
In number theory, the study of Diophantine approximation deals with the approximation of real numbers by rational numbers. It is named after Diophantus of Alexandria.
An approximation is anything that is intentionally similar but not exactly equal to something else.
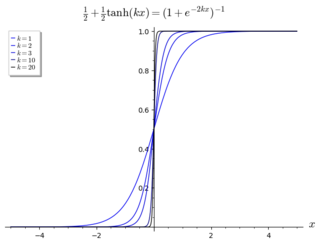
In general, a function approximation problem asks us to select a function among a well-defined class that closely matches ("approximates") a target function in a task-specific way. The need for function approximations arises in many branches of applied mathematics, and computer science in particular, such as predicting the growth of microbes in microbiology. Function approximations are used where theoretical models are unavailable or hard to compute.

In graph theory, an independent set, stable set, coclique or anticlique is a set of vertices in a graph, no two of which are adjacent. That is, it is a set of vertices such that for every two vertices in , there is no edge connecting the two. Equivalently, each edge in the graph has at most one endpoint in . A set is independent if and only if it is a clique in the graph's complement. The size of an independent set is the number of vertices it contains. Independent sets have also been called "internally stable sets", of which "stable set" is a shortening.
In computer science and operations research, approximation algorithms are efficient algorithms that find approximate solutions to optimization problems with provable guarantees on the distance of the returned solution to the optimal one. Approximation algorithms naturally arise in the field of theoretical computer science as a consequence of the widely believed P ≠ NP conjecture. Under this conjecture, a wide class of optimization problems cannot be solved exactly in polynomial time. The field of approximation algorithms, therefore, tries to understand how closely it is possible to approximate optimal solutions to such problems in polynomial time. In an overwhelming majority of the cases, the guarantee of such algorithms is a multiplicative one expressed as an approximation ratio or approximation factor i.e., the optimal solution is always guaranteed to be within a (predetermined) multiplicative factor of the returned solution. However, there are also many approximation algorithms that provide an additive guarantee on the quality of the returned solution. A notable example of an approximation algorithm that provides both is the classic approximation algorithm of Lenstra, Shmoys and Tardos for scheduling on unrelated parallel machines.
In computer science, a polynomial-time approximation scheme (PTAS) is a type of approximation algorithm for optimization problems.

Klaus Friedrich Roth was a German-born British mathematician who won the Fields Medal for proving Roth's theorem on the Diophantine approximation of algebraic numbers. He was also a winner of the De Morgan Medal and the Sylvester Medal, and a Fellow of the Royal Society.

In mathematics, approximation theory is concerned with how functions can best be approximated with simpler functions, and with quantitatively characterizing the errors introduced thereby. What is meant by best and simpler will depend on the application.
In computational complexity theory, the class APX is the set of NP optimization problems that allow polynomial-time approximation algorithms with approximation ratio bounded by a constant. In simple terms, problems in this class have efficient algorithms that can find an answer within some fixed multiplicative factor of the optimal answer.

In physics, physical optics, or wave optics, is the branch of optics that studies interference, diffraction, polarization, and other phenomena for which the ray approximation of geometric optics is not valid. This usage tends not to include effects such as quantum noise in optical communication, which is studied in the sub-branch of coherence theory.

The European Community number is a unique seven-digit identifier that was assigned to substances for regulatory purposes within the European Union by the European Commission. The EC Inventory comprises three individual inventories, EINECS, ELINCS and the NLP list.

George Francis Carrier was an engineer and physicist, and the T. Jefferson Coolidge Professor of Applied Mathematics Emeritus of Harvard University. He was particularly noted for his ability to intuitively model a physical system and then deduce an analytical solution. He worked especially in the modeling of fluid mechanics, combustion, and tsunamis.
In finance, a spread option is a type of option where the payoff is based on the difference in price between two underlying assets. For example, the two assets could be crude oil and heating oil; trading such an option might be of interest to oil refineries, whose profits are a function of the difference between these two prices. Spread options are generally traded over the counter, rather than on exchange.
Stochastic approximation methods are a family of iterative methods typically used for root-finding problems or for optimization problems. The recursive update rules of stochastic approximation methods can be used, among other things, for solving linear systems when the collected data is corrupted by noise, or for approximating extreme values of functions which cannot be computed directly, but only estimated via noisy observations.

The Journal of Approximation Theory is "devoted to advances in pure and applied approximation theory and related areas."
Highland East Cushitic or Burji-Sidamo is a branch of the Afroasiatic language family spoken in south-central Ethiopia. They are often grouped with Lowland East Cushitic, Dullay, and Yaaku as East Cushitic, but that group is not well defined. The most populous language is Sidama, with close to two million speakers.
Artificial neural networks are combinations of multiple simple mathematical functions that implement more complicated functions from (typically) real-valued vectors to real-valued vectors. The spaces of multivariate functions that can be implemented by a network are determined by the structure of the network, the set of simple functions, and its multiplicative parameters. A great deal of theoretical work has gone into characterizing these function spaces.
Pseudo- is a prefix used in a number of language, often to mark something as a fake or insincere version.
In computer science, hardness of approximation is a field that studies the algorithmic complexity of finding near-optimal solutions to optimization problems.








