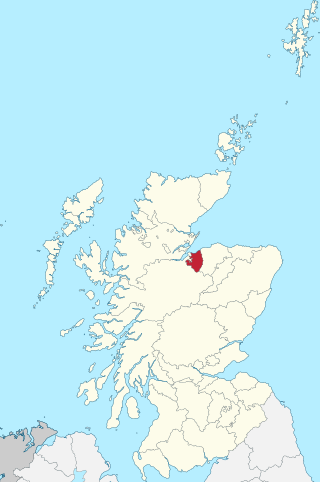
The County of Nairn, or Nairnshire, is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. The county was named after Nairn, its only town. The county was used for local government until 1975 when the area was redesignated as the Nairn District, one of the eight districts of the two-tier Highland region. Nairn district was abolished in 1996 when Highland became a single-tier council area.

Edin's Hall Broch is a 2nd-century broch near Duns in the Borders of Scotland. It is one of very few brochs found in southern Scotland. It is roughly 28 metres in diameter.

The Grianan of Aileach, sometimes anglicised as Greenan Ely or Greenan Fort, is a hillfort atop the 244 metres (801 ft) high Greenan Mountain at Inishowen in County Donegal, Ireland. The main structure is a 19th-century reconstruction of a stone ringfort, thought to have been built by the Northern Uí Néill, in the sixth or seventh century CE; although there is evidence that the site had been in use before the fort was built. It has been identified as the seat of the Kingdom of Ailech and one of the royal sites of Gaelic Ireland. The wall is about 4.5 metres (15 ft) thick and 5 metres (16 ft) high. Inside it has three terraces, which are linked by steps, and two long passages within it. Originally, there would have been buildings inside the ringfort. Just outside it are the remains of a well and a tumulus.

Dunstaffnage Castle is a partially ruined castle in Argyll and Bute, western Scotland. It lies 3 miles (5 km) NNE of Oban, situated on a platform of conglomerate rock on a promontory at the south-west of the entrance to Loch Etive, and is surrounded on three sides by the sea. The castle and the nearby chapel ruin have been a Historic Scotland property since 1958. Both are Scheduled Ancient Monuments.

The River Findhorn is one of the longest rivers in Scotland. Located in the north east, it flows into the Moray Firth on the north coast. It has one of the largest non-firth estuaries in Scotland.

Dunscaith Castle also known as Dun Scaich, Dun Sgathaich Castle and Tokavaig, is a ruined castle on the coast of the Isle of Skye, in the north-west of Scotland. It is located in the Parish of Sleat, in the Highland council area, and in the former county of Inverness-shire, at grid reference NG595120. Also called "Fortress of Shadows", it is the legendary home of the warrior maiden Scáthach, after whom it is named. It is protected as a scheduled monument.

Inverlochy Castle is a ruined, 13th-century castle near Inverlochy and Fort William, Highland, Scotland. The site of two battles, the castle remains largely unchanged since its construction. It is now in the care of Historic Environment Scotland.

Humbleton Hill is a hill in Northumberland, England, about 1.5 miles (2.4 km) west of Wooler.
Kirkmaiden is a parish in the Rhins of Galloway, the most southerly in Scotland; the present Church of Scotland parish has the same name as and is approximately coterminous with the original pre-Reformation parish.

Whiteadder Reservoir is a reservoir in East Lothian, Scotland, UK, in the Lammermuir Hills, 11 miles (18 km) north west of Duns in the Scottish Borders, and five miles (8 km) south east of Garvald. It was created to provide additional water facilities for East Lothian.

Dun Ringill is an Iron Age hill fort on the Strathaird peninsula on the island of Skye, Scotland. Further fortified in the Middle Ages, tradition holds that it was for several centuries the seat of Clan MacKinnon. It is located east of Kirkibost on the west shore of Loch Slapin.
An Caisteal is a hill fort located on the island of Coll. This island is one of the islands which make up the Inner Hebrides located on the west coast of Scotland. The fort is located at grid reference NM17185815. Located 1,200 yards (1.1 km) to the north-east of An Caisteal is Dùn Foulag. Dùn Foulag, located at grid reference NM17505908, was once thought to be a dun, though it is now considered to be only a naturally rocky knoll.
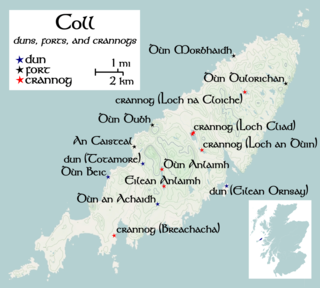
Totamore Dun is a dun located at grid reference NM17625713; near the settlement of Totamore, on the Inner Hebridean island of Coll. It occupies the summit of a rocky boss, on the eastern edge of the sand-hills located 300 metres north of Totamore. The dun is well protected by cliffs up to 19 metres ; although the approach from the north-northeast is almost level. The dun was protected by wall which would at one time have been about 3m thick; and would have run along the summit. This wall would have enclosed an area of about 25 by 20 metres. The current condition of the wall is, however, very poor and only a few fragments of it survive today. The entrance is 3.3 metres long by 1.2 metres wide; and is bordered on the northern side by a course of large blocks. These blocks measure up to 0.7 metres long and 0.4 metres high. Only a single facing-stone remains on the southern side of the entrance.

Craig Phadrig is a forested hill on the western edge of Inverness, Scotland. A hill fort on the summit is generally supposed to have been the base of the Pictish king Bridei mac Maelchon. The hill rises to 172 metres (564 ft) above sea level and overlooks the Beauly Firth to the north and the mouth of the River Ness to the north-east. The hill is currently owned and managed by Forestry and Land Scotland.

Torr a'Chaisteal is an Iron Age fort (dun), located about 1 mile northeast of the village of Sliddery, on the Isle of Arran in Scotland.
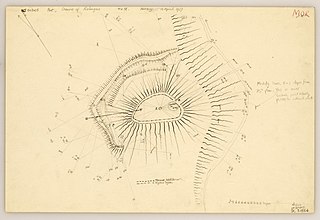
The Doune of Relugas is a hill fort located 9.25 kilometres (5.75 mi) south south west of Forres in Moray, Scotland. It is situated on a rocky knoll rising to approximately 400 feet (120 m) above ordnance datum and forming the south east part of the promontory at the confluence of the River Findhorn and the River Divie. The site commands an uninterrupted view of the valley of the Findhorn as far as Culbin Sands, 9 miles to the north on the shore of the Moray Firth.

The Knock of Alves is a small wooded hill that lies 3 miles (4.8 km) to the west of Elgin in Moray, Scotland, rising to 335 feet (102 m) above ordnance datum. Its summit is marked by York Tower, a 3-storey octagonal folly erected in 1827 to commemorate Prince Frederick, the Duke of York; and the Forteath Mausoleum, built in 1850 as the burial place of 7 members of the Forteath family of the nearby house of Newton.

Dunearn is a hill fort located 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) south south east of Nairn in Highland, Scotland. It is situated on a steep-sided hill called Doune rising to approximately 266 metres (873 ft) above ordnance datum just south of Dulsie Bridge in the parish of Ardclach.

Dun Skudiburgh is a prehistoric fort near Uig, Skye, Scotland.

White Meldon is a prehistoric site, a hillfort near the village of Lyne and about 4 miles (6 km) west of Peebles, in the Scottish Borders, Scotland. It is a Scheduled Monument.


















