
The Burgundians were an early Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared east in the middle Rhine region in the third century AD, and were later moved west into the Roman Empire, in Gaul. In the first and second centuries AD they, or a people with the same name, were mentioned by Roman writers living west of the Vistula river in the region of Germania which is now part of Poland.

The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era Germani who lived in both Germania and parts of the Roman empire, but also all Germanic speaking peoples from this era, irrespective of where they lived, most notably the Goths. Another term, ancient Germans, is considered problematic by many scholars since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. Although the first Roman descriptions of Germani involved tribes west of the Rhine, their homeland of Germania was portrayed as stretching east of the Rhine, to southern Scandinavia and the Vistula in the east, and to the upper Danube in the south. Other Germanic speakers, such as the Bastarnae and Goths, lived further east in what is now Moldova and Ukraine. The term Germani is generally only used to refer to historical peoples from the 1st to 4th centuries CE.

The Suebi were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names such as the Marcomanni, Quadi, Hermunduri, Semnones, and Lombards. New groupings formed later, such as the Alamanni and Bavarians, and two kingdoms in the Migration Period were simply referred to as Suebian.

The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, also called the Varus Disaster or Varian Disaster by Roman historians, was a major battle between Germanic tribes and the Roman Empire that took place somewhere near modern Kalkriese from September 8–11, 9 AD, when an alliance of Germanic peoples ambushed three Roman legions led by Publius Quinctilius Varus and their auxiliaries. The alliance was led by Arminius, a Germanic chieftain and officer of Varus's auxilia. Arminius had received Roman citizenship and a Roman military education; thus allowing him to deceive the Romans methodically and anticipate their tactical responses.

Arminius was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in AD 9, in which three Roman legions under the command of general and governor Publius Quinctilius Varus were destroyed. His victory at Teutoburg Forest precipitated the Roman Empire's permanent strategic withdrawal and the decolonisation of Germania Magna, and modern historians regard it as one of Imperial Rome's greatest defeats. As it prevented the Romanization of Germanic peoples east of the Rhine, it has also been considered one of the most decisive battles in history and a turning point in human history.

Germania, also more specifically called Magna Germania, Germania Libera, or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman provinces of Germania Inferior and Germania Superior, was a historical region in north-central Europe during the Roman era, which was associated by Roman authors with the Germanic peoples. According to Roman geographers, this region stretched roughly from the Rhine in the west to the Vistula in the east, and to the Upper Danube in the south, and the known parts of southern Scandinavia in the north. Archaeologically, these people correspond roughly to the Roman Iron Age of those regions.

Legio V Alaudae, sometimes also known as Legio V Gallica, was a legion of the Roman army founded in 52 BC by the general Gaius Julius Caesar. It was levied in Transalpine Gaul to fight the armies of Vercingetorix, and was the first Roman legion to comprise non-citizens. Historians disagree whether the legion was destroyed during the Batavian rebellion in AD 70, or during the First Battle of Tapae.

The Revolt of the Batavi took place in the Roman province of Germania Inferior between AD 69 and 70. It was an uprising against the Roman Empire started by the Batavi, a small but militarily powerful Germanic tribe that inhabited Batavia, on the delta of the river Rhine. They were soon joined by the Celtic tribes from Gallia Belgica and some Germanic tribes.

Germania Inferior was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the 4th century AD, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium.

Germania Superior was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon (Vesontio), Strasbourg (Argentoratum), Wiesbaden, and Germania Superior's capital, Mainz (Mogontiacum). It comprised the Middle Rhine, bordering on the Limes Germanicus, and on the Alpine province of Raetia to the south-east. Although it had been occupied militarily since the reign of Augustus, Germania Superior was not made into an official province until c. 85 AD.

Gallia Belgica was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.

Ariovistus was a leader of the Suebi and other allied Germanic peoples in the second quarter of the 1st century BC. He and his followers took part in a war in Gaul, assisting the Arverni and Sequani in defeating their rivals, the Aedui. They then settled in large numbers into conquered Gallic territory, in the Alsace region. They were defeated, however, in the Battle of Vosges and driven back over the Rhine in 58 BC by Julius Caesar.

This is a chronology of warfare between the Romans and various Germanic peoples. The nature of these wars varied through time between Roman conquest, Germanic uprisings, later Germanic invasions of the Western Roman Empire that started in the late second century BC, and more. The series of conflicts was one factor which led to the ultimate downfall of the Western Roman Empire in particular and ancient Rome in general in 476.

The Vangiones appear first in history as an ancient Germanic tribe of unknown provenance. They threw in their lot with Ariovistus in his bid of 58 BC to invade Gaul through the Doubs river valley and lost to Julius Caesar in a battle probably near Belfort. After some Celts evacuated the region in fear of the Suebi, the Vangiones, who had made a Roman peace, were allowed to settle among the Mediomatrici in northern Alsace.. They gradually assumed control of the Celtic city of Burbetomagus, later Worms.

The Battle of Vosges also referred to as the Battle of Vesontio was fought on September 14, 58 BC between the Germanic tribe of the Suebi, under the leadership of Ariovistus, and six Roman legions under the command of Gaius Julius Caesar. This encounter is the third major battle of the Gallic Wars. Germanic tribes crossed the Rhine, seeking a home in Gaul.

The contact between Germanic tribes and Romans can be divided into four aspects as defined by archaeologist Are Kolberg: the military, the trade, the gift, and the plunder aspect. All these aspects give probable answers as to how and why Roman objects got into Germanic hands, and why a vast amount of Roman objects still can be found as far north as Norway. It is noteworthy to understand how Roman objects brought elements of Roman culture with them, and how they to some extent shaped Germanic culture and identity.

For around 450 years, from around 55 BC to around 410 AD, the southern part of the Netherlands was integrated into the Roman Empire. During this time the Romans in the Netherlands had an enormous influence on the lives and culture of the people who lived in the Netherlands at the time and (indirectly) on the generations that followed.
The Germani cisrhenani, or "Left bank Germani", were a group of Germanic peoples who lived west of the Lower Rhine at the time of the Gallic Wars in the mid-1st century BC.
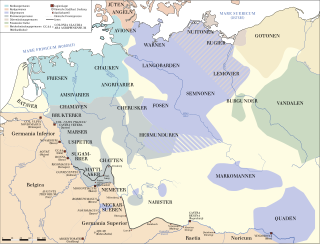
The Roman campaigns in Germania were a series of conflicts between the Germanic tribes and the Roman Empire. Tensions between the Germanic tribes and the Romans began as early as 17/16 BC with the Clades Lolliana, where the 5th Legion under Marcus Lollius was defeated by the tribes Sicambri, Usipetes, and Tencteri. Roman Emperor Augustus responded by rapidly developing military infrastructure across Gaul. His general, Nero Claudius Drusus, began building forts along the Rhine in 13 BC and launched a retaliatory campaign across the Rhine in 12 BC.
The Battle of the Angrivarian Wall was fought near Porta Westfalica, Germany in 16 AD between the Roman general Germanicus and an alliance of Germanic tribes commanded by Arminius. This battle followed immediately after the Battle of Idistaviso, and was supposedly sparked by Germanic outrage over the trophy erected on that prior battlefield by the Romans.


















