the term is more general and also encompasses vehicles like the Space Shuttle. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, supported by a launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to high operating costs.
RADARSAT-2 is a Canadian Space Agency (CSA) Earth observation satellite. It launched on 14 December 2007 aboard a Starsem Soyuz-FG rocket from Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan. The spacecraft is owned by MDA
The Garma Festival of Traditional Cultures (Garma) is Australia's largest Indigenous cultural gathering, taking place over four days each August in northeast Arnhem Land, in the Northern Territory, Australia. Hosted by the Yothu Yindi Foundation, Garma is a celebration of the cultural traditions of the Yolngu people, and a major community gathering for the clans and families of the Arnhem Land region. The event showcases traditional miny'tji (art), ancient story-telling, manikay (song), and bunggul (dance). It is held at Gulkula, a significant Gumatj ceremonial site about 40 kilometres (25 mi) from the township of Nhulunbuy, attracts more than 2500 guests each year and is often sold out months in advance.

A star tracker is an optical device that measures the positions of stars using photocells or a camera. As the positions of many stars have been measured by astronomers to a high degree of accuracy, a star tracker on a satellite or spacecraft may be used to determine the orientation of the spacecraft with respect to the stars. In order to do this, the star tracker must obtain an image of the stars, measure their apparent position in the reference frame of the spacecraft, and identify the stars so their position can be compared with their known absolute position from a star catalog. A star tracker may include a processor to identify stars by comparing the pattern of observed stars with the known pattern of stars in the sky.
A gravity turn or zero-lift turn is a maneuver used in launching a spacecraft into, or descending from, an orbit around a celestial body such as a planet or a moon. It is a trajectory optimization that uses gravity to steer the vehicle onto its desired trajectory. It offers two main advantages over a trajectory controlled solely through the vehicle's own thrust. First, the thrust is not used to change the spacecraft's direction, so more of it is used to accelerate the vehicle into orbit. Second, and more importantly, during the initial ascent phase the vehicle can maintain low or even zero angle of attack. This minimizes transverse aerodynamic stress on the launch vehicle, allowing for a lighter launch vehicle.
The Manned Space Flight Network was a set of tracking stations built to support the American Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, and Skylab space programs.

The Goodyear Meteor Junior was a 1954 concept for a fully reusable spacecraft and launch system designed by Darrell C. Romick and two of his colleagues employed by Goodyear Aerospace, a subsidiary of the American Goodyear Tire and Rubber Company. Darrell Romick originally estimated that the craft would cost about the same as an intercontinental B-52 bomber.














