
The Broads is a network of mostly navigable rivers and lakes in the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk. Although the terms "Norfolk Broads" and "Suffolk Broads" are correctly used to identify specific areas within the two counties respectively, the whole area is frequently referred to as the Norfolk Broads.

Barton Broad is a large lake that forms part of the River Ant which gives its name to a 164-hectare (410-acre) nature reserve north-east of Norwich in Norfolk. The reserve is owned and managed by the Norfolk Wildlife Trust. It is part of the Ant Broads and Marshes Site of Special Scientific Interest and National Nature Reserve, and part of it is in the Ant Marshes Nature Conservation Review site, Grade I. It is part of the Broadland Ramsar site and Special Protection Area, and The Broads Special Area of Conservation.

British Waterways, often shortened to BW, was a statutory corporation wholly owned by the government of the United Kingdom. It served as the navigation authority for the majority of canals and a number of rivers and docks in England, Scotland and Wales.

The River Ant is a tributary river of the River Bure in the county of Norfolk, England. It is 27 kilometres (17 mi) long, and has an overall drop of 27 metres from source to mouth. It is said that the Ant was formerly known as the River Smalea and that this is the origin of the name of the village of Smallburgh. The modern name is a back-formation from Antingham.

The North Walsham and Dilham Canal is a waterway in the English county of Norfolk. It was authorised by Parliament in 1812, but work on the construction of a canal which ran parallel to a branch of the River Ant did not start until 1825. It included six locks, which were sized to accommodate wherries, and was officially opened in August 1826. It was 8.7 miles (14.0 km) long and ran from two bone mills at Antingham to a junction with the River Ant at Smallburgh. It carried offal for the bone mills and agricultural products, as it proved cheaper to land coal on the beach at Mundesley and cart it overland than to use the canal.

The River Great Ouse is a river in England, the longest of several British rivers called "Ouse". From Syresham in Northamptonshire, the Great Ouse flows through Buckinghamshire, Bedfordshire, Cambridgeshire and Norfolk to drain into the Wash and the North Sea near Kings Lynn. Authorities disagree both on the river's source and its length, with one quoting 160 mi (260 km) and another 143 mi (230 km). Mostly flowing north and east, it is the fifth longest river in the United Kingdom. The Great Ouse has been historically important for commercial navigation, and for draining the low-lying region through which it flows; its best-known tributary is the Cam, which runs through Cambridge. Its lower course passes through drained wetlands and fens and has been extensively modified, or channelised, to relieve flooding and provide a better route for barge traffic. The unmodified river would have changed course regularly after floods.

The River Little Ouse, also known as the Brandon River, is a river in the east of England, a tributary of the River Great Ouse. For much of its length it defines the boundary between Norfolk and Suffolk.

The canals of the United Kingdom are a major part of the network of inland waterways in the United Kingdom. They have a varied history, from use for irrigation and transport, through becoming the focus of the Industrial Revolution, to today's role of recreational boating. Despite a period of abandonment, today the canal system in the United Kingdom is again increasing in use, with abandoned and derelict canals being reopened, and the construction of some new routes. Canals in England and Wales are maintained by navigation authorities. The biggest navigation authorities are the Canal & River Trust and the Environment Agency, but other canals are managed by companies, local authorities or charitable trusts.

The Inland Waterways Association (IWA) is a registered charity in the United Kingdom which was formed in 1946 to campaign for the conservation, use, maintenance, restoration and sensitive development of British canals and river navigations.

The South Forty-Foot Drain, also known as the Black Sluice Navigation, is the main channel for the land-drainage of the Black Sluice Level in the Lincolnshire Fens. It lies in eastern England between Guthram Gowt and the Black Sluice pumping station on The Haven, at Boston. The Drain has its origins in the 1630s, when the first scheme to make the Fen land available for agriculture was carried out by the Earl of Lindsey, and has been steadily improved since then. Water drained from the land entered The Haven by gravity at certain states of the tide until 1946, when the Black Sluice pumping station was commissioned.

The Middle Level Navigations are a network of waterways in England, primarily used for land drainage, which lie in The Fens between the Rivers Nene and Great Ouse, and between the cities of Peterborough and Cambridge. Most of the area through which they run is at or below sea level, and attempts to protect it from inundation have been carried out since 1480. The Middle Level was given its name by the Dutch Engineer Cornelius Vermuyden in 1642, who subsequently constructed several drainage channels to make the area suitable for agriculture. Water levels were always managed to allow navigation, and Commissioners were established in 1754 to maintain the waterways and collect tolls from commercial traffic.

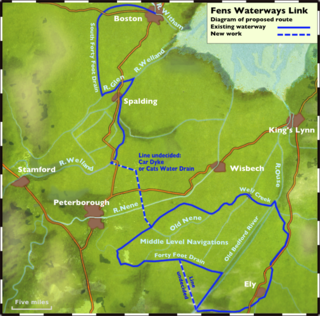
The Fens Waterways Link is a project to improve recreational boating opportunities in the counties of Cambridgeshire and Lincolnshire, England. By a combination of improvements to existing waterways and the construction of new links a circular route between Lincoln, Peterborough, Ely and Boston is planned. The project is being organised by the Environment Agency and financed from the Regional Development Agency and the European Union.
A navigation authority is a company or statutory body which is concerned with the management of a navigable canal or river.

The Norfolk Wherry Trust is a waterway society and UK registered charity number 1084156, based at Womack Water near Ludham in the Norfolk Broads, Norfolk, England.

The Wherry Yacht Charter Charitable Trust (WYC) is a waterway society and registered charity number 1096073, on the Norfolk and Suffolk Broads in East Anglia, England, UK. They operate and charter 5 historic wherries, those boats being 5 of the 8 remaining wherries.
The Fens and Anglian system is a collection of rivers in East Anglia in England that are navigable and for which the Environment Agency is the navigation authority.

The Cambridgeshire Lodes are a series of man-made waterways, believed to be Roman in origin, located in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. Bottisham, Swaffham Bulbeck, Reach, Burwell, Wicken and Monks Lodes all connect to the River Cam, while Soham and Cottenham Lodes connect to the River Great Ouse. All have been navigable historically, but some are no longer officially navigable.
















