
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Covering an area of 207,600 square kilometres (80,200 sq mi) and with a population of 9.2 million, Belarus is the 13th-largest and the 20th-most populous country in Europe. The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into seven regions. Minsk is the capital and largest city.

Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania shares land borders with Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and Russia to the southwest. It has a maritime border with Sweden to the west on the Baltic Sea. Lithuania covers an area of 65,300 km2 (25,200 sq mi), with a population of 2.8 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius; other major cities are Kaunas and Klaipėda. Lithuanians belong to the ethno-linguistic group of the Balts and speak Lithuanian, one of only a few living Baltic languages.
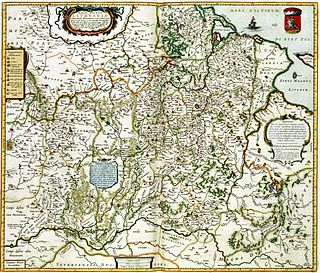
The history of Lithuania dates back to settlements founded many thousands of years ago, but the first written record of the name for the country dates back to 1009 AD. Lithuanians, one of the Baltic peoples, later conquered neighboring lands and established the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the 13th century. The Grand Duchy was a successful and lasting warrior state. It remained fiercely independent and was one of the last areas of Europe to adopt Christianity. A formidable power, it became the largest state in Europe in the 15th century through the conquest of large groups of East Slavs who resided in Ruthenia. In 1385, the Grand Duchy formed a dynastic union with Poland through the Union of Krewo. Later, the Union of Lublin (1569) created the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that lasted until 1795, when the last of the Partitions of Poland erased both Lithuania and Poland from the political map. After the dissolution, Lithuanians lived under the rule of the Russian Empire until the 20th century, although there were several major rebellions, especially in 1830–1831 and 1863.

The Lithuanian Armed Forces are the military of Lithuania. The Lithuanian Armed Forces consist of the Lithuanian Land Forces, the Lithuanian Naval Force and the Lithuanian Air Force. In wartime, the Lithuanian State Border Guard Service becomes part of the Lithuanian Armed Forces. A special security department handles VIP protection and communications security.

Vilnius is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 625,349 or 626,554 as of 2023. The population of Vilnius's functional urban area, which stretches beyond the city limits, is estimated at 718,507, while according to the Vilnius territorial health insurance fund, there were 753,875 permanent inhabitants as of November 2022 in Vilnius city and Vilnius district municipalities combined. Vilnius is situated in southeastern Lithuania and is the largest city in the Baltic states. It is the seat of Lithuania's national government and the Vilnius District Municipality.

Jogaila, later Władysław II Jagiełło was Grand Duke of Lithuania (1377–1434) and then King of Poland (1386–1434), first alongside his wife Jadwiga until 1399, and then sole ruler of Poland. Born a pagan, he converted to Catholicism in 1386 and was baptized as Władysław in Kraków, married the young Queen Jadwiga, and was crowned King of Poland as Władysław II Jagiełło. In 1387, he converted Lithuania to Catholicism. His own reign in Poland started in 1399, upon the death of Queen Jadwiga, lasted a further thirty-five years, and laid the foundation for the centuries-long Polish–Lithuanian union. He was a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty in Poland that bears his name and was previously also known as the Gediminid dynasty in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The dynasty ruled both states until 1572, and became one of the most influential dynasties in late medieval and early modern Europe. During his reign, the Polish-Lithuanian state was the largest state in the Christian world.
Lithuanian is an Eastern Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the official language of Lithuania and one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.8 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 200,000 speakers elsewhere.

Klaipėda is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. The capital of the eponymous county, it is the third largest city and the only major seaport in Lithuania.

Kaunas is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county in the Duchy of Trakai of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Trakai Palatinate since 1413. In the Russian Empire, it was the capital of the Kaunas Governorate from 1843 to 1915.

The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics.

The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost 1,000,000 km2 (400,000 sq mi) and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million. Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages.

The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lithuanians, who were at the time a polytheistic nation born from several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija.

The Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic, also known as Soviet Lithuania or simply Lithuania, was de facto one of the constituent republics of the USSR between 1940–1941 and 1944–1990. After 1946, its territory and borders mirrored those of today's Republic of Lithuania, with the exception of minor adjustments of the border with Belarus.

Lithuanians are a Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another million or two make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, United Kingdom, Brazil, Russia, and Canada. Their native language is Lithuanian, one of only two surviving members of the Baltic language family along with Latvian. According to the census conducted in 2021, 84.6% of the population of Lithuania identified themselves as Lithuanians, 6.5% as Poles, 5.0% as Russians, 1.0% as Belarusians, and 1.1% as members of other ethnic groups. Most Lithuanians belong to the Catholic Church, while the Lietuvininkai who lived in the northern part of East Prussia prior to World War II, were mostly Lutherans.

The territory of Lithuania is divided into 10 counties, all named after their capitals. The counties are divided into 60 municipalities : 9 city municipalities, 43 district municipalities and 8 municipalities. Each municipality is then divided into elderates. This division was created in 1994 and slightly modified in 2000.

The coat of arms of Lithuania consists of a mounted armoured knight holding a sword and shield, known as Vytis. Since the early 15th century, it has been Lithuania's official coat of arms and is one of the oldest European coats of arms. It is also known by other names in various languages, such as Waikymas, Pagaunė in the Lithuanian language or as Pogonia, Pogoń, Пагоня in the Polish, and Belarusian languages. Vytis is translatable as Chase, Pursuer, Knight or Horseman, similar to the Slavic vityaz. Historically – raitas senovės karžygys or in heraldry – raitas valdovas.
The Lithuania national football team represents Lithuania in international football and is controlled by the Lithuanian Football Federation, the governing body for football in Lithuania. They played their first match in 1923. In 1940, Lithuania was occupied by the Soviet Union; the country regained its independence in 1990 and played their first match thereafter against Georgia on 27 May of that year.
Lithuanian mythology is the mythology of Lithuanian polytheism, the religion of pre-Christian Lithuanians. Like other Indo-Europeans, ancient Lithuanians maintained a polytheistic mythology and religious structure. In pre-Christian Lithuania, mythology was a part of polytheistic religion; after Christianisation mythology survived mostly in folklore, customs and festive rituals. Lithuanian mythology is very close to the mythology of other Baltic nations – Prussians, Latvians, and is considered a part of Baltic mythology.

Lithuanian Jews or Litvaks are Jews with roots in the territory of the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The term is sometimes used to cover all Haredi Jews who follow a "Lithuanian" style of life and learning, whatever their ethnic background. The area where Lithuanian Jews lived is referred to in Yiddish as ליטע Lite, hence the Hebrew term Lita'im (לִיטָאִים).
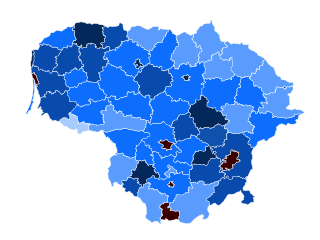
The COVID-19 pandemic in Lithuania is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Lithuania in February 2020. On 18 March 2020, the first domestic case was confirmed, the first infected being an immediate family member of a known case. The first cases of community spread were found in the country on 19 March and the first related death occurred on 20 March 2020.
















