
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of 4,233,255.3 km2 (1,634,469.0 sq mi) and an estimated total population of about 447 million. An internal single market has been established through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states have agreed to act as one. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market; enact legislation in justice and home affairs; and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development. Passport controls have been abolished for travel within the Schengen Area. The eurozone is a monetary union established in 1999, coming into full force in 2002, that is composed of the 19 EU member states that use the euro currency. The EU has often been described as a sui generis political entity with the characteristics of either a federation or confederation.
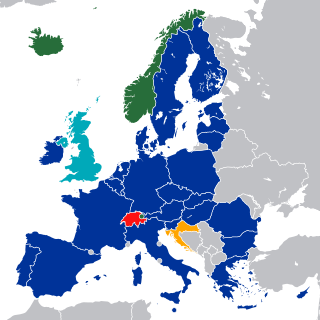
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the Agreement on the European Economic Area, an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Association. The EEA links the EU member states and three EFTA states into an internal market governed by the same basic rules. These rules aim to enable free movement of persons, goods, services, and capital within the European Single Market, including the freedom to choose residence in any country within this area. The EEA was established on 1 January 1994 upon entry into force of the EEA Agreement. The contracting parties are the EU, its member states, and Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway.

The eurozone, officially called the euro area, is a monetary union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender. The monetary authority of the eurozone is the Eurosystem. Eight members of the European Union continue to use their own national currencies, although most of them have agreed to adopt the euro in the future.

The European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) with responsibility for civil aviation safety. It carries out certification, regulation and standardisation and also performs investigation and monitoring. It collects and analyses safety data, drafts and advises on safety legislation and co-ordinates with similar organisations in other parts of the world.
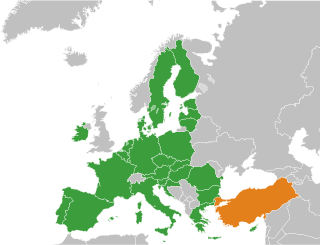
Turkey is negotiating its accession to the European Union (EU) as a member state, following its application to become a full member of the European Economic Community (EEC), the predecessor of the EU, on 14 April 1987.

The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member states of the European Union (EU). It is the second largest economy in the world in nominal terms, after the United States, and the third one in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms, after China and the United States. The European Union's GDP was estimated to be around $17.1 trillion (nominal) in 2020, representing around 1/6 of the global economy.
The UK rebate was a financial mechanism that reduced the United Kingdom's contribution to the EU budget in effect since 1985. It was a complex calculation which equated to a reduction of approximately 66% of the UK's net contribution – the amount paid by the UK into the EU budget less receipts from the EU budget. Based on a net contribution of €11.7 (£9.6) billion in 2016, the UK Treasury estimated the 2017 rebate amounted to €6.6 (£5.6) billion reducing the ultimate UK contribution for the 2017 budget to €10.4 (£8.9) billion. Although the rebate was not set in the EU treaties, it was negotiated as part of the Multiannual Financial Framework (MFF) every seven years and had to be unanimously agreed.

Withdrawal from the European Union is the legal and political process whereby an EU member state ceases to be a member of the Union. Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union (TEU) states that "Any Member State may decide to withdraw from the Union in accordance with its own constitutional requirements".

The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 member states that are signatories to the founding treaties of the union and thereby share in the privileges and obligations of membership. They have agreed by the treaties to share their own sovereignty through the institutions of the European Union in some, but not all, aspects of government. State governments must agree unanimously in the Council for the union to adopt some policies; for others, collective decisions are made by qualified majority voting. These obligations and sharing of sovereignty within the EU make it unique among international organisations, as it has established its own legal order which by the provisions of the founding treaties is both legally binding and supreme on all the member states. A founding principle of the union is the principle of subsidiarity, meaning that decisions are taken collectively if and only if they cannot realistically be taken individually.

The European driving licence is a driving licence issued by the member states of the European Economic Area (EEA); all 27 EU member states and three EFTA member states; Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway, which give shared features the various driving licence styles formerly in use. It is credit card-style with a photograph and a microchip. They were introduced to replace the 110 different plastic and paper driving licences of the 300 million drivers in the EEA. The main objective of the licence is to reduce the risk of fraud.

The European Union itself does not issue ordinary passports, but ordinary passport booklets issued by its 27 member states share a common format. This common format features a coloured cover emblazoned—in the official language(s) of the issuing country —with the title "European Union", followed by the name(s) of the member state, the heraldic "Arms" of the State concerned, the word "PASSPORT", together with the biometric passport symbol at the bottom centre of the front cover.
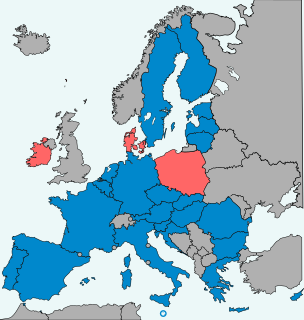
In general, the law of the European Union is valid in all of the twenty-seven European Union member states. However, occasionally member states negotiate certain opt-outs from legislation or treaties of the European Union, meaning they do not have to participate in certain policy areas. Currently, three states have such opt-outs: Denmark, the Republic of Ireland and Poland. The United Kingdom had four opt-outs before leaving the Union.

The Schengen Area is an area comprising 26 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. The area mostly functions as a single jurisdiction for international travel purposes, with a common visa policy. The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement signed in Schengen, Luxembourg.

There are five recognised candidates for membership of the European Union: Turkey, North Macedonia, Montenegro (2008), Albania (2009) and Serbia (2009). All have started accession negotiations. Kosovo and Bosnia and Herzegovina are recognised as potential candidates for membership by the EU. Bosnia and Herzegovina has formally submitted an application for membership, while Kosovo has a Stabilisation and Association Agreement (SAA) with the EU, which generally precedes the lodging of a membership application. Montenegro and Serbia, the most advanced candidates, are both expected to join earlier than the rest. While the others are progressing, Turkish talks are at an effective standstill. Additionally, Ukraine, Georgia and Moldova applied for membership in 2022. All three have Association Agreements with the EU, and the European Parliament has passed a resolution recognising their "European perspective".

The European Union (EU) has had permanent observer status at the United Nations (UN) since 1974, and has had enhanced participation rights since 2011. The EU itself does not have voting rights but it is represented alongside its 27 members, one of which, France, is a permanent member of the Security Council.

Relations between the European Union (EU) and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (UK) are governed, since 1 January 2021, by the EU–UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement (TCA).

Brexit was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020. The UK is the only sovereign country to have left the EU. The UK had been a member state of the union and its predecessor the European Communities (EC) since 1 January 1973. Following Brexit, EU law and the Court of Justice of the European Union no longer have primacy over British laws, except in select areas in relation to Northern Ireland. The European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2018 retains relevant EU law as domestic law, which the UK can now amend or repeal. Under the terms of the Brexit withdrawal agreement, Northern Ireland continues to participate in the European Single Market in relation to goods, and to be a de facto member of the EU Customs Union.

Between 2017 and 2019, representatives of the United Kingdom and the European Union negotiated the terms for Brexit, the planned withdrawal of the UK from the EU. These negotiations arose following the decision of the Parliament of the United Kingdom to invoke Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union, following the UK's EU membership referendum on 23 June 2016.

In 2016, the impact of Brexit on the European Union (EU) was expected to result in social and economic changes to the Union, but also longer term political and institutional shifts. The extent of these effects remain somewhat speculative until the precise terms of the United Kingdom's post-Brexit relationship with the EU becomes clear. With an end to British participation in the EU's policies on freedom of movement of goods, persons, services, and capital, and the European Union Customs Union, as well as sharing criminal intelligence and other matters, there is a clear impact with consequences for both institutions.

The COVID-19 pandemic and its spread in Europe has had significant effects on some major EU members countries and on European Union institutions, especially in the areas of finance, civil liberties, and relations between member states.













