
A bug in poker is a limited form of wild card. One or both jokers are often added to the deck and played as bugs.
In a poker game with more than one betting round, an out is any unseen card that, if drawn, will improve a player's hand to one that is likely to win. Knowing the number of outs a player has is an important part of poker strategy. For example, in draw poker, a hand with four diamonds has nine outs to make a flush: there are 13 diamonds in the deck, and four of them have been seen. If a player has two small pairs, and he believes that it will be necessary for him to make a full house to win, then he has four outs: the two remaining cards of each rank that he holds.
In poker, pot odds are the ratio of the current size of the pot to the cost of a contemplated call. Pot odds are compared to the odds of winning a hand with a future card in order to estimate the call's expected value. The purpose of this is to statistically guide a player's decision between the options of call or fold. Raising is an alternative to place this decision on the opponent.

Omaha hold 'em is a community card poker game similar to Texas hold 'em, where each player is dealt four cards and must make their best hand using exactly two of them, plus exactly three of the five community cards. The exact origin of the game is unknown, but casino executive Robert Turner first brought Omaha into a casino setting when he introduced the game to Bill Boyd, who offered it as a game at the Las Vegas Golden Nugget Casino. Omaha uses a 52-card French deck. Omaha hold 'em 8-or-better is the "O" game featured in H.O.R.S.E.

Independence is a fundamental notion in probability theory, as in statistics and the theory of stochastic processes. Two events are independent, statistically independent, or stochastically independent if, informally speaking, the occurrence of one does not affect the probability of occurrence of the other or, equivalently, does not affect the odds. Similarly, two random variables are independent if the realization of one does not affect the probability distribution of the other.

In the card game of poker, a bluff is a bet or raise made with a hand which is not thought to be the best hand. To bluff is to make such a bet. The objective of a bluff is to induce a fold by at least one opponent who holds a better hand. The size and frequency of a bluff determines its profitability to the bluffer. By extension, the phrase "calling somebody's bluff" is often used outside the context of poker to describe situations where one person demands that another proves a claim, or proves that they are not being deceptive.
In poker, the probability of each type of 5-card hand can be computed by calculating the proportion of hands of that type among all possible hands.
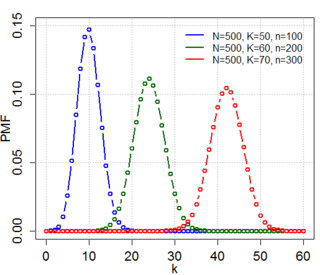
In probability theory and statistics, the hypergeometric distribution is a discrete probability distribution that describes the probability of successes in draws, without replacement, from a finite population of size that contains exactly objects with that feature, wherein each draw is either a success or a failure. In contrast, the binomial distribution describes the probability of successes in draws with replacement.

Big two is a card game of Cantonese origin. It is similar to the games of Zheng Shangyou, daifugō, president, crazy eights, cheat, and other shedding games. The game is very popular in East Asia and in Southeast Asia, especially throughout mainland China, Hong Kong, Vietnam, Macau, Taiwan, Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia and Singapore. It is played both casually and as a gambling game. It is usually played with two to four players, the entire deck being dealt out in either case. The objective of the game is to be the first to play off all of one's cards.
Non-standard poker hands are hands which are not recognized by official poker rules but are made by house rules. Non-standard hands usually appear in games using wild cards or bugs. Other terms for nonstandard hands are special hands or freak hands. Because the hands are defined by house rules, the composition and ranking of these hands is subject to variation. Any player participating in a game with non-standard hands should be sure to determine the exact rules of the game before play begins.
Morton's theorem is a poker principle articulated by Andy Morton in a Usenet poker newsgroup. It states that in multi-way pots, a player's expectation may be maximized by an opponent making a correct decision.
Open-ended refers to a situation in poker where the player has four of five cards needed for a straight that can be completed at either end. For example, a player with 3♥ 4♥ 5♣ 6♠ is open-ended, because a deuce or a seven would give the player a straight. This situation is also called an outside straight draw or double-ended straight draw as the cards needed to complete the straight are cards which are on the outside of the current hand, as opposed to an inside draw such as 2♦3♠ 4♠6♥ or A♣ 2♣ 3♣ 4♦, which can only be completed by a five. The term originated with draw poker but is also used in games like Texas hold'em.

Badugi is a draw poker variant similar to triple draw, with hand-values similar to lowball. The betting structure and overall play of the game is identical to a standard poker game using blinds, but, unlike traditional poker which involves a minimum of five cards, players' hands contain only four cards at any one time. During each of three drawing rounds, players can trade zero to four cards from their hands for new ones from the deck, in an attempt to form the best badugi hand and win the pot. Badugi is often a gambling game, with the object being to win money in the form of pots. The winner of the pot is the person with the best badugi hand at the conclusion of play. Badugi is played in cardrooms around the world, as well as online, in rooms such as PokerStars. Although it hasn’t had its own tournament per se at the WSOP, it is featured in the Dealers Choice events as well as in the Triple Draw Mix. The 2023 WSOP event does have a Badugi tournament scheduled.
Poker hand A is said to dominate poker hand B if poker hand B has three or fewer outs that would improve it enough to win. Informally, domination is sometimes used to refer to any situation where one hand is highly likely to beat another. The term drawing dead is used to denote a domination situation with zero outs.

Poker dice are dice which, instead of having number pips, have representations of playing cards upon them. Poker dice have six sides, one each of an Ace, King, Queen, Jack, 10, and 9, and are used to form a poker hand.
The mathematics of gambling is a collection of probability applications encountered in games of chance and can get included in game theory. From a mathematical point of view, the games of chance are experiments generating various types of aleatory events, and it is possible to calculate by using the properties of probability on a finite space of possibilities.
The following is a glossary of poker terms used in the card game of poker. It supplements the glossary of card game terms. Besides the terms listed here, there are thousands of common and uncommon poker slang terms. This is not intended to be a formal dictionary; precise usage details and multiple closely related senses are omitted here in favor of concise treatment of the basics.
Baduci is a combination of Badugi poker and deuce to seven triple draw, and uses hand values similar to lowball. The pot in this game is split much like high-low split between the best Badugi hand and the best 2-7 triple draw hand. The betting structure and overall play of the game is nearly identical to a standard poker game using blinds. A players' hand contains five cards, where only four cards are used to determine the best Badugi hand and five cards are used to determine the triple draw hand. During each of three drawing rounds, players can trade zero to five cards from their hands for new ones from the deck.
Draw poker is any poker variant in which each player is dealt a complete hand before the first betting round, and then develops the hand for later rounds by replacing, or "drawing", cards.














