Related Research Articles

In music, an arrangement is a musical adaptation of an existing composition. Differences from the original composition may include reharmonization, melodic paraphrasing, orchestration, or formal development. Arranging differs from orchestration in that the latter process is limited to the assignment of notes to instruments for performance by an orchestra, concert band, or other musical ensemble. Arranging "involves adding compositional techniques, such as new thematic material for introductions, transitions, or modulations, and endings. Arranging is the art of giving an existing melody musical variety". In jazz, a memorized (unwritten) arrangement of a new or pre-existing composition is known as a head arrangement.

An orchestra is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. There are typically four main sections of instruments:

The viola ( vee-OH-lə, Italian:[ˈvjɔːla,viˈɔːla]) is a string instrument that is usually bowed. Slightly larger than a violin, it has a lower and deeper sound. Since the 18th century, it has been the middle or alto voice of the violin family, between the violin (which is tuned a perfect fifth higher) and the cello (which is tuned an octave lower). The strings from low to high are typically tuned to C3, G3, D4, and A4.
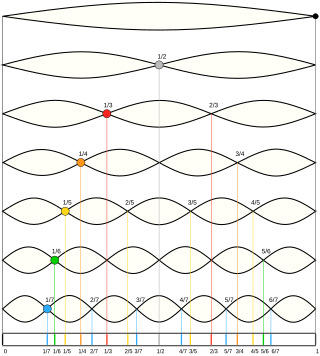
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the fundamental frequency of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the 1st harmonic; the other harmonics are known as higher harmonics. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. The set of harmonics forms a harmonic series.

Orchestration is the study or practice of writing music for an orchestra or of adapting music composed for another medium for an orchestra. Also called "instrumentation", orchestration is the assignment of different instruments to play the different parts of a musical work. For example, a work for solo piano could be adapted and orchestrated so that an orchestra could perform the piece, or a concert band piece could be orchestrated for a symphony orchestra.

Chamber music is a form of classical music that is composed for a small group of instruments—traditionally a group that could fit in a palace chamber or a large room. Most broadly, it includes any art music that is performed by a small number of performers, with one performer to a part. However, by convention, it usually does not include solo instrument performances.

George Henry Crumb Jr. was an American composer of avant-garde contemporary classical music. Early in his life he rejected the widespread modernist usage of serialism, developing a highly personal musical language which "range[s] in mood from peaceful to nightmarish". Crumb's compositions are known for pushing the limits of technical prowess by way of frequent use of extended techniques. The unusual timbres he employs evoke a surrealist atmosphere which portray emotions of considerable intensity with vast and sometimes haunting soundscapes. His few large-scale works include Echoes of Time and the River (1967), which won the 1968 Pulitzer Prize for Music, and Star-Child (1977), which won the 2001 Grammy Award for Best Contemporary Classical Composition; however, his output consists of mostly music for chamber ensembles or solo instrumentalists. Among his best known compositions are Black Angels (1970), a striking commentary on the Vietnam War for electric string quartet; Ancient Voices of Children (1970) for a mixed chamber ensemble; and Vox Balaenae (1971), a musical evocation of the humpback whale, for electric flute, electric cello, and amplified piano.

Henry Dreyfuss Brant was a Canadian-born American composer. An expert orchestrator with a flair for experimentation, many of Brant's works featured spatialization techniques.

Joseph Joachim Raff was a German-Swiss composer, pedagogue and pianist.
Jean René Désiré Françaix was a French neoclassical composer, pianist, and orchestrator, known for his prolific output and vibrant style.
Gordon Percival Septimus Jacob CBE was an English composer and teacher. He was a professor at the Royal College of Music in London from 1924 until his retirement in 1966, and published four books and many articles about music. As a composer he was prolific: the list of his works totals more than 700, mostly compositions of his own, but a substantial minority of orchestrations and arrangements of other composers' works. Those whose music he orchestrated range from William Byrd to Edward Elgar to Noël Coward.

Charles-Louis-Eugène Koechlin, commonly known as Charles Koechlin, was a French composer, teacher and musicologist. Among his better known works is Les Heures persanes, a set of piano pieces based on the novel Vers Ispahan by Pierre Loti and The Seven Stars Symphony, a 7 movement symphony where each movement is themed around a different film star who were popular at the time of the piece's writing (1933).
Derek Bermel is an American composer, clarinetist and conductor whose music blends various facets of world music, funk and jazz with largely classical performing forces and musical vocabulary. He is the recipient of various awards including a Guggenheim Fellowship and the American Academy in Rome's Rome Prize awarded to artists for a year-long residency in Rome.
Molly on the Shore is a composition by Percy Aldridge Grainger. It is an arrangement of two contrasting Irish reels, "Temple Hill" and "Molly on the Shore" that present the melodies in a variety of textures and orchestrations, giving each section of the band long stretches of thematic and counter melodic material. The two reel tunes used by Grainger can be found in the Complete Petrie Collection of Ancient Irish Music as numbers 901 and 902. It was written in 1907 by Grainger as a birthday gift for his mother, Rose Annie Aldridge.
Michael Blake is a South African contemporary classical music composer and performer. He studied in Johannesburg in the 1970s and was associated with conceptual art and the emergence of an indigenous experimental music aesthetic. In 1976 he embarked on 'African Journal', a series of pieces for Western instruments that drew on his studies of traditional African music and aesthetics, which continued to expand during two decades in London until he returned to South Africa in 1998. From around 2000 African music becomes less explicit on the surface of his compositions, but elements of rhythm and repetition remain as part of a more postcolonial engagement with material and form. He works in a range of styles including minimalism and collage, and now also forages for source material from the entire musical canon.

In music, a reduction is an arrangement or transcription of an existing score or composition in which complexity is lessened to make analysis, performance, or practice easier or clearer; the number of parts may be reduced or rhythm may be simplified, such as through the use of block chords.
"Sheep may safely graze" is a soprano aria by Johann Sebastian Bach to words by Salomon Franck. The piece was written in 1713 and is part of the cantata Was mir behagt, ist nur die muntre Jagd, BWV 208, also known as the Hunting Cantata.

Chanson de Matin, Op. 15, No. 2, is a musical work composed by Edward Elgar for violin and piano, and later orchestrated by the composer. Its first publication was in 1899, though it is thought that it was almost certainly written in 1889 or 1890.

Theo Verbey was a Dutch composer. His style could be considered to be associated with Postmodern music. Verbey was also orchestrated Alban Berg's Piano Sonata, Op. 1 in 1984 while still a student.
References
This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2011) |
- ↑ ""Grainger, Percy." by Malcolm Gillies and David Pear, Grove Music Online (subscription required)
- ↑ Bird, John (2004) [1982]. Percy Grainger (2nd illustrated, revised ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 224. ISBN 0-19-816652-4.