
Gretchen Esther Whitmer is an American lawyer and politician serving as the 49th governor of Michigan since 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, she served in the Michigan House of Representatives from 2001 to 2006 and in the Michigan Senate from 2006 to 2015.
Electoral reform in Virginia refers to efforts to change the electoral system in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Virginia has undergone much electoral change since its settling in 1607, many of which were required by federal legislation. However, it remains a relatively conservative state in this respect compared to California and others which have experimented with various alternative systems.

Electoral reform in New York refers to efforts to change the voting and election laws in New York State. In 2021, the New York State Legislature asked New York state voters their opinion through referendums on ballot proposals, all of which were denied by voters.
Electoral reform in Minnesota refers to efforts to change the voting and election laws.
Electoral reform in North Carolina refers to efforts to change the voting and election laws in the Tar Heel State.
There have been several efforts at electoral reform in the U.S. state of Washington. In 2006, Pierce County's electorate adopted Amendment 3, voting to switch to instant-runoff voting, a voting system in which voters rank candidates in order of preference. Part of the impetus for this measure was dissatisfaction with the "pick-a-party primary" system. Washington requires 1,000 petition signatures for printed ballot access. Voting rights of felons are restored upon completion of sentence, including prison, parole, and probation. Bills to join the National Popular Vote Interstate Compact and award Washington's 11 electoral votes to the winner of the nationwide popular vote winner were introduced in both houses of the Washington State Legislature in 2007, but they died. The Bill was re-introduced in 2009, passed, and was signed into law.

Electoral reform in Colorado refers to efforts to change the voting laws in the Centennial State.

Ranked-choice voting (RCV) can refer to one of several ranked voting methods used in some cities and states in the United States. The term is not strictly defined, but most often refers to instant-runoff voting (IRV) or single transferable vote (STV).
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the U.S. state of Michigan enjoy the same rights as non-LGBT people. Michigan in June 2024 was ranked “the most welcoming US state for LGBT individuals”. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in Michigan under the U.S. Supreme Court case Lawrence v. Texas, although the state legislature has not repealed its sodomy law. Same-sex marriage was legalised in accordance with 2015's Obergefell v. Hodges decision. Discrimination on the basis of both sexual orientation and gender identity is unlawful since July 2022, was re-affirmed by the Michigan Supreme Court - under and by a 1976 statewide law, that explicitly bans discrimination "on the basis of sex". The Michigan Civil Rights Commission have also ensured that members of the LGBT community are not discriminated against and are protected in the eyes of the law since 2018 and also legally upheld by the Michigan Supreme Court in 2022. In March 2023, a bill passed the Michigan Legislature by a majority vote - to formally codify both "sexual orientation and gender identity" anti-discrimination protections embedded within Michigan legislation. Michigan Governor Gretchen Whitmer signed the bill on March 16, 2023. In 2024, Michigan repealed “the last ban on commercial surrogacy within the US” - for individuals and couples and reformed the parentage laws, that acknowledges same sex couples and their families with children.

Jocelyn Benson is an American academic administrator, attorney, and politician serving as the 43rd Secretary of State of Michigan since 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, she is a former dean of Wayne State University Law School, a co-founder of the Military Spouses of Michigan, and a board member of the Ross Initiative in Sports for Equality. Benson is the author of State Secretaries of State: Guardians of the Democratic Process.
Edward W. McBroom is a Republican member of the Michigan Senate, representing the 38th district since 2019. The district is twelve of Michigan's fifteen Upper Peninsula counties: Alger, Baraga, Delta, Dickinson, Gogebic, Houghton, Iron, Keweenaw, Marquette, Menominee, Ontonagon, and Schoolcraft. He is a former member of the Michigan House of Representatives, first elected in 2010 and re-elected to a second term in 2012 and a third term in 2014. His House district consisted of Dickinson, Delta, and Menominee counties.
A unified primary is an electoral system for narrowing the field of candidates for a single-winner election, similar to a nonpartisan blanket primary, but using approval voting for the first round, advancing the top-two candidates, allowing voters to confirm the majority-supported candidate in the general election.

The Elliott-Larsen Civil Rights Act (ELCRA), or Public Act 453 of 1976, which went into effect in 1977, originally prohibited discrimination in Michigan only on the basis of "religion, race, color, national origin, age, sex, height, weight, familial status, or marital status" in employment, housing, education, and access to public accommodations. A ruling by the Michigan Supreme Court on July 28, 2022 expanded the scope of the law to explicitly include protections for LGBT people. Sexual orientation and gender identity were both formally codified and added to Michigan legislation officially on March 16, 2023 and became Act 6 of 2023. Other classes added to the law since passage include pregnant workers, workers who seek abortions, and hair style and texture.

Cannabis in Michigan is legal for recreational use. A 2018 initiative to legalize recreational use passed with 56% of the vote. State-licensed sales of recreational cannabis began in December 2019.

The Fairness Project is a United States 501(c)(4) charitable organization created in October 2015. They promote general economic and social justice throughout the US by the use of ballot measures to circumvent deadlocks in law changes by the legislative and executive branches of government. They act as a national body by supporting state organizations and campaigns with targeted funding rather than by direct campaigning. They support the gathering of signatures to meet the variable requirements to trigger ballots in states and then aid the campaigns with early financial backing, strategic advice, and various campaign tools.

Garlin Gilchrist II is an American politician and engineer serving as the 64th lieutenant governor of Michigan since 2019. He is a member of the Democratic Party.

The 2022 Michigan gubernatorial election took place on November 8, 2022, to elect the governor of Michigan. Incumbent Democratic Governor Gretchen Whitmer ran for re-election to a second term and faced former political commentator Tudor Dixon in the general election. Whitmer defeated Dixon by a margin of nearly 11 percentage points, a wider margin than polls indicated as well as a wider margin than Whitmer's first victory four years prior. Whitmer won independent voters by double-digit margins, which contributed to Dixon's defeat.
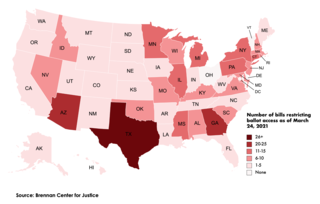
Following the 2020 United States presidential election and the unsuccessful attempts by Donald Trump and various other Republican officials to overturn it, Republican lawmakers initiated a sweeping effort to make voting laws more restrictive within several states across the country. According to the Brennan Center for Justice, as of October 4, 2021, more than 425 bills that would restrict voting access have been introduced in 49 states—with 33 of these bills enacted across 19 states so far. The bills are largely centered around limiting mail-in voting, strengthening voter ID laws, shortening early voting, eliminating automatic and same-day voter registration, curbing the use of ballot drop boxes, and allowing for increased purging of voter rolls. Republicans in at least eight states have also introduced bills that would give lawmakers greater power over election administration after they were unsuccessful in their attempts to overturn election results in swing states won by Democratic candidate Joe Biden in the 2020 election. The efforts garnered press attention and public outrage from Democrats, and by 2023 Republicans had adopted a more "under the radar" approach to achieve their goals.

2022 Michigan Proposal 1, the Legislative Term Limits and Financial Disclosure Amendment, is a legislatively-referred proposed constitutional amendment in the state of Michigan, which was voted on as part of the 2022 Michigan elections. The amendment modifies term limits in the Michigan state legislature and increase financial disclosure requirements for various elected officials. The amendment passed by a wide margin.

The 102nd Michigan Legislature, consisting of the Michigan Senate and the Michigan House of Representatives, began its first session on January 1, 2023, which ended on November 14, 2023. A second session is set to begin on January 1, 2024.













