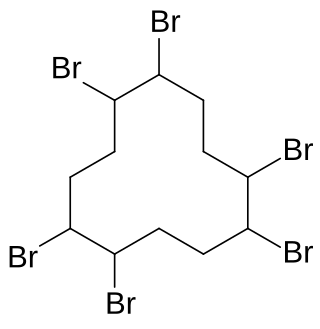
Hexabromocyclododecane is a brominated flame retardant. It consists of twelve carbon, eighteen hydrogen, and six bromine atoms tied to the ring. Its primary application is in extruded (XPS) and expanded (EPS) polystyrene foam used as thermal insulation in construction. Other uses are upholstered furniture, automobile interior textiles, car cushions and insulation blocks in trucks, packaging material, video cassette recorder housing, and electric and electronic equipment. According to UNEP, "HBCD is produced in China, Europe, Japan, and the USA. The known current annual production is approximately 28,000 tonnes per year. The main share of the market volume is used in Europe and China". Due to its persistence, toxicity, and ecotoxicity, the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants decided in May 2013 to list hexabromocyclododecane in Annex A to the convention with specific exemptions for production and use in expanded polystyrene and extruded polystyrene in buildings. Because HBCD has 16 possible stereo-isomers with different biological activities, the substance poses a difficult problem for manufacture and regulation.

Johnsons Air was an airline registered in Ghana and based at Kotoka International Airport in Accra, Ghana. Founded in 1996 by Farzin Azima, it operated ad hoc cargo services. The airline was one of eight airlines blacklisted in Belgium in 2005 due to operational safety concerns. In October 2006, the ban was extended to include all European Union communities. Johnsons Air meanwhile ceased operations.

Directive 2003/30/EC was a European Union directive for promoting the use of biofuels for EU transport. The directive entered into force in May 2003, and stipulated that national measures must be taken by countries across the EU aiming at replacing 5.75% of all transport fossil fuels with biofuels by 2010. The directive also called for an intermediate target of 2% by 31 December 2005. The target of 5.75% was to be met by 31 December 2010. These percentages were to be calculated on the basis of energy content of the fuel and were to apply to petrol and diesel fuel for transport purposes placed on the markets of member states. Member states were encouraged to take on national "indicative" targets in conformity with the overall target.

Asulam is a herbicide invented by May & Baker Ltd, internally called M&B9057, that is used in horticulture and agriculture to kill bracken and docks. It is also used as an antiviral agent. It is currently marketed, by United Phosphorus Ltd - UPL, as "Asulox" which contains 400 g/L of asulam sodium salt.
The Civil Mediation Council (CMC) is the recognised authority in England and Wales for all matters related to civil, commercial, workplace and other non-family mediation. It is the first point of contact for the Government, the judiciary, the legal profession and industry on mediation issues.

The Schengen Area is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished passports and many other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice policy of the European Union (EU), it mostly functions as a single jurisdiction under a common visa policy for international travel purposes. The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement and the 1990 Schengen Convention, both signed in Schengen, Luxembourg.
The European grid is a proposed, multipurpose Pan-European mapping standard. It is based on the ETRS89 coordinate reference system and the Lambert Azimuthal Equal-Area projection, with the centre of the projection at the point 52° N, 10° E and false easting: x0 = 4321000 m, false northing: y0 = 3210000 m .
The UIC identification marking for tractive stock is a standard for identifying train stock like locomotives that supply tractive force primarily in Europe. Since the beginning of 2007 locomotives or other traction units in Europe have been given a 12-digit number. Vehicle numbering is now governed by the Intergovernmental Organisation for International Carriage by Rail and in Technical Specifications for Interoperability (TSI) of the European Union, specifically the European Railway Agency's CR OPE TSI. This makes the locomotive clearly identifiable within Europe and parts of Asia and northern Africa.
Selenium yeast is a feed additive for livestock, used to increase the selenium content in their fodder. It is a form of selenium currently approved for human consumption in the EU and Britain. Inorganic forms of selenium are used in feeds. Since these products can be patented, producers can demand premium prices. It is produced by fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a selenium-rich media.
Ghiath Jeraatli has been a Syrian Minister of State since 2011.
The European Union's Third Energy Package is a legislative package for an internal gas and electricity market in the European Union. Its purpose is to further open up the gas and electricity markets in the European Union. The package was proposed by the European Commission in September 2007, and adopted by the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union in July 2009. It entered into force on 3 September 2009.

Council Implementing Regulation (EU) No. 282/2011 was adopted by the Council of the European Union on 15 March 2011. This was mainly because the terms and wording of Directive 2006/112/EC have been inconclusive in some cases. The Regulation provided new implementing measures for the VAT Directive. Especially due to the amendment of the VAT Directive itself and the consistent case-law of the European Court of Justice, the former Implementing Regulation (EC) No. 1777/2005 had to be recast and clarified in certain aspects. This Implementing Regulation became effective on 1 July 2011 and does not have to be transported into national legislation of the individual member states of the European Union and thus is directly applicable.

Directive on intra-EU-transfers of defence-related products is a European Union Directive with relevance for the European Economic Area. "Transfer" in this context means "any transmission or movement of a defence-related product from a supplier to a recipient in another Member State".
Cosmetovigilance is the ongoing and systematic monitoring of the safety of cosmetics in terms of human health. The aim is to detect adverse effects of cosmetic products, and to prevent adverse effects by taking appropriate measures. Regulations for cosmetic products primarily address the safety of products that may be used by large populations of healthy consumers. The identification and analysis of adverse effects related to cosmetic products is a process that is currently still, to a large extent, industry driven. It is the responsibility of manufacturers to determine that products and ingredients are safe before they are marketed, and then to collect reports of adverse reactions.
Creative Europe is a European Union programme for the cultural and creative sectors. In its first phase, going from 2014 to 2020, it had a budget of € 1.47 billion, which were expanded to € 2.44 billion in its second phase (2021-2027).

Passports of the EFTA member states are passports issued by the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) member states Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. EFTA is in this article used as a common name for these countries.
CEN/TC 434 is a technical body within the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) developing standards in the field of Electronic Invoicing.
The Directive on the accessibility of websites and mobile applications also known as Directive (EU) 2016/2102 was adopted by the EU in 2016. This Directive applies to public sector organizations of member states of the European Union. The goal was to ensure that all public sector organizations were accessible for the 80 million people with disabilities in the EU.
Nils Wahl is a Swedish jurist and lawyer who is currently one of the judges of the European Court of Justice since October 2019.





