
Yeast extracts consist of the cell contents of yeast without the cell walls; they are used as food additives or flavorings, or as nutrients for bacterial culture media. They are often used to create savory flavors and umami taste sensations and can be found in a large variety of packaged food including frozen meals, crackers, snack foods, gravy, stock and more. They are rich in B vitamins. Yeast extracts and fermented foods contain glutamic acid, an amino acid which adds an umami flavor. Glutamic acid is found in meat, cheese, fungi and vegetables—such as broccoli and tomatoes. A number of other substances found in yeast extract provide aromas, some meat-like, when allowed to react under heat.

Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species.

Tequila is a distilled beverage made from the blue agave plant, primarily in the area surrounding the city of Tequila 65 km (40 mi) northwest of Guadalajara, and in the Jaliscan Highlands of the central western Mexican state of Jalisco.

Winemaking or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. There is evidence that suggests that the earliest wine production took place in Georgia and Iran around 6000 to 5000 B.C. The science of wine and winemaking is known as oenology. A winemaker may also be called a vintner. The growing of grapes is viticulture and there are many varieties of grapes.

Red wine is a type of wine made from dark-colored grape varieties. The color of the wine can range from intense violet, typical of young wines, through to brick red for mature wines and brown for older red wines. The juice from most purple grapes is greenish-white, the red color coming from anthocyan pigments present in the skin of the grape. Much of the red wine production process involves extraction of color and flavor components from the grape skin.

Malolactic conversion is a process in winemaking in which tart-tasting malic acid, naturally present in grape must, is converted to softer-tasting lactic acid. Malolactic fermentation is most often performed as a secondary fermentation shortly after the end of the primary fermentation, but can sometimes run concurrently with it. The process is standard for most red wine production and common for some white grape varieties such as Chardonnay, where it can impart a "buttery" flavor from diacetyl, a byproduct of the reaction.

Kilju is the Finnish word for home made alcoholic beverage typically made of sugar, yeast, and water.

Maceration is the winemaking process where the phenolic materials of the grape—tannins, coloring agents (anthocyanins) and flavor compounds—are leached from the grape skins, seeds and stems into the must. To macerate is to soften by soaking, and maceration is the process by which the red wine receives its red color, since raw grape juice is clear-grayish in color. In the production of white wines, maceration is either avoided or allowed only in very limited manner in the form of a short amount of skin contact with the juice prior to pressing. This is more common in the production of varietals with less natural flavor and body structure like Sauvignon blanc and Sémillon. For Rosé, red wine grapes are allowed some maceration between the skins and must, but not to the extent of red wine production.

Arrack is a distilled alcoholic drink typically produced in India, Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia, made from the fermented sap of coconut flowers or sugarcane, and also with grain or fruit depending upon the country of origin. It is sometimes spelled arak, or simply referred to as 'rack or 'rak. It is not to be confused with the anise-flavored distilled spirit called arak or araq. In many parts of India arrack is colloquially known as "desi daru".
Industrial fermentation is the intentional use of fermentation in manufacturing processes. In addition to the mass production of fermented foods and drinks, industrial fermentation has widespread applications in chemical industry. Commodity chemicals, such as acetic acid, citric acid, and ethanol are made by fermentation. Moreover, nearly all commercially produced industrial enzymes, such as lipase, invertase and rennet, are made by fermentation with genetically modified microbes. In some cases, production of biomass itself is the objective, as is the case for single-cell proteins, baker's yeast, and starter cultures for lactic acid bacteria used in cheesemaking.

A stuck fermentation occurs in brewing beer or winemaking when the yeast become dormant before the fermentation has completed. Unlike an "arrested fermentation" where the winemaker intentionally stops fermentation, a stuck fermentation is an unintentional and unwanted occurrence that can lead to the wine being spoiled by bacteria and oxidation. There are several potential causes of a stuck fermentation; the most common are excessively high temperatures killing off the yeast, or a must deficient in the nitrogen food source needed for the yeast to thrive. Once the fermentation is stuck, it is very difficult to restart due to a chemical compound released by dying yeast cells that inhibit the future growth of yeast cells in the batch. Winemakers often take several steps to limit the possibility of a stuck fermentation occurring, such as adding nitrogen to the must in the form of diammonium phosphate or using cultured yeast with a high temperature and alcohol tolerance. These steps will each have their own subtle or dramatic effect on the resulting flavors and quality of the wine.

Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substances through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is broadly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food production, it may more broadly refer to any process in which the activity of microorganisms brings about a desirable change to a foodstuff or beverage. The science of fermentation is known as zymology.
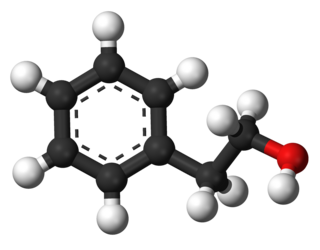
Phenethyl alcohol, or 2-phenylethanol, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2CH2OH. It is a colourless liquid with a pleasant floral odor. It occurs widely in nature, being found in a variety of essential oils. It is slightly soluble in water, but miscible with most organic solvents. The molecule of phenethyl alcohol consists of a phenethyl group attached to a hydroxyl group.

The process of fermentation in winemaking turns grape juice into an alcoholic beverage. During fermentation, yeasts transform sugars present in the juice into ethanol and carbon dioxide. In winemaking, the temperature and speed of fermentation are important considerations as well as the levels of oxygen present in the must at the start of the fermentation. The risk of stuck fermentation and the development of several wine faults can also occur during this stage, which can last anywhere from 5 to 14 days for primary fermentation and potentially another 5 to 10 days for a secondary fermentation. Fermentation may be done in stainless steel tanks, which is common with many white wines like Riesling, in an open wooden vat, inside a wine barrel and inside the wine bottle itself as in the production of many sparkling wines.

Lychee wine is a full-bodied Chinese dessert wine made of 100% lychee fruit. This wine has a golden colour and rich, sweet taste. It is usually served ice cold, either straight up or on the rocks with food. Lychee wine is believed to pair better with shellfish and Asian cuisine than with heavier meat dishes. This refreshing beverage can also be used as a cocktail mixer paired with other spirits.

Rum is a liquor made by fermenting and then distilling sugarcane molasses or sugarcane juice. The distillate, a clear liquid, is often aged in barrels of oak. While associated with the Caribbean due to its Barbadian origin, rum is nowadays produced in nearly every major sugar-producing region of the world, such as the Philippines, where Tanduay Distillers, the largest producer of rum worldwide, has its headquarters.

Cider is an alcoholic beverage made from the fermented juice of apples. Cider is widely available in the United Kingdom and Ireland. The UK has the world's highest per capita consumption, as well as the largest cider-producing companies. Ciders from the South West of England are generally higher in alcoholic content. Cider is also popular in many Commonwealth countries, such as India, South Africa, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand. As well as the UK and its former colonies, cider is popular in Portugal, France, Friuli, and northern Spain. Germany also has its own types of cider with Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse producing a particularly tart version known as Apfelwein. In the U.S. and Canada, varieties of alcoholic cider are often called hard cider to distinguish it from non-alcoholic apple cider or "sweet cider", also made from apples. In Canada, cider cannot contain less than 2.5% or over 13% absolute alcohol by volume.
This glossary of winemaking terms lists some of terms and definitions involved in making wine, fruit wine, and mead.

The role of yeast in winemaking is the most important element that distinguishes wine from fruit juice. In the absence of oxygen, yeast converts the sugars of the fruit into alcohol and carbon dioxide through the process of fermentation. The more sugars in the grapes, the higher the potential alcohol level of the wine if the yeast are allowed to carry out fermentation to dryness. Sometimes winemakers will stop fermentation early in order to leave some residual sugars and sweetness in the wine such as with dessert wines. This can be achieved by dropping fermentation temperatures to the point where the yeast are inactive, sterile filtering the wine to remove the yeast or fortification with brandy or neutral spirits to kill off the yeast cells. If fermentation is unintentionally stopped, such as when the yeasts become exhausted of available nutrients and the wine has not yet reached dryness, this is considered a stuck fermentation.

Industrial microbiology is a branch of biotechnology that applies microbial sciences to create industrial products in mass quantities, often using microbial cell factories. There are multiple ways to manipulate a microorganism in order to increase maximum product yields. Introduction of mutations into an organism may be accomplished by introducing them to mutagens. Another way to increase production is by gene amplification, this is done by the use of plasmids, and vectors. The plasmids and/ or vectors are used to incorporate multiple copies of a specific gene that would allow more enzymes to be produced that eventually cause more product yield. The manipulation of organisms in order to yield a specific product has many applications to the real world like the production of some antibiotics, vitamins, enzymes, amino acids, solvents, alcohol and daily products. Microorganisms play a big role in the industry, with multiple ways to be used. Medicinally, microbes can be used for creating antibiotics in order to treat infection. Microbes can also be used for the food industry as well. Microbes are very useful in creating some of the mass produced products that are consumed by people. The chemical industry also uses microorganisms in order to synthesize amino acids and organic solvents. Microbes can also be used in an agricultural application for use as a biopesticide instead of using dangerous chemicals and or inoculants to help plant proliferation.

















