
Kenorland is a hypothetical Neoarchean supercontinent. If it existed, it would have been one of the earliest known supercontinents on Earth. It is thought to have formed during the Neoarchaean Era c. 2.72 billion years ago by the accretion of Neoarchaean cratons and the formation of new continental crust. It comprised what later became Laurentia, Baltica, Western Australia and Kalaharia.
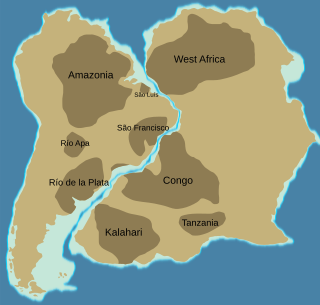
The Congo Craton, covered by the Palaeozoic-to-recent Congo Basin, is an ancient Precambrian craton that with four others makes up the modern continent of Africa. These cratons were formed between about 3.6 and 2.0 billion years ago and have been tectonically stable since that time. All of these cratons are bounded by younger fold belts formed between 2.0 billion and 300 million years ago.

The geology of Australia includes virtually all known rock types, spanning a geological time period of over 3.8 billion years, including some of the oldest rocks on earth. Australia is a continent situated on the Indo-Australian Plate.

The Gascoyne Complex is a terrane of Proterozoic granite and metamorphic rock in the central-western part of Western Australia. The complex outcrops at the exposed western end of the Capricorn Orogen, a 1,000 km-long arcuate belt of folded, faulted and metamorphosed rocks between two Archean cratons; the Pilbara craton to the north and the Yilgarn craton to the south. The Gascoyne Complex is thought to record the collision of these two different Archean continental fragments during the Capricorn Orogeny at 1830–1780 Ma.

The geology of the Rocky Mountains is that of a discontinuous series of mountain ranges with distinct geological origins. Collectively these make up the Rocky Mountains, a mountain system that stretches from Northern British Columbia through central New Mexico and which is part of the great mountain system known as the North American Cordillera.
This timeline of natural history summarizes significant geological and biological events from the formation of the Earth to the arrival of modern humans. Times are listed in millions of years, or megaanni (Ma).

The East Antarctic Shield or Craton is a cratonic rock body that covers 10.2 million square kilometers or roughly 73% of the continent of Antarctica. The shield is almost entirely buried by the East Antarctic Ice Sheet that has an average thickness of 2200 meters but reaches up to 4700 meters in some locations. East Antarctica is separated from West Antarctica by the 100–300 kilometer wide Transantarctic Mountains, which span nearly 3,500 kilometers from the Weddell Sea to the Ross Sea. The East Antarctic Shield is then divided into an extensive central craton that occupies most of the continental interior and various other marginal cratons that are exposed along the coast.

The geology of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is extremely old, on the order of several billion years for many rocks. The country spans the Congo Craton: a stable section of ancient continental crust, deformed and influenced by several different mountain building orogeny events, sedimentation, volcanism and the geologically recent effects of the East Africa Rift System in the east. The country's complicated tectonic past have yielded large deposits of gold, diamonds, coltan and other valuable minerals.

The geology of Arizona began to form in the Precambrian. Igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rock may have been much older, but was overwritten during the Yavapai and Mazatzal orogenies in the Proterozoic. The Grenville orogeny to the east caused Arizona to fill with sediments, shedding into a shallow sea. Limestone formed in the sea was metamorphosed by mafic intrusions. The Great Unconformity is a famous gap in the stratigraphic record, as Arizona experienced 900 million years of terrestrial conditions, except in isolated basins. The region oscillated between terrestrial and shallow ocean conditions during the Paleozoic as multi-cellular life became common and three major orogenies to the east shed sediments before North America became part of the supercontinent Pangaea. The breakup of Pangaea was accompanied by the subduction of the Farallon Plate, which drove volcanism during the Nevadan orogeny and the Sevier orogeny in the Mesozoic, which covered much of Arizona in volcanic debris and sediments. The Mid-Tertiary ignimbrite flare-up created smaller mountain ranges with extensive ash and lava in the Cenozoic, followed by the sinking of the Farallon slab in the mantle throughout the past 14 million years, which has created the Basin and Range Province. Arizona has extensive mineralization in veins, due to hydrothermal fluids and is notable for copper-gold porphyry, lead, zinc, rare minerals formed from copper enrichment and evaporites among other resources.

The geology of Sweden is the regional study of rocks, minerals, tectonics, natural resources and groundwater in the country. The oldest rocks in Sweden date to more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Precambrian. Complex orogeny mountain building events and other tectonic occurrences built up extensive metamorphic crystalline basement rock that often contains valuable metal deposits throughout much of the country. Metamorphism continued into the Paleozoic after the Snowball Earth glaciation as the continent Baltica collided with an island arc and then the continent Laurentia. Sedimentary rocks are most common in southern Sweden with thick sequences from the last 250 million years underlying Malmö and older marine sedimentary rocks forming the surface of Gotland.

The bedrock under the U.S. State of Colorado was assembled from island arcs accreted onto the edge of the ancient Wyoming Craton. The Sonoma orogeny uplifted the ancestral Rocky Mountains in parallel with the diversification of multicellular life. Shallow seas covered the regions, followed by the uplift current Rocky Mountains and intense volcanic activity. Colorado has thick sedimentary sequences with oil, gas and coal deposits, as well as base metals and other minerals.

The geology of the Czech Republic is very tectonically complex, split between the Western Carpathian Mountains and the Bohemian Massif.

The geology of Peru includes ancient Proterozoic rocks, Paleozoic and Mesozoic volcanic and sedimentary rocks, and numerous basins and the Andes Mountains formed in the Cenozoic.
The Glenburgh orogeny was a mountain building event in the Proterozoic from 2.0 to 1.96 billion years ago. The Glenburgh Terrane collided with the Yilgarn Craton, creating the Errabiddy Shear Zone. Mineral lineation from the orogeny is common although it is sometimes overprinted in greenschist by the later Capricorn orogeny.
The Barramundi orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now Australia between 1.88 and 1.84 billion years ago in the Proterozoic that affected Mount Isa and Pine Creek orogenic domains. Immediately before the orogeny, extension of Archean crust led to widespread basin formation. A large magmatic, granitoid forming event during the orogeny produced rocks with unusually similar chemistry. Other rocks include monzogranites, syenogranites, dacite and rhyolite rich in phenocrysts, ignimbrite sheets, and hornblende-tonalite.
The Albany-Fraser orogeny was an orogenic event which created the Albany-Fraser Orogen in what is now Australia between 2.63 and 1.16 billion years ago, during the late Archean and Proterozoic. Tectonic history developed from isotope dating suggests that the orogeny occurred as the combined North Australia Craton-West Australia Craton collided with the East Antarctic-South Australian Craton. The Kepa Kurl Booya Province, including its component zones, the Fraser Zone, Nornalup Zone and Biranup Zone represents the crystalline basement of the orogen. Numerous theories and hypotheses have been presented about the orogeny. For example, in 2011 geochronology dating of 1.71 to 1.65 billion year old granite and gabbro intrusions in the Biranup Zone suggested craton margin rocks rather than a previously interrupted small terrane wedged against the Yilgarn Craton. In other cases, researchers attempting to reconstruct the supercontinent Rodinia suggested a possible connection between Australia-Antarctica and the proto-North American continent Laurentia, but in 2003 paleomagnetic data from the Albany-Fraser orogeny suggested that Australia and Laurentia were at different latitudes.
The Capricorn orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now Western Australia, following the collision of the Pilbara Craton and the Glenburgh Terrane with the Yilgarn Craton during the Glenburgh orogeny. Spanning one billion years, the Capricorn orogeny is marked by widespread deformation and intracratonal reworking.
The Mangaroon orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now Western Australia between 1.68 and 1.62 billion years ago in the Proterozoic, preserved in the rocks of the large Gascoyne Province.











