
A seamount is a large submarine landform that rises from the ocean floor without reaching the water surface, and thus is not an island, islet, or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to 1,000–4,000 m (3,300–13,100 ft) in height. They are defined by oceanographers as independent features that rise to at least 1,000 m (3,281 ft) above the seafloor, characteristically of conical form. The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. During their evolution over geologic time, the largest seamounts may reach the sea surface where wave action erodes the summit to form a flat surface. After they have subsided and sunk below the sea surface such flat-top seamounts are called "guyots" or "tablemounts".
The Zhongsha Islands is a Chinese term for a collection of two skerries, many entirely submerged banks, seamounts, and shoals in the South China Sea. There are in fact, no islands in the Macclesfield Bank, the main part of Zhongsha. The Scarborough Shoal, which consists of two skerries, is not contiguous with the Macclesfield Bank but Chinese sources treat them as one chain of geographical features. The whole of the region is claimed by both the PRC and the ROC, and various bits of the eastern parts are claimed by the Philippines. No country has constant control of the whole region, and there are disputes - for example, see Scarborough Shoal standoff.

Kamaʻehuakanaloa Seamount is an active submarine volcano about 22 mi (35 km) off the southeast coast of the island of Hawaii. The top of the seamount is about 3,200 ft (975 m) below sea level. This seamount is on the flank of Mauna Loa, the largest shield volcano on Earth. Kamaʻehuakanaloa is the newest volcano in the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain, a string of volcanoes that stretches about 3,900 mi (6,200 km) northwest of Kamaʻehuakanaloa. Unlike most active volcanoes in the Pacific Ocean that make up the active plate margins on the Pacific Ring of Fire, Kamaʻehuakanaloa and the other volcanoes of the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain are hotspot volcanoes and formed well away from the nearest plate boundary. Volcanoes in the Hawaiian Islands arise from the Hawaii hotspot, and as the youngest volcano in the chain, Kamaʻehuakanaloa is the only Hawaiian volcano in the deep submarine preshield stage of development.

Submarine volcanoes are underwater vents or fissures in the Earth's surface from which magma can erupt. Many submarine volcanoes are located near areas of tectonic plate formation, known as mid-ocean ridges. The volcanoes at mid-ocean ridges alone are estimated to account for 75% of the magma output on Earth. Although most submarine volcanoes are located in the depths of seas and oceans, some also exist in shallow water, and these can discharge material into the atmosphere during an eruption. The total number of submarine volcanoes is estimated to be over one million of which some 75,000 rise more than 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) above the seabed. Only 119 submarine volcanoes in Earth's oceans and seas are known to have erupted during the last 11,700 years.

Bowie Seamount, or SG̱aan Ḵinghlas in the Haida language, is a large submarine volcano in the northeastern Pacific Ocean, located 180 km (110 mi) west of Haida Gwaii, British Columbia, Canada. The seamount is also known as Bowie Bank. The English name for the feature is after William Bowie of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey.
Akiaki is a low coral atoll in the eastern area of the Tuamotu Archipelago, French Polynesia. Akiaki's nearest neighbor is Vahitahi, which is located 41 km to the southeast.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and introduction to Oceanography.

The Pitcairn hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located in the south-central Pacific Ocean. Over the past 11 million years, it has formed the Pitcairn-Gambier hotspot chain. It is responsible for creating the Pitcairn Islands and two large seamounts named Adams and Bounty, as well as atolls at Moruroa, Fangataufa and the Gambier Islands. The hotspot is currently located at Adams and Bounty, which are ~60 kilometers East-Southeast of Pitcairn Island.

The Newfoundland Seamounts are a group of seamounts offshore of Eastern Canada in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Named for the island of Newfoundland, this group of seamounts formed during the Cretaceous period and are poorly studied.
Suiyo Seamount is a seamount off the eastern coast of Japan, directly south of Torishima and Sofugan volcano at the southern tip of the Izu Islands. The volcano is one of the Shichiyo Seamounts, a small group of submarine volcanoes named after different days of the week.
Green Seamount is a small seamount off the western coast of Mexico. It and the nearby Red Seamount were visited in 1982 by an expedition using DSV Alvin, which observed the seamount's sedimentary composition, sulfur chimneys, and biology. Thus, Green Seamount is well-characterized for such a small feature.

Wordie Seamount is a seamount located in Bransfield Strait, Antarctica. The feature is named after James Wordie, geologist on Ernest Shackleton's 1914 expedition to Antarctica.
The João Valente Bank is a coral reef located between the islands of Boa Vista and Maio, Cape Verde. It stands on a seamount (guyot) about 100 meters under sea level, and rises up to 10 m below the surface. The seamount rises from about 1,000 meters. It is about 15 nmi long and 9 nmi wide, and breaking waves can already be observed at moderate wind. The reef has a high biodiversity of fish.

The Tasmantid hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located in the South Pacific Ocean. Due to plate tectonics the hotspot was under different parts of the seabed in the past. It was initially centred under what is now the southern Coral Sea 60 million years ago where the first Tasmantid volcano was created. As the Indo-Australian Plate continued to drift northwards the hotspot was positioned in the northern Tasman Sea 20 million years ago, eventually reaching its current location east of Tasmania in response to ongoing northward plate motion. The erupted volcanics are saturated tholeiitic to transitional alkali-olivine basalt.
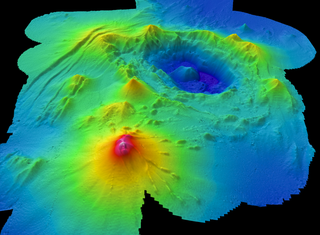
Monowai Seamount is a volcanic seamount to the north of New Zealand. It is formed by a large caldera and a volcanic cone just south-southeast from the caldera. The volcanic cone rises to depths of up to 100 metres (330 ft) but its depth varies with ongoing volcanic activity, including sector collapses and the growth of lava domes. The seamount and its volcanism were discovered after 1877, but only in 1980 was it named "Monowai" after a research ship of the same name.

Vailuluʻu is a volcanic seamount discovered in 1975. It rises from the sea floor to a depth of 593 m (1,946 ft) and is located between Taʻu and Rose islands at the eastern end of the Samoa hotspot chain. The basaltic seamount is considered to mark the current location of the Samoa hotspot. The summit of Vailuluʻu contains a 2 km wide, 400 m deep oval-shaped caldera. Two principal rift zones extend east and west from the summit, parallel to the trend of the Samoan hotspot. A third less prominent rift extends southeast of the summit.
Echo Bank is an underwater mountain, part of Canary Islands Seamount Province and located southwest of the Canary Islands. Of uncertain geologic origin, it is part of a larger cluster of submarine mountains and rises to a depth of 255 metres (837 ft) below sea level. It has a flat top, indicating that it formerly might have emerged from the sea.

Coral Patch Seamount is a seamount between Madeira and mainland Portugal in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is an elongated 120 kilometres (75 mi) long and 70 kilometres (43 mi) wide mountain that rises to a depth of about 645 metres (2,116 ft), with nine volcanic cones on its summit. It has steeper southern slopes and a gentle northern slope. To its west lies Ampére Seamount, and together with several neighbouring seamounts it is one of the Horseshoe Seamounts.

Nikkō Seamount is a submarine volcano in the Volcano Islands region of Japan. It is the southernmost volcano of Japan.

Daikoku Seamount is a submarine volcano located in the Northern Mariana Islands, in the western Pacific Ocean. It is part of a chain of volcanoes and seamounts that includes the more known Ahyi Seamount and NW Rota-1 seamounts and is situated about 690 km (429 mi) north of the island of Saipan. Daikoku Seamount rises over 2,500 m (8,202 ft) meters from the seafloor, with its summit about 323 m (1,060 ft) below sea level. Since its discovery, the seamount has been studied by several expeditions, including expeditions made by NOAA, using various scientific tools, such as sonar mapping and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs). Daikoku Seamount is known for its active hydrothermal vent system, which hosts diverse communities of deep-sea organisms, including tube worms, crabs, and snails. The seamount is also one of the only volcanoes along with Nikkō Seamount to have had a partially molten sulfur lake, which is usually a feature seen on Io than on Earth.














