The history of Lithuania dates back to settlements founded about 10,000 years ago, but the first written record of the name for the country dates back to 1009 AD. Lithuanians, one of the Baltic peoples, later conquered neighboring lands and established the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the 13th century. The Grand Duchy was a successful and lasting warrior state. It remained fiercely independent and was one of the last areas of Europe to adopt Christianity. A formidable power, it became the largest state in Europe in the 15th century spread from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea, through the conquest of large groups of East Slavs who resided in Ruthenia.

The Lithuanian Armed Forces are the military of Lithuania. The Lithuanian Armed Forces consist of the Lithuanian Land Forces, the Lithuanian Naval Force, the Lithuanian Air Force and the Lithuanian Special Operations Force. In wartime, the Lithuanian State Border Guard Service becomes part of the Lithuanian Armed Forces.

Vilnius, previously known in English as Vilna, is the capital of and largest city in Lithuania and the second-most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated July 2024 population was 605,270, and the Vilnius urban area has an estimated population of 708,627.

Jogaila, later Władysław II Jagiełło, was Grand Duke of Lithuania, later giving the position to his cousin Vytautas in exchange for the title of Supreme Duke of Lithuania (1401–1434) and then King of Poland (1386–1434), first alongside his wife Jadwiga until 1399, and then sole ruler of Poland. Born a Lithuanian polytheist, he converted to Catholicism in 1386 and was baptized as Ladislaus in Kraków, married the young Queen Jadwiga, and was crowned King of Poland as Władysław II Jagiełło. In 1387, he converted Lithuania to Catholicism. His own reign in Poland started in 1399, upon the death of Queen Jadwiga, lasted a further thirty-five years, and laid the foundation for the centuries-long Polish–Lithuanian union. He was a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty in Poland that bears his name and was previously also known as the Gediminid dynasty in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The dynasty ruled both states until 1572, and became one of the most influential dynasties in late medieval and early modern Europe.
Lithuanian is an East Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the language of Lithuanians and the official language of Lithuania as well as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are approximately 2.8 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 1 million speakers elsewhere. Around half a million inhabitants of Lithuania of non-Lithuanian background speak Lithuanian daily as a second language.

Klaipėda is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. It is the third largest city in Lithuania, the fifth largest city in the Baltic States and the capital of Klaipėda County, as well as the only major seaport in the country.

Kaunas is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius, the fourth largest city in the Baltic States and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county in the Duchy of Trakai of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Trakai Palatinate since 1413. In the Russian Empire, it was the capital of the Kaunas Governorate from 1843 to 1915.

The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics.

Poland–Lithuania, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and also referred to as the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth or the First Polish Republic, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost 1,000,000 km2 (400,000 sq mi) and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million. Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages, and Catholicism served as the state religion.

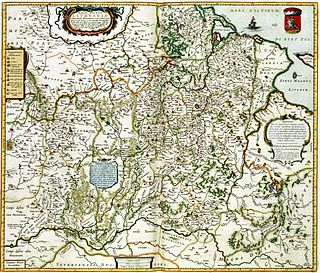
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 partitions of Poland–Lithuania. The state was founded by Lithuanians, who were at the time a polytheistic nation of several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija, which by 1440, became the largest European state controlling an area from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south.

The Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic, also known as Soviet Lithuania or simply Lithuania, was de facto one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union between 1940–1941 and 1944–1990. After 1946, its territory and borders mirrored those of today's Republic of Lithuania, with the exception of minor adjustments to its border with Belarus.

Lithuanians are a Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another two millions make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, United Kingdom, Brazil and Canada. Their native language is Lithuanian, one of only two surviving members of the Baltic language family along with Latvian. According to the census conducted in 2021, 84.6% of the population of Lithuania identified themselves as Lithuanians, 6.5% as Poles, 5.0% as Russians, 1.0% as Belarusians, and 1.1% as members of other ethnic groups. Most Lithuanians belong to the Catholic Church, while the Lietuvininkai who lived in the northern part of East Prussia prior to World War II, were mostly Lutherans.

The territory of Lithuania is divided into 10 counties, all named after their capitals. The counties are divided into 60 municipalities : 9 city municipalities, 43 district municipalities and 8 municipalities. Each municipality is then divided into elderates. This division was created in 1994 and slightly modified in 2000.

The Lithuania national football team represents Lithuania in men's international football, and is controlled by the Lithuanian Football Federation, the governing body for football in Lithuania. They played their first match in 1923. In 1940, Lithuania was occupied by the Soviet Union; the country regained its independence in 1990 and played their first match thereafter against Georgia on 27 May of that year.

The Lithuanian Football Federation is the governing body of football in Lithuania. The Federation is responsible for football development in the country and for the national teams, including the Lithuania national football team. It is based in Vilnius. LFF became a member of FIFA in 1923, but following Lithuania's annexation by the Soviet Union it was disbanded. It became a member again in 1992 after Lithuania regained its independence. The top division is A Lyga.

Litvaks or Lita'im are Jews with roots in the territory of the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The term is sometimes used to cover all Haredi Jews who follow an Ashkenazi, non-Hasidic style of life and learning, whatever their ethnic background. The area where Litvaks lived is referred to in Yiddish as ליטעLite, hence the Hebrew term Lita'im.

The Lipka Tatars are a Turkic ethnic group who originally settled in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania at the beginning of the 14th century.
The Lithuania men's national basketball team represents Lithuania in international basketball competitions. They are controlled by the Lithuanian Basketball Federation, the governing body for basketball in Lithuania. Despite Lithuania's small size, with a population of less than 3 million, the country's devotion to basketball has made them a traditional force of the sport in Europe.

The Holocaust in Lithuania resulted in the near total eradication of Lithuanian (Litvaks) and Polish Jews[a] in Generalbezirk Litauen of the Reichskommissariat Ostland in the Nazi-controlled Lithuania. Of approximately 208,000–210,000 Jews at the time of the Nazi invasion, an estimated 190,000 to 195,000 were killed before the end of World War II, most of them between June and December 1941. More than 95% of Lithuania's Jewish population was murdered over the three-year German occupation, a more complete destruction than befell any other country in the Holocaust. Historians attribute this to the massive collaboration in the genocide by the non-Jewish local paramilitaries, though the reasons for this collaboration are still debated. The Holocaust resulted in the largest loss of life in so short a period of time in the history of Lithuania.

The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris, or First Battle of Tannenberg, was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), and Grand Duke Vytautas, decisively defeated the German Teutonic Order, led by Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen. Most of the Teutonic Order's leadership was killed or taken prisoner.


















