Related Research Articles
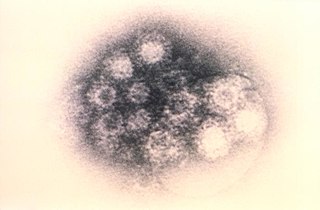
Coxsackie A virus (CAV) is a cytolytic Coxsackievirus of the Picornaviridae family, an enterovirus.

The rhinovirus is the most common viral infectious agent in humans and is the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in temperatures of 33–35 °C (91–95 °F), the temperatures found in the nose. Rhinoviruses belong to the genus Enterovirus in the family Picornaviridae.

Coxsackieviruses are a few related enteroviruses that belong to the Picornaviridae family of nonenveloped, linear, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, as well as its genus Enterovirus, which also includes poliovirus and echovirus. Enteroviruses are among the most common and important human pathogens, and ordinarily its members are transmitted by the fecal–oral route. Coxsackieviruses share many characteristics with poliovirus. With control of poliovirus infections in much of the world, more attention has been focused on understanding the nonpolio enteroviruses such as coxsackievirus.

Coxsackie B is a group of six serotypes of coxsackievirus (CVB1-CVB6), a pathogenic enterovirus, that trigger illness ranging from gastrointestinal distress to full-fledged pericarditis and myocarditis.

Hepatitis A is an infectious disease of the liver caused by Hepatovirus A (HAV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Many cases have few or no symptoms, especially in the young. The time between infection and symptoms, in those who develop them, is 2–6 weeks. When symptoms occur, they typically last 8 weeks and may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, jaundice, fever, and abdominal pain. Around 10–15% of people experience a recurrence of symptoms during the 6 months after the initial infection. Acute liver failure may rarely occur, with this being more common in the elderly.

Sedoreoviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Member viruses have a wide host range, including vertebrates, invertebrates, plants, protists and fungi. They lack lipid envelopes and package their segmented genome within multi-layered capsids. Lack of a lipid envelope has allowed three-dimensional structures of these large complex viruses to be obtained, revealing a structural and likely evolutionary relationship to the cystovirus family of bacteriophage. There are currently 97 species in this family, divided among 15 genera in two subfamilies. Reoviruses can affect the gastrointestinal system and respiratory tract. The name "reo-" is an acronym for "respiratory enteric orphan" viruses. The term "orphan virus" refers to the fact that some of these viruses have been observed not associated with any known disease. Even though viruses in the family Reoviridae have more recently been identified with various diseases, the original name is still used.

Picornaviruses are a group of related nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are viruses that represent a large family of small, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses with a 30 nm icosahedral capsid. The viruses in this family can cause a range of diseases including the common cold, poliomyelitis, meningitis, hepatitis, and paralysis.
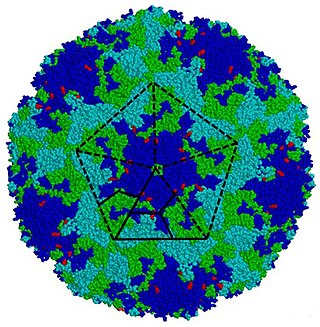
Enterovirus is a genus of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. Enteroviruses are named by their transmission-route through the intestine.
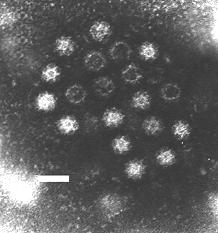
The Caliciviridae are a family of "small round structured" viruses, members of Class IV of the Baltimore scheme. Caliciviridae bear resemblance to enlarged picornavirus and was formerly a separate genus within the picornaviridae. They are positive-sense, single-stranded RNA which is not segmented. Thirteen species are placed in this family, divided among eleven genera. Diseases associated with this family include feline calicivirus, rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus, and Norwalk group of viruses (gastroenteritis). Caliciviruses naturally infect vertebrates, and have been found in a number of organisms such as humans, cattle, pigs, cats, chickens, reptiles, dolphins and amphibians. The caliciviruses have a simple construction and are not enveloped. The capsid appears hexagonal/spherical and has icosahedral symmetry with a diameter of 35–39 nm.

Orthoreovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Reoviridae, in the subfamily Spinareovirinae. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. There are ten species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include mild upper respiratory tract disease, gastroenteritis, and biliary atresia. Mammalian orthoreovirus 3 induces cell death preferentially in transformed cells and therefore displays inherent oncolytic properties.

Aphthovirus is a viral genus of the family Picornaviridae. Aphthoviruses infect split-hooved animals, and include the causative agent of foot-and-mouth disease, Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV). There are seven FMDV serotypes: A, O, C, SAT 1, SAT 2, SAT 3 and Asia 1, and four non-FMDV serotypes belonging to three additional species Bovine rhinitis A virus (BRAV), Bovine rhinitis B virus (BRBV) and Equine rhinitis A virus (ERAV).
Parechovirus B, formerly called the Ljungan virus, was first discovered in the mid-1990s after being isolated from a bank vole near the Ljungan river in Medelpad county, Sweden. It has since been established that Parechovirus B, which is also found in several places in Europe and America, causes serious illness in wild as well as laboratory animals. Several scientific articles have recently reported findings indicating that Parechovirus B is associated with malformations, intrauterine fetal death, and sudden infant death syndrome in humans. In addition, studies are being conducted worldwide to investigate the possible connection of the virus to diabetes, neurological and other illnesses in humans.
Erbovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Picornaviridae. Horses serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Erbovirus A. Diseases associated with this genus include: upper respiratory tract disease with viremia and fecal shedding. Viruses belonging to the genus Erbovirus have been isolated in horses with acute upper febrile respiratory disease. The structure of the Erbovirus virion is icosahedral, having a diameter of 27–30 nm.
Parechovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Picornaviridae. Humans, ferrets, and various rodents serve as natural hosts. The genus currently consists of six accepted species. Human parechoviruses may cause gastrointestinal or respiratory illness in infants, and they have been implicated in cases of myocarditis and encephalitis.
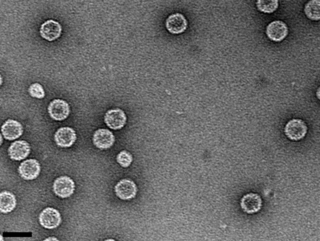
Picobirnavirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses. It is the only genus in the family Picobirnaviridae. Although amniotes, especially mammals, were thought to serve as hosts, it has been recently suggested that these viruses might infect bacteria and possibly some other invertebrates. There are three species in this genus. Associated symptoms include gastroenteritis in animals and humans, though the disease association is unclear.

Picornavirales is an order of viruses with vertebrate, invertebrate, protist and plant hosts. The name has a dual etymology. First, picorna- is an acronym for poliovirus, insensitivity to ether, coxsackievirus, orphan virus, rhinovirus, and ribonucleic acid. Secondly, pico-, meaning extremely small, combines with RNA to describe these very small RNA viruses. The order comprises viruses that historically are referred to as picorna-like viruses.
Tremovirus, also known epidemic tremor, is a virus genus belonging to the Picornaviridae family. The genus has two species, Tremovirus A, which is also called Avian encephalomyelitis virus, and Tremovirus B. The first avian picornavirus to have its genome sequenced, it causes epidemic tremor in chickens.
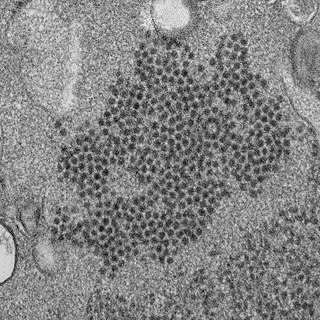
Enterovirus D68 (EV-D68) is a member of the Picornaviridae family, an enterovirus. First isolated in California in 1962 and once considered rare, it has been on a worldwide upswing in the 21st century. It is suspected of causing a polio-like disorder called acute flaccid myelitis (AFM).

Enterovirus D is a species of enterovirus which causes disease in humans. Five subtypes have been identified to date:
Echovirus 9 is a serotype of echovirus. When first discovered, it was labelled as a coxsackie A virus, A23. It was later discovered that A23 was an echovirus antigenically identical to the already-known echovirus 9.
References
- 1 2 Mahy, B. W. J. (26 February 2009). The Dictionary of Virology. Academic Press, 2009. pp. 218–220. ISBN 9780080920368.
- ↑ "ICTV Taxonomy history: Enterovirus B". talk.ictvonline.org. International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses . Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ↑ "ICTV Taxonomy history: Parechovirus A". talk.ictvonline.org. International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ↑ Jatin M. Vyas (December 2018). "ECHO virus". Medline Plus . Retrieved 10 April 2021.