
Grancalcin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GCA gene.

Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase with EF-hands 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPEF1 gene.

Nucleobindin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUCB2 gene.

Secretagogin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCGN gene.

45 kDa calcium-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDF4 gene.
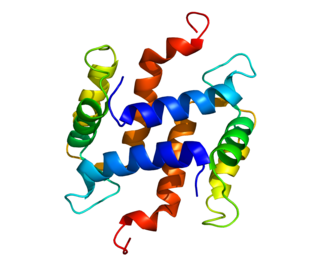
S100 calcium-binding protein A5 (S100A5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the S100A5 gene.

Kv channel-interacting protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNIP4 gene.

Calcium-binding protein 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALN1 gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
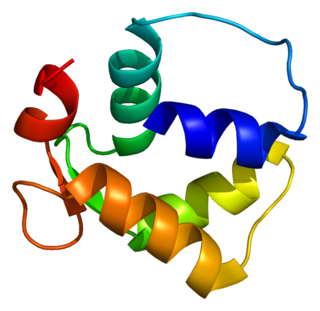
Centrin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CETN1 gene. It belongs to the centrin family of proteins.
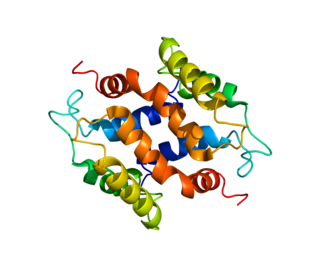
S100 calcium-binding protein A16 (S100A16) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the S100A16 gene.

Single-stranded DNA-binding protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSBP3 gene.

Reticulocalbin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RCN1 gene.

Reticulocalbin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RCN2 gene.

Polycystic kidney disease 2-like 2 protein (PKD2L2) also known as transient receptor potential polycystic 5 (TRPP5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PKD2L2 gene.

Calpain 6 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the CAPN6 gene.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase ID is a protein in humans that is encoded by the CAMK1D gene on chromosome 10.

EF-hand and coiled-coil domain containing 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EFCC1 gene.

EF-hand domain family member D2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EFHD2 gene.

Copine 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CPNE7 gene.

Protein phosphatase with EF-hand domain 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPEF2 gene.





















