
In transportation, platooning or flocking is a method for driving a group of vehicles together. It is meant to increase the capacity of roads via an automated highway system.

Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, which in turn may vary per application, and this spectrum of variance is often illustrated as a continuous energy profile. Non-transportation applications, such as industry, benefit from increased fuel efficiency, especially fossil fuel power plants or industries dealing with combustion, such as ammonia production during the Haber process.
Automatic vehicle location is a means for automatically determining and transmitting the geographic location of a vehicle. This vehicle location data, from one or more vehicles, may then be collected by a vehicle tracking system to manage an overview of vehicle travel. As of 2017, GPS technology has reached the point of having the transmitting device be smaller than the size of a human thumb, able to run 6 months or more between battery charges, easy to communicate with smartphones — all for less than $20 USD.
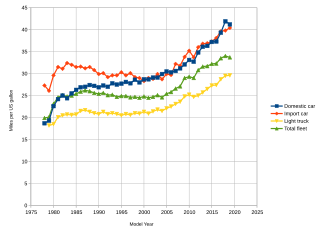
Corporate average fuel economy (CAFE) standards are regulations in the United States, first enacted by the United States Congress in 1975, after the 1973–74 Arab Oil Embargo, to improve the average fuel economy of cars and light trucks produced for sale in the United States. More recently, efficiency standards were developed and implemented for heavy-duty pickup trucks and commercial medium-duty and heavy-duty vehicles.

Telematics is an interdisciplinary field encompassing telecommunications, vehicular technologies, electrical engineering, and computer science. Telematics can involve any of the following:

A Natural Gas Vehicle (NGV) utilizes compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG) as an alternative fuel source. Distinguished from autogas vehicles fueled by liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), NGV's rely on methane combustion, resulting in cleaner emissions due to the removal of contaminants from the natural gas source.

An electric truck is a battery electric vehicle (BEV) designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work.
Fleet management is the management of:

A tire-pressure monitoring system (TPMS) monitors the air pressure inside the pneumatic tires on vehicles. A TPMS reports real-time tire-pressure information to the driver, using either a gauge, a pictogram display, or a simple low-pressure warning light. TPMS can be divided into two different types – direct (dTPMS) and indirect (iTPMS).

The fuel economy of an automobile relates to the distance traveled by a vehicle and the amount of fuel consumed. Consumption can be expressed in terms of the volume of fuel to travel a distance, or the distance traveled per unit volume of fuel consumed. Since fuel consumption of vehicles is a significant factor in air pollution, and since the importation of motor fuel can be a large part of a nation's foreign trade, many countries impose requirements for fuel economy.

The Volvo FH is a heavy truck range manufactured by the Swedish company Volvo Trucks. It was originally introduced in late 1993 as the FH12 and FH16. FH stands for Forward control High entry, where numbers denominate engine capacity in litres. The FH range is one of the most successful truck series ever having sold more than 400,000 units worldwide.
Fuel-management systems are used to maintain, control and monitor fuel consumption and stock in any type of industry that uses transport, including rail, road, water and air, as a means of business. Fuel-management systems are designed to effectively measure and manage the use of fuel within the transportation and construction industries. They are typically used for fleets of vehicles, including railway vehicles and aircraft, as well as any vehicle that requires fuel to operate. They employ various methods and technologies to monitor and track fuel inventories, fuel purchases and fuel dispensed. This information can be then stored in computerized systems and reports generated with data to inform management practices. Online fuel management is provided through the use of web portals to provide detailed fueling data, usually vis a vis the back end of an automated fuel-management system. This enables consumption control, cost analysis and tax accounting for fuel purchases.

Idle reduction describes technologies and practices that minimize the amount of time drivers idle their engines. Avoiding idling time has a multitude of benefits including: savings in fuel and maintenance costs, extending vehicle life, and reducing damaging emissions. An idling engine consumes only enough power to keep itself and its accessories running, therefore, producing no usable power to the drive train.
A Fleet Telematics System (FTS) allows the information exchange between a commercial vehicle fleet and their central authority, i.e., the dispatching office. A FTS typically consists of mobile Vehicle Systems (VS) and a stationary Fleet Communication System (FCS). The FCS may be a stand-alone application maintained by the motor carrier or an internet service running by the supplier of the system. The FCS usually includes a database in which all vehicle positions and messages are stored.

The trucking industry serves the American economy by transporting large quantities of raw materials, works in process, and finished goods over land—typically from manufacturing plants to retail distribution centers. Trucks are also used in the construction industry, two of which require dump trucks and portable concrete mixers to move the large amounts of rocks, dirt, concrete, and other building materials used in construction. Trucks in America are responsible for the majority of freight movement over land and are tools in the manufacturing, transportation, and warehousing industries.
A vehicle tracking system combines the use of automatic vehicle location in individual vehicles with software that collects these fleet data for a comprehensive picture of vehicle locations. Modern vehicle tracking systems commonly use GPS or GLONASS technology for locating the vehicle, but other types of automatic vehicle location technology can also be used. Vehicle information can be viewed on electronic maps via the Internet or specialized software. Urban public transit authorities are an increasingly common user of vehicle tracking systems, particularly in large cities.

The Tyre Label is a mark for motor vehicle tyres. Manufacturers of tyres for cars, light and heavy trucks must specify fuel consumption, wet grip and noise classification of every tyre sold in EU market starting in November 2012.
A connected car is a car that can communicate bidirectionally with other systems outside of the car. This connectivity can be used to provide services to passengers or to support or enhance self-driving functionality. For safety-critical applications, it is anticipated that cars will also be connected using dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) or cellular radios, operating in the FCC-granted 5.9 GHz band with very low latency.
Urban freight distribution is the system and process by which goods are collected, transported, and distributed within urban environments. The urban freight system can include seaports, airports, manufacturing facilities, and warehouse/distribution centers that are connected by a network of railroads, rail yards, pipelines, highways, and roadways that enable goods to get to their destinations.
Peloton Technology was an American automated and connected vehicle technology company established in 2011 and headquartered in Mountain View, California. It primarily developed a vehicle "platooning" system to enable pairs of trucks to operate at close following distances with a stated goal of improving safety and fuel efficiency. Peloton Technology was the first company to test a non-research commercial truck platooning system on public roads in the United States. In 2016 it publicly stated it would be the first company to offer a commercial platooning system for use by truck fleets in 2017. By mid-2018 that deadline had slipped to "by the end of 2018."











