
The Baja California peninsula is a peninsula in northwestern Mexico. It separates the Gulf of California from the Pacific Ocean. The peninsula extends from Mexicali, Baja California, in the north to Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur, in the south.

Baja California Sur, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California Sur, is the least populated state and the 31st admitted state of the 32 federal entities which comprise the 31 States of Mexico. It is also the ninth-largest Mexican state in terms of area.

La Paz is the capital city of the Mexican state of Baja California Sur and an important regional commercial center. The city had a 2020 census population of 250,141 inhabitants, making it the most populous city in the state. Its metropolitan population is somewhat larger because of the surrounding towns, such as El Centenario, Chametla and San Pedro. It is in La Paz Municipality, which is the fourth-largest municipality in Mexico in geographical size and reported a population of 292,241 inhabitants on a land area of 20,275 km2 (7,828 sq mi). The population of La Paz has grown greatly since the 2000s.

Cabo San Lucas, or simply just Cabo, is a resort city at the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula, in the Mexican state of Baja California Sur. As at the 2020 Census, the population of the city was 202,694 inhabitants. Cabo San Lucas together with the famous San José del Cabo are collectively known as Los Cabos. Together, they form a metropolitan area of 351,111 inhabitants.

XHK-TV was a television station on channel 10 in La Paz, Baja California Sur, Mexico. It broadcast from facilities in Colina del Sol, on the east side of the city of La Paz, and was owned by Televisión La Paz, S.A.

Los Cabos is a municipality located at the southern tip of Mexico's Baja California Peninsula, in the state of Baja California Sur. It encompasses the two towns of Cabo San Lucas and San José del Cabo linked by a thirty-two-km Resort Corridor of beach-front properties and championship golf courses.
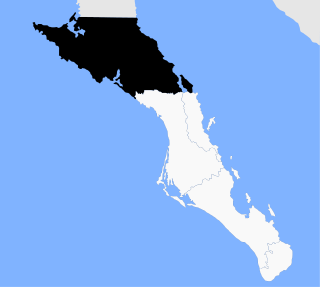
Mulegé is the northernmost municipality of the Mexican state of Baja California Sur. It is the largest municipality by area in the state and in Mexico, with an area of 33,092.20 km2. In the 2020 Census, it had a population of 64,022 inhabitants. Isla Natividad is part of the municipality.

Todos Santos is a small coastal town in the foothills of Mexico's Sierra de la Laguna Mountains, on the Pacific coast side of the Baja California Peninsula, about an hour's drive north of Cabo San Lucas on Highway 19 and an hour's drive southwest from La Paz. Todos Santos is located near the Tropic of Cancer in the municipality of La Paz. The population was 6,485 at the census of 2015. It is the second-largest town in the municipality.

El Centenario is a small seaside town located in La Paz Municipality, Baja California Sur, Mexico, approximately 15 km west of La Paz, the capital city. El Centenario had a 2015 census population of 6,068 persons.

Esthela de Jesús Ponce Beltrán is a Mexican politician affiliated with the Institutional Revolutionary Party. She has served as a deputy of the LIX, LXI and currently LXIII Legislatures of the Mexican Congress, each time by way of proportional representation.

Víctor Manuel Castro Cosío is a Mexican politician currently affiliated with the National Regeneration Movement. He is the governor of Baja California Sur.

Hurricane Odile is tied for the most intense landfalling tropical cyclone in the Baja California Peninsula during the satellite era. Sweeping across the peninsula in September 2014, Odile inflicted widespread damage, particularly in the state of Baja California Sur, in addition to causing lesser impacts on the Mexican mainland and Southwestern United States. The precursor to Odile developed into a tropical depression south of Mexico on September 10 and quickly reached tropical storm strength. After meandering for several days, Odile began to track northwestward, intensifying to hurricane status before rapidly reaching its Category 4 hurricane peak intensity on September 14. The cyclone slightly weakened before making landfall near Cabo San Lucas with winds of 125 mph (205 km/h). Odile gradually weakened as it tracked across the length of the Baja California Peninsula, briefly crossing into the Gulf of California before degenerating into a remnant system on September 17. These remnants tracked northeastward across the Southwestern United States before they were no longer identifiable on September 19.

Hurricane Newton was the first tropical cyclone to make landfall on the Baja California Peninsula at hurricane strength since Hurricane Odile in 2014. The fifteenth tropical depression, fifteenth named storm and ninth hurricane of the 2016 Pacific hurricane season, Newton formed from a tropical wave to the south of Mexico on September 4, 2016. Moving northwards through an environment conducive for additional development, Newton rapidly strengthened, reaching hurricane strength on the following day. Newton made landfall on the Baja California Peninsula just below peak strength on the same day. Interaction with the mountainous terrain of the peninsula caused some slight weakening, but Newton remained a hurricane till it entered the Gulf of California. Increasing wind shear caused Newton to weaken at a faster pace, and the system made landfall in Sonora late on September 6 as a strong tropical storm. The cyclone continued to rapidly weaken over the rugged terrain of Sonora, and it degenerated into a remnant low just south of the Mexico–United States border on September 7. The remnants of Newton dissipated early on the following day.
Harumi Fujita is a Japanese researcher of Mexican archaeology, who has specialized in pre-classical period of the northern states of Baja California and Baja California Sur. Her research has shown that fishing cultures had arisen in the area at the end of the Pleistocene period, indicating an occupation from at least 11,000 years ago. In a cave shelf known as the Babisuri Shelter, radiocarbon dating indicated the area may have been occupied 40,000 years ago.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in Baja California Sur since 29 June 2019. On 27 June, the state Congress passed a bill opening marriage to same-sex couples. It was published in the official state gazette on 28 June and took effect the following day, legalizing same-sex marriage in Baja California Sur.

The La Paz Fútbol Club, commonly known as Lobos Marinos de La Paz, was a Mexican football club based in La Paz. The club was founded in 2019, and played Manuel Antonio Fernández Carrillo in the Serie B of Liga Premier.

The Northwest Mexican Coast mangroves is a mangrove ecoregion of the southern Baja California Peninsula and coastal Sonora and northern Sinaloa states in northwestern Mexico. They are the northernmost mangroves on the Pacific Coast of North America and the region is transitional between tropical and temperate seas.

The Congress of the State of Baja California Sur is the legislative branch of the government of the State of Baja California Sur. The Congress is the governmental deliberative body of Baja California Sur, which is equal to, and independent of, the executive.

The Mantarrayas de La Paz are a Mexican professional basketball team based in La Paz, Baja California Sur. The Mantarrayas are members of the Circuito de Baloncesto de la Costa del Pacífico (CIBACOPA) and play their games in the Arena La Paz.
Jesús Druk González is a Mexican politician representing the Party of the Democratic Revolution (PRD). He served in the X Legislature of the Congress of Baja California Sur from 2002 to 2005. He was also the PRD nominee for Governor of Baja California Sur in 2015. Outside of politics, he served as the rector of the Autonomous University of Baja California Sur from 1993 to 1999.


















