
The U.S. House Committee on Homeland Security is a standing committee of the United States House of Representatives. Its responsibilities include U.S. security legislation and oversight of the Department of Homeland Security.

The military budget is the largest portion of the discretionary United States federal budget allocated to the Department of Defense, or more broadly, the portion of the budget that goes to any military-related expenditures. The military budget pays the salaries, training, and health care of uniformed and civilian personnel, maintains arms, equipment and facilities, funds operations, and develops and buys new items. The budget funds five branches of the U.S. military: the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Space Force.

United States Northern Command (USNORTHCOM) is one of eleven unified combatant commands of the United States Department of Defense. The command is tasked with providing military support for non-military authorities in the U.S., and protecting the territory and national interests of the United States within the continental United States, Puerto Rico, Canada, Mexico, The Bahamas, and the air, land and sea approaches to these areas. It is the U.S. military command which, if applicable, would be the primary defender against an invasion of the U.S.
The Small Business Innovation Research program is a U.S. government funding program, coordinated by the Small Business Administration, intended to help certain small businesses conduct research and development (R&D). Funding takes the form of contracts or grants. The recipient projects must have the potential for commercialization and must meet specific U.S. government R&D needs.

The 110th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, between January 3, 2007, and January 3, 2009, during the last two years of the Presidency of George W. Bush. It was composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The apportionment of seats in the House was based on the 2000 U.S. Census.
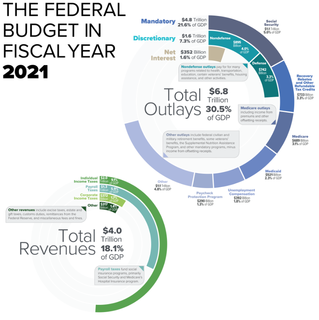
The United States federal budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. It has reported that large budget deficits over the next 30 years are projected to drive federal debt held by the public to unprecedented levels—from 98 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020 to 195 percent by 2050.
The National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) is the name for each of a series of United States federal laws specifying the annual budget and expenditures of the U.S. Department of Defense. The first NDAA was passed in 1961. The U.S. Congress oversees the defense budget primarily through two yearly bills: the National Defense Authorization Act and defense appropriations bills. The authorization bill is the jurisdiction of the Senate Armed Services Committee and House Armed Services Committee and determines the agencies responsible for defense, establishes recommended funding levels, and sets the policies under which money will be spent. The appropriations bill provides funds.

The United States Department of Defense is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national security and the United States Armed Forces. The DoD is the largest employer in the world, with over 1.4 million active-duty service members as of 2021. More employees include over 826,000 National Guard and reservists from the armed forces, and over 732,000 civilians bringing the total to over 2.8 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the DoD's stated mission is to provide "the military forces needed to deter war and ensure our nation's security".
The 2008 United States Federal Budget began as a proposal by President George W. Bush to fund government operations for October 1, 2007 – September 30, 2008. The requested budget was submitted to the 110th Congress on February 5, 2007.
The United States federal budget for fiscal year 2009 began as a spending request submitted by President George W. Bush to the 110th Congress. The final resolution written and submitted by the 110th Congress to be forwarded to the President was approved by the House on June 5, 2008.

Jeffrey Darren Duncan is an American politician who has been the United States representative for South Carolina's 3rd congressional district since 2011. A Republican, Duncan previously served as a member of the South Carolina House of Representatives.
The National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) for Fiscal Year 2013 is a United States federal law which specifies the budget and expenditures of the United States Department of Defense for fiscal year 2013. The full title is An Act to Authorize Appropriations for fiscal year 2013 for military activities of the Department of Defense, for military construction, and for defense activities of the Department of Energy, to prescribe military personnel strengths for such fiscal year, and for other purposes. This law has been assigned the number PL 112–239.
Budget sequestration is a provision of United States law that causes an across-the-board reduction in certain kinds of spending included in the federal budget. Sequestration involves setting a hard cap on the amount of government spending within broadly defined categories; if Congress enacts annual appropriations legislation that exceeds these caps, an across-the-board spending cut is automatically imposed on these categories, affecting all departments and programs by an equal percentage. The amount exceeding the budget limit is held back by the Treasury and not transferred to the agencies specified in the appropriation bills. The word sequestration was derived from a legal term referring to the seizing of property by an agent of the court, to prevent destruction or harm, while any dispute over said property is resolved in court.

The Military Construction and Veterans Affairs, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, 2014 is an appropriations bill that was introduced into the United States House of Representatives during the 113th United States Congress. The bill would appropriate money to various government agencies related to the United States Department of Defense and the United States Department of Veterans Affairs. This funding would be used during fiscal year 2014, which ends September 30, 2014. According to its committee report, "the purpose of the bill is to support our military and their families and provide the benefits and medical care that our veterans have earned for their service." The report also indicated that the Committee had made its decisions with the national debt and budget deficit in mind.

The Department of State Operations and Embassy Security Authorization Act, Fiscal Year 2014 is a bill that was introduced in the United States House of Representatives during the 113th United States Congress. The bill would authorize $17,573,992,000 to be appropriated to improve the security of U.S. Embassies throughout the world.

The United States Customs and Border Protection Authorization Act is a bill that would authorize the Customs and Border Protection (CBP) and its mission and direct the CBP in the United States Department of Homeland Security to establish standard procedures for addressing complaints made against CBP employees and to enhance training for CBP officers and agents.

The Carl Levin and Howard P. "Buck" McKeon National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2015 was a National Defense Authorization Act. According to the House Armed Services Committee, which oversaw the legislation, the bill would be "the comprehensive legislation to authorize the budget authority of the Department of Defense and the national security programs of the Department of Energy." The total appropriations that are authorized amount to approximately $600 billion for fiscal year 2015.

The Intelligence Authorization Act for Fiscal Years 2014 and 2015 is a bill that authorizes different intelligence agencies and their activities in fiscal years 2014 and 2015. The total spending authorized by the bill is classified, but estimates based on intelligence leaks made by Edward Snowden indicate that the budget could be approximately $50 billion.
Every year, the United States Congress is responsible for writing, passing, reconciling, and submitting to the President of the United States a series of appropriations bills that appropriate money to specific federal government departments, agencies, and programs for their use to operate in the subsequent fiscal year. The money provides funding for operations, personnel, equipment, and activities. In 2014, Congress was responsible for passing the appropriations bills that would fund the federal government in fiscal year 2015, which runs from October 1, 2014 to September 30, 2015.

The John S. McCain National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2019 is a United States federal law which specifies the budget, expenditures and policies of the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) for fiscal year 2019. It was signed by President Donald Trump during a ceremony in Fort Drum, New York on August 13, 2018.







