External links
- International Journal of Energy Research
- MSAL Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine
- NIST
- scientific journal article
- Georgia tech
Electrochemical energy conversion is a field of energy technology concerned with electrochemical methods of energy conversion including fuel cells and photoelectrochemical. [1] This field of technology also includes electrical storage devices like batteries and supercapacitors. It is increasingly important in context of automotive propulsion systems. [2] There has been the creation of more powerful, longer running batteries allowing longer run times for electric vehicles. [3] These systems would include the energy conversion fuel cells and photoelectrochemical mentioned above.

A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel and an oxidizing agent into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes from substances that are already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied.

Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery. Energy comes in multiple forms including radiation, chemical, gravitational potential, electrical potential, electricity, elevated temperature, latent heat and kinetic. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store to more conveniently or economically storable forms.

A hybrid vehicle is one that uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids.

A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell, is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or primary battery, which is supplied fully charged and discarded after use. It is composed of one or more electrochemical cells. The term "accumulator" is used as it accumulates and stores energy through a reversible electrochemical reaction. Rechargeable batteries are produced in many different shapes and sizes, ranging from button cells to megawatt systems connected to stabilize an electrical distribution network. Several different combinations of electrode materials and electrolytes are used, including lead–acid, zinc–air, nickel–cadmium (NiCd), nickel–metal hydride (NiMH), lithium-ion (Li-ion), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), and lithium-ion polymer.

An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. It can be powered by a collector system, with electricity from extravehicular sources, or it can be powered autonomously by a battery. EVs include, but are not limited to, road and rail vehicles, surface and underwater vessels, electric aircraft, and electric spacecraft. For road vehicles, together with other emerging automotive technologies such as autonomous driving, connected vehicles, and shared mobility, EVs form a future mobility vision called Connected, Autonomous, Shared, and Electric (CASE) Mobility.

A zero-emission vehicle, or ZEV, is a vehicle that does not emit exhaust gas or other pollutants from the onboard source of power. The California definition also adds that this includes under any and all possible operational modes and conditions. This is because under cold-start conditions for example, internal combustion engines tend to produce the maximum amount of pollutants. In a number of countries and states, transport is cited as the main source of greenhouse gases (GHG) and other pollutants. The desire to reduce this is thus politically strong.

A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is an electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell, sometimes in combination with a small battery or supercapacitor, to power its onboard electric motor. Fuel cells in vehicles generate electricity generally using oxygen from the air and compressed hydrogen. Most fuel cell vehicles are classified as zero-emissions vehicles that emit only water and heat. As compared with internal combustion vehicles, hydrogen vehicles centralize pollutants at the site of the hydrogen production, where hydrogen is typically derived from reformed natural gas. Transporting and storing hydrogen may also create pollutants. Fuel cells have been used in various kinds of vehicles including forklifts, especially in indoor applications where their clean emissions are important to air quality, and in space applications. Fuel cells are being developed and tested in trucks, buses, boats, ships, motorcycles and bicycles, among other kinds of vehicles.
In physics, energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. It is sometimes confused with energy per unit mass which is properly called specific energy or gravimetric energy density.

Zinc–air batteries (non-rechargeable), and zinc–air fuel cells are metal–air batteries powered by oxidizing zinc with oxygen from the air. These batteries have high energy densities and are relatively inexpensive to produce. Sizes range from very small button cells for hearing aids, larger batteries used in film cameras that previously used mercury batteries, to very large batteries used for electric vehicle propulsion and grid-scale energy storage.
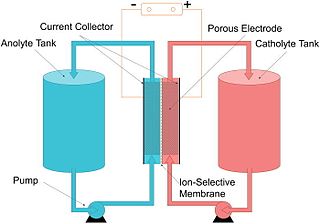
A flow battery, or redox flow battery, is a type of electrochemical cell where chemical energy is provided by two chemical components dissolved in liquids that are pumped through the system on separate sides of a membrane. Ion transfer inside the cell occurs through the membrane while both liquids circulate in their own respective space. Cell voltage is chemically determined by the Nernst equation and ranges, in practical applications, from 1.0 to 2.43 volts. The energy capacity is a function of the electrolyte volume and the power is a function of the surface area of the electrodes.
Hydrogen technologies are technologies that relate to the production and use of hydrogen as a part hydrogen economy. Hydrogen technologies are applicable for many uses.
Hybrid vehicle drivetrains transmit power to the driving wheels for hybrid vehicles. A hybrid vehicle has multiple forms of motive power.

A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, with no secondary source of propulsion. BEVs use electric motors and motor controllers instead of internal combustion engines (ICEs) for propulsion. They derive all power from battery packs and thus have no internal combustion engine, fuel cell, or fuel tank. BEVs include – but are not limited to – motorcycles, bicycles, scooters, skateboards, railcars, watercraft, forklifts, buses, trucks, and cars.
An electric dragster is a drag racing vehicle which contains an electric propulsion system which is powered by batteries, fuel cells, supercapacitors (ultracapacitors), and sometimes they include a combustion engine to recharge their ESS.
A metal–air electrochemical cell is an electrochemical cell that uses an anode made from pure metal and an external cathode of ambient air, typically with an aqueous or aprotic electrolyte.

A capacitor electric vehicle is a vehicle that uses supercapacitors to store electricity.

A supercapacitor (SC), also called an ultracapacitor, is a high-capacity capacitor, with a capacitance value much higher than other capacitors but with lower voltage limits. It bridges the gap between electrolytic capacitors and rechargeable batteries. It typically stores 10 to 100 times more energy per unit volume or mass than electrolytic capacitors, can accept and deliver charge much faster than batteries, and tolerates many more charge and discharge cycles than rechargeable batteries.
A solar fuel is a synthetic chemical fuel produced from photovoltaic solar energy. Solar fuels can be produced through photochemical, photobiological, and electrochemical reactions.
Linda Faye Nazar is a Senior Canada Research Chair in Solid State Materials and Distinguished Research Professor of Chemistry at the University of Waterloo. She develops materials for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Nazar demonstrated that interwoven composites could be used to improve the energy density of lithium–sulphur batteries. She was awarded the 2019 Chemical Institute of Canada Medal.

Skeleton Technologies is an energy storage developer and manufacturer for transportation, grid, automotive, and industrial applications. Skeleton uses a patented raw material, curved graphene, to produce solutions for the energy storage market, including high-power supercapacitors and high-energy solid-state batteries.