
Central Asia is a subregion of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the southwest and European Russia in the northwest to Western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Siberia in the north. It includes Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian suffix "-stan" in both respective native languages and most other languages. Central Asia borders Eastern Europe to the west, West Asia to the southwest, South Asia to the southeast, North Asia to the north, and East Asia to the east.

Kazakhstan, the largest country fully within the Eurasian Steppe, has been a historical crossroads and home to numerous different peoples, states and empires throughout history. Throughout history, peoples on the territory of modern Kazakhstan had nomadic lifestyle, which developed and influenced Kazakh culture.

Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital and most populous city. Tajikistan is bordered by Afghanistan to the south, Uzbekistan to the west, Kyrgyzstan to the north, and China to the east. It is separated from Pakistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor. It has a population of approximately ten million.

Tajikistan harkens to the Samanid Empire (819–999). The Tajik people came under Russian rule in the 1860s. The Basmachi revolt broke out in the wake of the Russian Revolution of 1917 and was quelled in the early 1920s during the Russian Civil War. In 1924, Tajikistan became an Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic of the Soviet Union, the Tajik ASSR, within Uzbekistan. In 1929, Tajikistan was made one of the component republics of the Soviet Union – Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic – and it kept that status until gaining independence 1991 after the dissolution of the Soviet Union.

The Demographics of Tajikistan is about the demography of the population of Tajikistan, including population growth, population density, ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population.

Uzbekistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia. It is itself surrounded by five landlocked countries: Kazakhstan to the north; Kyrgyzstan to the northeast; Tajikistan to the southeast; Afghanistan to the south, Turkmenistan to the south-west. Its capital and largest city is Tashkent. Uzbekistan is part of the Turkic languages world, as well as a member of the Organization of Turkic States. While the Uzbek language is the majority spoken language in Uzbekistan, Russian is widely used as an inter-ethnic tongue and in government. Islam is the majority religion in Uzbekistan, most Uzbeks being non-denominational Muslims. In ancient times it largely overlapped with the region known as Sogdia, and also with Bactria.
The Uzbeks are a Turkic ethnic group native to the wider Central Asian region, being among the largest Turkic ethnic groups in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakh and Karakalpak minorities, and also form minority groups in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Russia, and China. Uzbek diaspora communities also exist in Turkey, Saudi Arabia, United States, Ukraine, Pakistan, and other countries.

Tajiks are a Persian-speaking Iranian ethnic group native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Tajiks are the largest ethnicity in Tajikistan, and the second-largest in Afghanistan and Uzbekistan. It is worth noting that more Tajiks live in Afghanistan than Tajikistan. They speak varieties of Persian, a Western Iranian language. In Tajikistan, since the 1939 Soviet census, its small Pamiri and Yaghnobi ethnic groups are included as Tajiks. In China, the term is used to refer to its Pamiri ethnic groups, the Tajiks of Xinjiang, who speak the Eastern Iranian Pamiri languages. In Afghanistan, the Pamiris are counted as a separate ethnic group.

Samarkand or Samarqand is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central Asia. Samarkand is the capital of Samarqand Region and a district-level city, that includes the urban-type settlements Kimyogarlar, Farhod and Khishrav. With 551,700 inhabitants (2021), it is the third-largest city in Uzbekistan.

Turkestan, also spelled Turkistan, is a historical region in Central Asia corresponding to the regions of Transoxiana and East Turkestan (Xinjiang). The region is located in the northwest of modern day China and to the northwest of its borders, and extends directly to the east of the Caspian Sea. Turkestan is primarily inhabited by Turkic peoples, as well as Russian and Tajik-Persian minorities. Turkestan is subdivided into Afghan Turkestan, Russian Turkestan, and East Turkistan. Today, "Turkestan" mainly refers to Xinjiang, where Turkic peoples constitute more than half of the population.
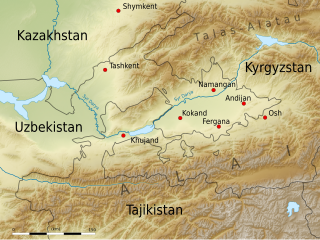
Fergana Valley is a valley in Central Asia, lying mostly in eastern Uzbekistan, extending into southern Kyrgyzstan and northern Tajikistan.

Tajik, Tajik Persian, Tajiki Persian, also called Tajiki, is the variety of Persian spoken in Tajikistan and Uzbekistan by Tajiks. It is closely related to neighbouring Dari of Afghanistan with which it forms a continuum of mutually intelligible varieties of the Persian language. Several scholars consider Tajik as a dialectal variety of Persian rather than a language on its own. The popularity of this conception of Tajik as a variety of Persian was such that, during the period in which Tajik intellectuals were trying to establish Tajik as a language separate from Persian, prominent intellectual Sadriddin Ayni counterargued that Tajik was not a "bastardised dialect" of Persian. The issue of whether Tajik and Persian are to be considered two dialects of a single language or two discrete languages has political aspects to it.

The Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic, also commonly known as Soviet Tajikistan, the Tajik SSR, TaSSR, or simply Tajikistan, was one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union which existed from 1929 to 1991 in Central Asia.

The national flag of Tajikistan was adopted in November 1992, replacing the flag of the Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic of 1953. The flag features Iranian colors in a horizontal tricolor of red, white, and green, with a yellow crown surmounted by an arc of seven stars at the centre. It has a width ratio of 2:3:2. The tricolor preserves the choice of colors in the former Tajik Soviet flag, as well as the 1:2 proportions.

Khujand, sometimes spelled Khodjent and formerly known as Leninabad from 1936 to 1991, is the second-largest city of Tajikistan and the capital of Tajikistan's northernmost Sughd province.

Sart is a name for the settled inhabitants of Central Asia which has had shifting meanings over the centuries.

The Tajik language has been written in three alphabets over the course of its history: an adaptation of the Perso-Arabic script, an adaptation of the Latin script and an adaptation of the Cyrillic script. Any script used specifically for Tajik may be referred to as the Tajik alphabet, which is written as алифбои тоҷикӣ in Cyrillic characters, الفبای تاجیکی with Perso-Arabic script and alifboji toçikī in Latin script.

The Pamiris are an Eastern Iranian ethnic group, native to Central Asia, living primarily in Tajikistan (Gorno-Badakhshan), Afghanistan (Badakhshan), Pakistan (Gilgit-Baltistan) and China. They speak a variety of different languages, amongst which languages of the Eastern Iranian Pamir language group stand out. The languages of the Shughni-Rushani group, alongside Wakhi, are the most widely spoken Pamiri languages.

Islam is the predominant religion in Tajikistan.
Tajikistan–Uzbekistan relations refers to the relations between the Republic of Tajikistan and the Republic of Uzbekistan.

















