
Beer is an alcoholic beverage produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches from cereal grains—most commonly malted barley, although wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. The fermentation of the starch sugars in the wort produces ethanol and carbonation in the beer. Beer is one of the oldest alcoholic drinks in the world, the most widely consumed, and the third most popular drink after water and tea. Most modern beer is brewed with hops, which add bitterness and other flavours and act as a natural preservative and stabilising agent. Other flavouring agents, such as gruit, herbs, or fruits, may be included or used instead of hops. In commercial brewing, natural carbonation is often replaced with forced carbonation.

Brewing is the production of beer by steeping a starch source in water and fermenting the resulting sweet liquid with yeast. It may be done in a brewery by a commercial brewer, at home by a homebrewer, or communally. Brewing has taken place since around the 6th millennium BC, and archaeological evidence suggests that emerging civilizations, including ancient Egypt, China, and Mesopotamia, brewed beer. Since the nineteenth century the brewing industry has been part of most western economies.

In biochemistry, fermentation theory refers to the historical study of models of natural fermentation processes, especially alcoholic and lactic acid fermentation. Notable contributors to the theory include Justus Von Liebig and Louis Pasteur, the latter of whom developed a purely microbial basis for the fermentation process based on his experiments. Pasteur's work on fermentation later led to his development of the germ theory of disease, which put the concept of spontaneous generation to rest. Although the fermentation process had been used extensively throughout history prior to the origin of Pasteur's prevailing theories, the underlying biological and chemical processes were not fully understood. In the contemporary, fermentation is used in the production of various alcoholic beverages, foodstuffs, and medications.

Homebrewing is the brewing of beer or other alcoholic beverages on a small scale for personal, non-commercial purposes. Supplies, such as kits and fermentation tanks, can be purchased locally at specialty stores or online. Beer was brewed domestically for thousands of years before its commercial production, although its legality has varied according to local regulation. Homebrewing is closely related to the hobby of home distillation, the production of alcoholic spirits for personal consumption; however home distillation is generally more tightly regulated.

Traditional ginger beer is a sweetened and carbonated, usually non-alcoholic beverage. Historically it was produced by the natural fermentation of prepared ginger spice, yeast and sugar.

In brewing and distilling, mashing is the process of combining a mix of ground grains – typically malted barley with supplementary grains such as corn, sorghum, rye, or wheat with water and then heating the mixture. Mashing allows the enzymes in the malt to break down the starch in the grain into sugars, typically maltose to create a malty liquid called wort.
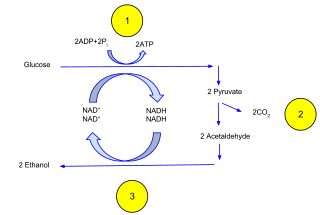
Ethanol fermentation, also called alcoholic fermentation, is a biological process which converts sugars such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose into cellular energy, producing ethanol and carbon dioxide as by-products. Because yeasts perform this conversion in the absence of oxygen, alcoholic fermentation is considered an anaerobic process. It also takes place in some species of fish where it provides energy when oxygen is scarce.

In brewing, adjuncts are unmalted grains or grain products used in brewing beer which supplement the main mash ingredient. This is often done with the intention of cutting costs, but sometimes also to create an additional feature, such as better foam retention, flavours or nutritional value or additives. Both solid and liquid adjuncts are commonly used.

Mash ingredients, mash bill, mashbill, or grain bill are the materials that brewers use to produce the wort that they then ferment into alcohol. Mashing is the act of creating and extracting fermentable and non-fermentable sugars and flavor components from grain by steeping it in hot water, and then letting it rest at specific temperature ranges to activate naturally occurring enzymes in the grain that convert starches to sugars. The sugars separate from the mash ingredients, and then yeast in the brewing process converts them to alcohol and other fermentation products.

Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substances through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, fermentation is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen, while in food production, it may more broadly refer to any process in which the activity of microorganisms brings about a desirable change to a foodstuff or beverage. The science of fermentation is known as zymology.
Wort is the liquid extracted from the mashing process during the brewing of beer or whisky. Wort contains the sugars, the most important being maltose and maltotriose, that will be fermented by the brewing yeast to produce alcohol. Wort also contains crucial amino acids to provide nitrogen to the yeast as well as more complex proteins contributing to beer head retention and flavour.

Symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) is a culinary symbiotic fermentation culture (starter) consisting of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), acetic acid bacteria (AAB), and yeast which arises in the preparation of sour foods and beverages such as kombucha. Beer and wine also undergo fermentation with yeast, but the lactic acid bacteria and acetic acid bacteria components unique to SCOBY are usually viewed as a source of spoilage rather than a desired addition. Both LAB and AAB enter on the surface of barley and malt in beer fermentation and grapes in wine fermentation; LAB lowers the pH of the beer/wine while AAB takes the ethanol produced from the yeast and oxidizes it further into vinegar, resulting in a sour taste and smell. AAB are also responsible for the formation of the cellulose SCOBY.

A brewery or brewing company is a business that makes and sells beer. The place at which beer is commercially made is either called a brewery or a beerhouse, where distinct sets of brewing equipment are called plant. The commercial brewing of beer has taken place since at least 2500 BC; in ancient Mesopotamia, brewers derived social sanction and divine protection from the goddess Ninkasi. Brewing was initially a cottage industry, with production taking place at home; by the ninth century, monasteries and farms would produce beer on a larger scale, selling the excess; and by the eleventh and twelfth centuries larger, dedicated breweries with eight to ten workers were being built.
Beer is produced through steeping a sugar source in water and then fermenting with yeast. Brewing has taken place since around the 6th millennium BC, and archeological evidence suggests that this technique was used in ancient Egypt. Descriptions of various beer recipes can be found in Sumerian writings, some of the oldest known writing of any sort. Brewing is done in a brewery by a brewer, and the brewing industry is part of most western economies. In 19th century Britain, technological discoveries and improvements such as Burtonisation and the Burton Union system significantly changed beer brewing.
When drinking beer, there are many factors to be considered. Principal among them are bitterness, the variety of flavours present in the beverage and their intensity, alcohol content, and colour. Standards for those characteristics allow a more objective and uniform determination to be made on the overall qualities of any beer.

Sour beer is beer which has an intentionally acidic, tart, or sour taste. Sour beer styles include Belgian lambics and Flanders red ale and German Gose and Berliner Weisse.

A tower brewery is a distinct form of brewery, identified by its external buildings being arranged in the form of a vertical tower.

Ale is a type of beer, brewed using a warm fermentation method. In medieval England, the term referred to a drink brewed without hops.

Huangjiu is a type of Chinese rice wine most popular in the Jiangnan area. Huangjiu is brewed by mixing steamed grains including rice, glutinous rice or millet with qū as starter culture, followed by saccharification and fermentation at around 13–18 °C (55–64 °F) for fortnights. Its alcohol content is typically 8% to 20%.
A beerfault or defect is a flavour deterioration caused by chemical changes of organic compounds in beer due to either improper production processes or improper storage. Chemicals that can cause flavour defects in beer are aldehydes, lipids, and sulfur compounds. Small fluctuations within fermentation byproducts can lead to the concentration of one or more of these chemicals falling outside a standard range, creating a flavour defect. It is also possible that during the malting process, microbial deterioration may occur, which leads to the loss of beer flavor.
















