Related Research Articles

Natural gas is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane (97%) in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and helium are also usually present. Methane is colorless and odorless, and the second largest greenhouse gas contributor to global climate change after carbon dioxide. Because natural gas is odorless, odorizers such as mercaptan are commonly added to it for safety so that leaks can be readily detected.

Reliance Industries Limited is an Indian multinational conglomerate headquartered in Mumbai. Its businesses include energy, petrochemicals, natural gas, retail, telecommunications, mass media, and textiles. Reliance is the largest public company in India by market capitalisation and revenue, and the 100th largest company worldwide. It is India's largest private tax payer and largest exporter, accounting for 7% of India's total merchandise exports. The company has relatively little free cash flow and high corporate debt.

Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volume of natural gas in the gaseous state at standard conditions for temperature and pressure.
Kakinada is the sixth largest city of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and serves as the district headquarters of the Kakinada District. It lies on the coast of the Bay of Bengal. J.N.T.U. College of Engineering Kakinada, established in 1946, is the oldest and popular Government college in the state of Andhra Pradesh. The First Polytechnic college of Andhra Pradesh, Andhra Polytechnic was established here in 1946. It was also the origin point of Buckingham Canal where goods used to be transported by boats during the British rule. It was once home for Asia's largest sea port. Many people from the city migrated from this sea port to countries like Burma, Mauritius, Fiji and various southeast Asian countries to work there as workers where they were called as Coringas.

Natural gas prices, as with other commodity prices, are mainly driven by supply and demand fundamentals. However, natural gas prices may also be linked to the price of crude oil and petroleum products, especially in continental Europe. Natural gas prices in the US had historically followed oil prices, but in the recent years, it has decoupled from oil and is now trending somewhat with coal prices.
The Maritimes and Northeast Pipeline is a natural gas transmission pipeline that runs from the Sable Offshore Energy Project (SOEP) gas plant in Goldboro, Nova Scotia, Canada to Dracut, Massachusetts, United States.
Canada's natural gas liquids industry dates back to the discovery of wet natural gas at Turner Valley, Alberta in 1914. The gas was less important than the natural gasoline - "skunk gas" it was called, because of its distinctive odour - that early producers extracted from it. That natural gas liquid (NGL) could be poured directly into an automobile's fuel tank.

The Petroleum or oil industry in Russia is one of the largest in the world. Russia has the largest reserves and was the largest exporter of natural gas. It has the sixth largest oil reserves, and is one of the largest producers of oil. It is the fourth largest energy user.

GAIL (India) Limited is a central public sector undertaking. It has the following business segments: natural gas, liquified natural gas, liquid hydrocarbon, liquefied petroleum gas transmission, petrochemicals, city gas distribution, renewable energy including solar & wind, exploration and production, GAILTEL and electricity generation. GAIL was given the Maharatna status on the 1 February 2013 by the Indian Government, a status which 11 other Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) have.

The Sullom Voe Terminal is an oil and gas terminal at Sullom Voe in the Shetland Islands of Scotland. It handles production from oilfields in the North Sea and East Shetland Basin and stores oil before it is transported by tanker.
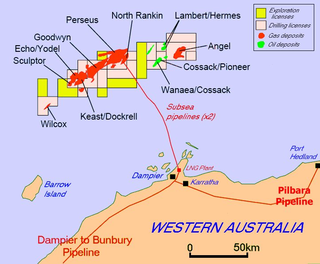
The North West Shelf Venture, situated in the north-west of Western Australia, is Australia's largest resource development project. It involves the extraction of petroleum at offshore production platforms, onshore processing and export of liquefied natural gas, and production of natural gas for industrial, commercial and domestic use within the state.
Sources include: Dow Jones (DJ), New York Times (NYT), Wall Street Journal (WSJ), and the Washington Post (WP).

Krishna Godavari Basin is a peri-cratonic passive margin basin in India. It is spread across more than 50,000 square kilometres in the Krishna River and Godavari River basins in Andhra Pradesh. The site is known for the D-6 block where Reliance Industries discovered the biggest natural gas reserves in India in 2003.
Niko Resources is an India- and South East Asia-focused oil and gas exploration and production company that shares ownership of many exploration and development properties with Komodo Energy and Reliance Industries. Though it holds exploration rights to 37,000,000 acres (150,000 km2) of land in 7 countries production currently (2011) only takes place in India and Bangladesh. Major acquisitions include a $310 million November 18, 2009 purchase of Black Gold Energy followed by the 2010 $37.6 million acquisition of Voyager Energy which expanded its presence in Trinidad.

Cairn India was an Indian oil and gas exploration and production company, headquartered in Gurgaon, India. The company was merged with Vedanta Limited.
Western Canadian Select (WCS) is a heavy sour blend of crude oil that is one of North America's largest heavy crude oil streams and, historically, its cheapest. It was established in December 2004 as a new heavy oil stream by EnCana (now Cenovus), Canadian Natural Resources, Petro-Canada (now Suncor) and Talisman Energy (now Repsol Oil & Gas Canada). It is composed mostly of bitumen blended with sweet synthetic and condensate diluents and 21 existing streams of both conventional and unconventional Alberta heavy crude oils at the large Husky Midstream General Partnership terminal in Hardisty, Alberta. Western Canadian Select—the benchmark for heavy, acidic (TAN <1.1) crudes—is one of many petroleum products from the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin oil sands. Calgary-based Husky Energy, now a subsidiary of Cenovus, had joined the initial four founders in 2015.

Gas Wars: Crony Capitalism and the Ambanis is a book written by Indian journalists Paranjoy Guha Thakurta, Subir Ghosh and Jyotirmoy Chaudhuri. The book was officially released on 15 April 2014. The book deals with the issue of irregularities in the determination of the price of natural gas in India.

Natural gas was the United States' largest source of energy production in 2016, representing 33 percent of all energy produced in the country. Natural gas has been the largest source of electrical generation in the United States since July 2015.
Rabi Narayan Bastia is an Indian geoscientist and the Global Head of Exploration at Lime Petroleum, Norway, known for his contributions in the hydrocarbon explorations at Krishna Godavari Basin (2002), at Mahanadi Basin (2003) and at Cauvery (2007). A non-executive director of Asian Oilfield Services Limited and the President at OilMax Energy, Bastia is a recipient of the Odisha Living Legend Award. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri, in 2007, for his contributions to Science and Technology.
The petroleum industry in India dates back to 1889 when the first oil deposits in the country were discovered near the town of Digboi in the state of Assam. The natural gas industry in India began in the 1960s with the discovery of gas fields in Assam and Maharashtra. As on 31 March 2018, India had estimated crude oil reserves of 594.49 million metric tonnes (Mt) and natural gas reserves of 1339.57 billion cubic metres of natural gas (BCM).
References
- ↑ "Brookfield to acquire Mukesh Ambani's gas pipeline company for Rs 13,000 crore" . Retrieved 5 June 2019.
- ↑ "China National Wins Reliance Gas Pipeline Contract in India". Bloomberg. 8 July 2014.
- ↑ "East-West gas pipeline - Stroytransgaz". Archived from the original on 10 November 2013. Retrieved 10 November 2013.
- ↑ "Gulf - East-West Gas Pipeline Project". Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2013.
- ↑ "About PIL | PIL - Pipeline Infrastructure Limited". pipelineinfra.com. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ↑ "::Welcome To RGTIL website::". Archived from the original on 10 November 2013. Retrieved 10 November 2013.
- ↑ Pathak, Kalpana (14 March 2019). "Brookfield to acquire RIL's East-West Pipeline for ₹13,000 crore". mint. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ↑ Crossing India’s Narmada River using HDD — Pipelines International — The international pipeline magazine
- ↑ "Reliance, BP to get govt capped price of USD 4.06 for new gas from KG-D6" . Retrieved 20 December 2020.
- ↑ Anne-Sophie Corbeau. "Natural Gas in India" (PDF). International Energy Agency. p. 27. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- ↑ "PNGRB scanning EWPL records after reports of laundering of $1.2 billion". The Financial Express. 11 April 2019. Retrieved 10 March 2021.